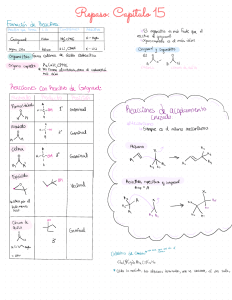
Table 7-1 Common Reactions of Organotransition Metal Complexes Schematic example Reaction type ∆ Coordination number of M ∆ e− count Text section 0 0 0 7-1 Ligand substitution L'' + LnML' LnML'' + L' Oxidative addition LnM + X-Y LnM(X)(Y) +2 +2 +2 7-2 Reductive elimination LnM(X)(Y) LnM + X−Y −2 −2 −2 7-3 0 −1 −2 8-1-1 0 −1 −2 8-1-1 0c 0 0 8-2 0 0 0 8-3 0 0 0 8-4 0 0 0 8-4 Y 1,1-Insertion a 1,2-Insertion a Z LnM X Y LnM Y LnM X Y Z 1 1 X1 LnM X Z Z2 X 1 Nucleophilic additionb LnM Nucleophilic abstractionb LnM CR + Nuc−H Electrophilic additionb LnM−X=Z + E+ Electrophilic abstractionb LnM−X−Z−Y + E+ R π- and σ-Bond metathesisd C C R' a ∆ Oxidation state of M + Nuc:− Y 2 [LnM−X−Z−Nuc]− Z O O LnM−H + Nuc [LnM=X−Z−E]+ LnM+ X Z + E-Y CR R + C C or X Y + W Z R C C R X W or + + Y Z R' C C R' 11-1 and 11-4 R' The reverse reaction, called deinsertion or elimination, is also possible. There is no one general reaction; several variations are possible. cDepends upon change in hapticity; e.g., X=Z going from η3 to η2 results in a 2 e− reduction. d∆ oxidation state, coordination number, and e− count are not applicable here, especially in π-bond metathesis where the metal complex is a catalyst. b