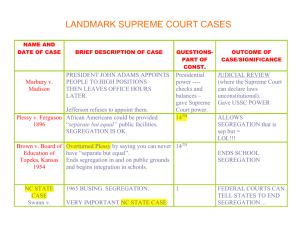
LANDMARK SUPREME COURT CASES NAME AND DATE OF CASE Marbury v. Madison BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF CASE PRESIDENT JOHN ADAMS APPOINTS PEOPLE TO HIGH POSITIONS THEN LEAVES OFFICE HOURS LATER. Jefferson refuses to appoint them. Plessy v. Ferguson African Americans could be provided 1896 “separate but equal” public facilities. SEGREGATION IS OK. Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, Kansas 1954 Swann v. CharlotteMecklenburg Board of Ed QUESTIONS/ PART OF CONSTITUTION OUTCOME OF CASE/SIGNIFICANCE Presidential power ---- checks and balances – gave Supreme Court power. JUDICIAL REVIEW (where the Supreme Court can declare laws unconstitutional). 14TH ALLOWS SEGREGATION that is sep but = Overturned Plessy by saying you can never 14TH have “separate but equal”. Ends segregation in and on public grounds and begins integration in schools. 1965 BUSING. SEGREGATION. 14TH AMENDMENT VERY IMPORTANT NC STATE CASE ENDS SCHOOL SEGREGATION FEDERAL COURTS CAN TELL STATES TO END SEGREGATION… Gibbons owned a ferry operation with a Gibbons v. Ogden federal license, and Ogden had a NY license to do the same thing. Ogden tried to shut down the Gibbons ferry, and Gibbons sued to the Supreme Court. Korematsu v. US Japanese internment camps during WWII. Heart of Atlanta HOTEL REFUSED TO serve AFRICAN Motel, Inc. v. US AMERICANS. 1964. Article I, section 8 – “the commerce clause”. AND Supremacy Clause Gibbons wins – The Supreme Court said the NATIONAL GOVERNMENT REGULATES INTERSTATE COMMERCE/ Supremacy WAR POWERS, 14TH ALLOWS FOR JAPANESE AMERICAN INTERNMENT CAMPS. 14TH and Civil Rights Act SUPREME COURT of 1964 SAID THEY HAD TO ACCEPT ALL CITIZENS -- all public facilities had to accept all citizens. Furman v. Georgia GUN GOES OFF WHEN DROPPED, KILLING PERSON. Furman gets death penalty. TH 8 , 14th Death penalty Gregg kills two people in a robbery. Is the Gregg v. Georgia death penalty cruel and unusual in all 8TH cases? Gideon v. Wainwright Regents of the University of California v. Bakke New Jersey v. T.L.O. POOR GUY DIDN’T HAVE LAWYER AND WAS FOUND GUILTY. 6TH, Was retried with an attorney and found innocent. DEATH PENALTY CAN BE CRUEL AND UNUSUAL IN CERTAIN CASES. DEATH PENALTY IN ITSELF IS NOT CRUEL AND UNUSUAL. EVERYONE HAS A RIGHT TO A LAWYER – EVEN POOR PEOPLE. Bakke (white guy) applies to college and is 14th, Civil Rights denied admission. He sues claiming act of 1964. discrimination because several African Americans with lower test scores are accepted. AFFIRMATIVE ACTION IS OK, BUT NO QUOTAS T.L.O. was a 14-year-old girl who was Did the search accused of smoking in the restroom at violate the 4th and school. A principal questioned her and 14th amendments? searched her purse, yielding marijuana and other drug items plus a list of buyers. No. STUDENTS CAN BE SEARCHED WITHOUT PROBABLE CAUSE ON SCHOOL GROUNDS. Bethel School District v. Frasier Tinker v. Des Moines Hazelwood v. Kuhlmeier 1st amendment SCHOOLS MAY PROHIBIT VULGAR AND OFFENSIVE LANGUAGE. 1st amendment STUDENTS MAY WEAR ARMBANDS TO PROTEST. 1st amendment PRINCIPALS HAVE THE RIGHT TO EDIT / CENSOR STUDENT SPEECH. 1st amendment. FLAG BURNING IS LEGAL 5TH AMENDMENT – DUE PROCESS Miranda wins. A PERSON MUST BE READ HIS RIGHTS WHILE BEING ARRESTED. Student gives speech to 11-14 yr olds with sexual innuendo. Students wear black arm bands to protest the Vietnam war. Students publish articles about teen pregnancy and divorced parents in the student newspaper. Texas v. Johnson Johnson burns a flag in protest. Miranda v. Arizona Ernesto Miranda arrested for kidnapping and rape – found guilty after signed confession. Police admitted that Miranda had not been advised of his right to an attorney during questioning. Mapp v. Ohio Dred Scott v. Sandford NY Times v. US US v. Nixon Police search a house without a search warrant, and find pornographic materials even though they were looking for a fugitive. Is this evidence admissible in court? Dred Scott a slave -- his owner dies in a free state. Dred then sues the Supreme Court for his freedom. 4TH AMENDMENT No. NEED A SEARCH WARRANT OR EVIDENCE CANNOT BE USED! Missouri Compromise because there was no 14th Amendment yet. Slaves were not people, but property. This is a pro-slavery court decision. Roger B. Taney was Chief Justice. Pentagon Papers (classified info.) was 1st leaked to the NY Times. New York Times then prints information, and the United States takes them to the Supreme Court. NY Times wins 6-3. Proves freedom of the press since the publication did not result in the immediate harm to the people. Watergate audiotapes of Nixon (oops). Nixon states that "Executive Privilege" allows him to withhold tapes from investigators. Court ruled against Nixon. Took power away from the President and gave more authority to Congress. Solidified Checks and Balances. Article I and II of the Constitution dealing with Congress, the President, and Executive power. Roe v. Wade Roe wanted to be allowed to have an abortion but it was against Texas law. 14th and 9th. McCulloch v. Maryland, 1819 National/Federal Bank versus Maryland’s(State) right to tax the bank Necessary and Proper Clause When a federal and state law are in conflict, the federal law is supreme Gibbons had a federal permit for a steamboat business; Ogden had a state permit for the same waters. Siding with Gibbons, the Court said that, in matters of interstate commerce, the “Supremacy Clause” tilts the balance of power in favor of federal legislation. Supremacy Clause National Supremacy Gibbons v Ogden Abortions are legal in the 1st trimester and in the second and third in certain circumstances (ie. if mother's life is at risk) Necessary and Proper to establish banks State v Mann NC State Case In 1829, Elizabeth Jones, who owned a slave named Lydia, hired her out for a year to John Mann of Chowan County. Mann shot and wounded Lydia when she struggled to escape a whipping. Mann was found guilty of battery by a jury of twelve white men drawn from his community and the court (Superior Court Judge Joseph J. Daniel) imposed a five dollar fine. The North Carolina Supreme Court overruled the conviction on the grounds that slaves were the absolute property of their owners who could not be punished at common law unless the legislature authorized such punishment. State Constitutional Supremacy over Superior Court/local law Supremacy Clause