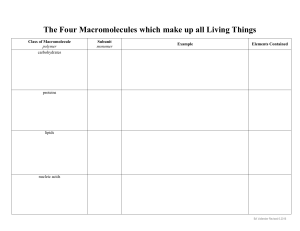
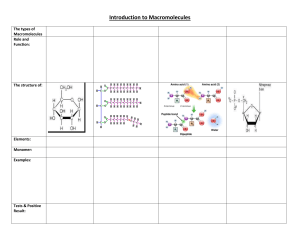
NOVEMBER 11TH, 2015 (DAY 2) Obj: Relate the characteristics & functions of the 4 classes of macromolecules. Do Now: What elements are the most important to living things? HW: Macromolecule Coloring due Friday Macromolecules Chapter 2 Section 3 What are the 6 elements most common to living things? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Phosphorus Sulfur Next to each write down the # of valence e’s & how many bonds each one can form. Carbon forms the backbone of macromolecules Why? 4 valence electrons 4 bonds Forms long chains Carbon Macromolecules • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Name Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Sugar, Bread, Carbohydrate Pasta Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Function Elements Subunit Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Carbohydrate Example Function Energy (quick & long term) Not storage Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Elements Subunit Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Function Elements C,H,O Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Special Ratio 1:2:1 Subunit Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Which one of the following molecules are carbohydrates? Name Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Example Function Elements Subunit Saccarides - mono (glucose) - di (sucrose) - poly (starch or cellulose) Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Exists as Chains or Rings Misc. Name Example Sugar, Bread, Pasta Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Function Energy (quick & long term) Elements C,H,O Special Ratio 1:2:1 Subunit Saccarides - mono - di - poly Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Exists as Ends in ose Chains or Rings Iodine is an indicator Indicator Iodine is an indicator for carbohydrates! Changes Demo from a yellow/brown to a blue/black Macromolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids November th 12 , 2015 (Day 3) Obj: Relate the characteristics & functions of the 4 classes of macromolecules. Do Now: What do you think of when you hear the word “lipid”? HW: Name Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Carbohydrate Lipid Oils, Fats, butters, milk, cheese, Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Function Oils, Fats, butters, milk, cheese, yogurt 1. Long term storage of energy 2. Protection 3. Insulation 4. Messengers – Hormones 5. Cell Membrane – Phospholipids Carbohydrate Lipid Elemen ts Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Function Elements Carbohydrate C,H,O Lipid No fixed ratio Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Carbohydrate Fatty acids 3 fatty Lipid acids + 1 glycerol triglyceride Misc. Name Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. 3 fatty acids + 1 glycerol triglyceride (fig 1.19) Saturated & Unsaturated Carbohydrate C,H,O Lipid No fixed ratio Fatty acids Count the C,H,O! Write down the ratio! NOVEMBER 16TH, 2015 (DAY) Obj: Relate the characteristics & functions of the 4 classes of macromolecules. Do Now: What do you think of when you hear the word “protein”? HW: DNA Article w/ Questions Macromolecules • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Name Example Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Muscles, meat, fish, peanuts enzymes Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Function Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Muscles, meat, fish, beans 1. Structural 2. Movement 3. Reactions Elements Subunit/ Monomer Name Example Function Elements Carbohydrate Lipid C,H,O, & N Protein Nucleic Acid Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Muscles, meat, fish, beans Structural Movement Enzymes Send & Receive Messages (receptors) C,H,O, & N Amino acid 5 groups 1. Central C 2. Hydrogen 3. Amino (NH2) 4. Acid (COOH) 5. Variable (R) Misc. Peptide Bond Bond between acid and amino group in a protein Polypeptide Name Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. 5 groups 1. Central C 2. Hydrogen 3. Amino (NH2) 4. Acid (COOH) 5. Variable (R) Primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Muscles, meat, fish, beans Structural Movement Enzymes Send & Receive Messages (receptors) C,H,O, & N Amino acid End in -ine Shape is Important! November 17th, 2014 (Day) Obj: Relate the characteristics & functions of the 4 classes of macromolecules. Do Now: What is the last macromolecule we have to learn about? HW: DNA Article w/ Questions Macromolecules • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Name Example Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid DNA & RNA Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Function DNA & RNA • Makes up genetic material (chromosomes) • Instructions that tell the cell what to do! • Control protein production Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid E Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Carbohydrate Lipid Protein DNA & RNA Nucleic Acid C,H,O,N, Nucleotide &P Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Name Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Carbohydrate Lipid Protein DNA & RNA Nucleic Acid nucleotide 3 groups 1. 5 carbon sugar 2. Base – N 3. Phosphate Misc. Nucleotide Structure Name Example Function Elements Subunit/ Monomer Structure/ Functional groups Misc. Carbohydrate Lipid Protein DNA & RNA Nucleic Acid Discovered by Watson & Crick!