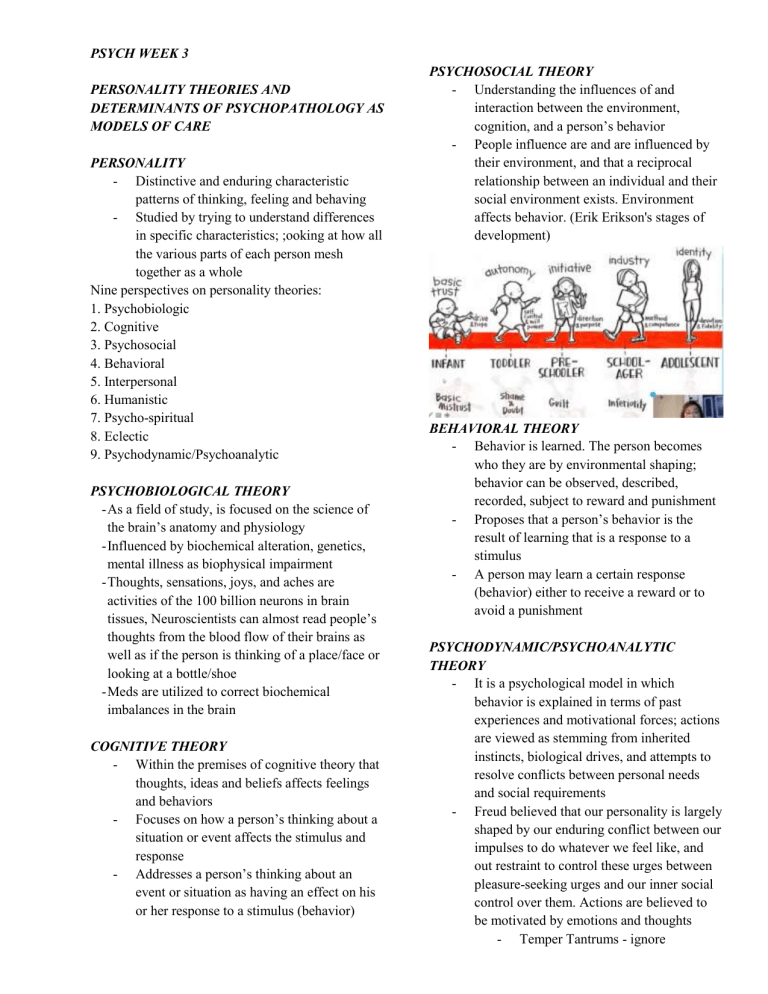
PSYCH WEEK 3 PERSONALITY THEORIES AND DETERMINANTS OF PSYCHOPATHOLOGY AS MODELS OF CARE PERSONALITY - Distinctive and enduring characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling and behaving - Studied by trying to understand differences in specific characteristics; ;ooking at how all the various parts of each person mesh together as a whole Nine perspectives on personality theories: 1. Psychobiologic 2. Cognitive 3. Psychosocial 4. Behavioral 5. Interpersonal 6. Humanistic 7. Psycho-spiritual 8. Eclectic 9. Psychodynamic/Psychoanalytic PSYCHOBIOLOGICAL THEORY - As a field of study, is focused on the science of the brain’s anatomy and physiology - Influenced by biochemical alteration, genetics, mental illness as biophysical impairment - Thoughts, sensations, joys, and aches are activities of the 100 billion neurons in brain tissues, Neuroscientists can almost read people’s thoughts from the blood flow of their brains as well as if the person is thinking of a place/face or looking at a bottle/shoe - Meds are utilized to correct biochemical imbalances in the brain COGNITIVE THEORY - Within the premises of cognitive theory that thoughts, ideas and beliefs affects feelings and behaviors - Focuses on how a person’s thinking about a situation or event affects the stimulus and response - Addresses a person’s thinking about an event or situation as having an effect on his or her response to a stimulus (behavior) PSYCHOSOCIAL THEORY - Understanding the influences of and interaction between the environment, cognition, and a person’s behavior - People influence are and are influenced by their environment, and that a reciprocal relationship between an individual and their social environment exists. Environment affects behavior. (Erik Erikson's stages of development) BEHAVIORAL THEORY - Behavior is learned. The person becomes who they are by environmental shaping; behavior can be observed, described, recorded, subject to reward and punishment - Proposes that a person’s behavior is the result of learning that is a response to a stimulus - A person may learn a certain response (behavior) either to receive a reward or to avoid a punishment PSYCHODYNAMIC/PSYCHOANALYTIC THEORY - It is a psychological model in which behavior is explained in terms of past experiences and motivational forces; actions are viewed as stemming from inherited instincts, biological drives, and attempts to resolve conflicts between personal needs and social requirements - Freud believed that our personality is largely shaped by our enduring conflict between our impulses to do whatever we feel like, and out restraint to control these urges between pleasure-seeking urges and our inner social control over them. Actions are believed to be motivated by emotions and thoughts - Temper Tantrums - ignore - Freud believed that anxiety comes from the part of the ego getting all stressed out about losing control over the id and superego so he proposed that our ego used a series of defense mechanisms as a method of reducing anxiety - Castration Complex - Ego - mostly conscious; make peace between the id and the superego (Personality principle) Id - Unconscious energy (Pleasure Principle) Superego - Internalized ideas (Morality Principle) Preconscious: anything that potentially brought to conscious even if you forgot; storehouse of memories______; Psychoanalysis, sleep within each individual regardless of belief system and serves as a force for interconnectedness between the self and others, the environment, and a higher power - The earliest practices- focused on spiritual treatment (insanity was considered a disruption of mind and spirit. - Reeves and Reynolds - a large volume of contemporary research (>60 studies) demonstrating the value of spirituality for both medical and psychiatric pts is influencing this change. *Religious articles, bibles are not allowed in the ward due to risk of enhancement of religious preoccupation. INTERPERSONAL THEORY - Unsatisfactory interpersonal relations primarily cause maladaptive behavior - Sullivan believed that poor relationships cause anxiety - basis for all emotional problems - Hildegard Peplau (mother of psychiatric nursing) considers nursing to be an interpersonal process between nurse and client (nurse-client therapeutic relationship) ECLECTIC THEORY - Selects combines and incorporates the diverse techniques from several theories - Utilizes more than one personality theories and determinants of psychopathology as models of care and joins those models into an integrated approach increasing the parameters involved. *Simultaneous use of different therapeutic approaches: meds, psychoanalysis, physical, etc. HUMANISTIC THEORY - Focuses on the present and the “here & now” with nothing to do with the past. - It moved traditional concepts of mental health and illness from a focus on illness, determinism, the unconscious, and reductionism to a focus on health. - Humanistic theories reflected the theoretical shift towards a more holistic, interpersonal, positive perspective. E.g. the pt says “I am an alcoholic and I need help from the psych team.” Don’t consider the past (humanistic theory) unless the pt’s father and grandfather are alcoholics (Psychobiological theorygenetics), or the pt has not ascended the “oral stage” of development (psychoanalytic/psychodynamic theory - freud) mhGAP - Depression- leading causes of disability - Suicide - 2nd leading cause of death (15-29 years old) - People with severe mental health conditions die prematurely-due to preventable physical condtions - 1 psychiatrists for every 100,000 people; Fewer neurologists - mhGAP used to scale ups services, allocation of financial and human resources of care for mental neurological and substance use disorders for countries esp in low-income countries. - Obj. to achieve much higher coverage with key interventions in the countries with low and lower-middle incomes that have a large proportion of the global burden of MNS disorders Development of the mhGAP Intervention Guide (mhGAP-IG) PSYCHO-SPIRITUAL THEORY - Spirituality is the human quality that gives meaning and sense of purpose to an individual’s existence. Spirituality exists - - - Resource to facilitate delivery of the mhGAP evidence-based guidelines in nonspecialized health care settings Grounded on the best available scientific and epidemiological evidence on priority conditions Demonstrated the feasibility of delivery of pharmacological and psychosocial interventions in non-specialized healthcare settings PRIORITY CONDITIONS ● Depression (DEP) pink ● Psychoses (PSY) ● Epilepsy(EPI) ● Child and Adolescent Mental and Behavioral Disorders (CMH) ● Dementia (DEM) ● Disorders due to Substance use (SUB) ● Suicide Masterchart - guides the clinician on the priorities Parts: Essential Care & Practice; Master Chart; Module (Assessment, Management, Followup PFA/mhGAP - Anyone can learn (Priority are the hospital care team to the grassroots) Crisis Intervention/Critical Incidence Stress Debriefer - Nurses and Psychologists Important: to describe thru assessment the status of the FRAMEWORK FOR COUNTRY ACTION - Political commitment (main foundation) - Establish a core group of stakeholders with expertise for guidance - Acquisition of the necessary human and financial resources ASSESSMENT OF NEEDS AND RESOURCES - Describe the status of the burden of MNS disorders - Identify human, financial and material resources - Examine the coverahe and quality of essential interventions, and any reasons for low or ineffective coverage - Describe any current policies that are relevant to MNS disorders - Synthesize the information to highlight important gaps that must be addressed for scaling up care for MNS disorders DEVELOPMENT OF A POLICY - Draft or revise policy to set out its vision, values, and principles, its objectives, and key areas for action; - Incorporate existing knowledge about the improvement of treatment and care and prevention of MNS disorders - Involve all relevant stakeholders - Work with other relevant sectors, and review other relevant policies; and - Develop means for implementation of the policy DELIVERY OF INTERVENTION PACKAGE - The decision about how best to deliver the chosen interventions at health facility, community, and household levels are critical to ensure maximum, high quality and equitable coverage of the interventions (on non-specialized hospitals only) STRENGTHENING OF HUMAN RESOURCES - Appropriate pers-service and in-service training of different cadres of health professionals with curricula that are needs-based and fit-for-purpose - Improvement of access to information and knowledge resources - Development of supportive supervision - Development of simplified diagnostic and treatment tools MOBILIZATION OF FINANCIAL RESOURCES - Accurate costing - Probable need to increase the budget - External funding could be used MONITORING AND EVALUATION - The indicators for measurement can be programe inputs and activities, outputs, outcomes and impact/health status BUILDING PARTNERSHIPS - UN agencies (UNICEF) - Government ministries - Donors - NGOs and WHO collaborating centers - Civil society







