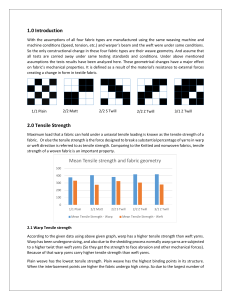
TT 3063 ASSIGNMENT 2 NAME – WANIGASUNDARA H.K.A.S. INDEX – 181051M D.O.S – 03/13/2022 1.0 Introduction With the assumptions of all four fabric types are manufactured using the same weaving machine and machine conditions (Speed, tension, etc.) and warper’s beam and the weft were under same conditions. So the only constructional change in these four fabric types are their weave geometry. And assume that all tests are carried away under same testing standards and conditions. Under above mentioned assumptions the tests results have been analyzed here. These geometrical changes have a major effect on fabric’s mechanical properties. It is defined as a result of the material's resistance to external forces creating a change in form in textile fabric. 2/2 Matt 1/1 Plain 2/2 S Twill 3/1 Z Twill 2/2 Z Twill 2.0 Tensile Strength Maximum load that a fabric can hold under a uniaxial tensile loading is known as the tensile strength of a fabric. Or else the tensile strength is the force designed to break a substantial percentage of yarns in warp or weft direction is referred to as tensile strength. Comparing to the Knitted and nonwoven fabrics, tensile strength of a woven fabric is an important property. Mean Tensile strength and fabric geometry 500 400 300 200 100 0 1/1 Plain 2/2 Matt 2/2 S Twill Mean Tensile Strength - Warp 2/2 Z Twill 3/1 Z Twill Mean Tensile Strength - Weft 2.1 Warp Tensile strength According to the given data using above given graph, warp has a higher tensile strength than weft yarns. Warp has been undergone sizing, and also due to the shedding process normally warp yarns are subjected to a higher twist than weft yarns (So they get the strength to face abrasion and other mechanical forces). Because of that warp yarns carry higher tensile strength than weft yarns. Plain weave has the lowest tensile strength. Plain weave has the highest binding points in its structure. When the interlacement points are higher the fabric undergo high crimp. So due to the largest number of biding points warp and weft yarns have a very less amount of slippage within the fabric. Due to this phenomena fabric can get easily break under lesser tensile strength. Thus the plain fabric has the lowest tensile strength. Matt weave has lower interlacement points than plain due to their grouped structure (Bucket weave). So due to this it has a slightly higher warp tensile strength than plain weave. 3/1 twill weave has the lesser number of binding points in warp direction. Thus it shows the highest tensile strength. And comparative to the plain weave, 2/2 S and Z twills also have lower binding points, thus they have higher tensile strength than plain weave. 2.2 Weft Tensile strength As per the theoretical explanation, higher the crimp, lesser the tensile strength. But weft way tensile strengths are quite different than warp way results. Plain weave, 2/2 S twill, 2/2 Z twill, 3/1 Z Twill, 2/2 Matt shows consecutively highest to lowest weft tensile strength. Here we can make an assumption that with the increment of binding points in weft direction the friction of the weft yarns and the resistance to slippage of yarn will increase and also it gives floats to the weave. So due to that plain weft yarns have the highest tensile strength. And due to the lesser binding points in Twill it has decreased. Matt also shows lesser binding points. Thus their friction between yarns are less so they have lower tensile strength in weft direction. 3.0 Tearing Strength Tearing strength of a fabric is under specific circumstances, the force necessary to begin or continue tearing a cloth in weft or warp direction. A rupture in a fabric or garment usually happens in a straight line and can be caused by a moving cloth snagging on a sharp item. Mean Tearing strength VS Fabric length 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1/1 Plain 2/2 Matt 2/2 S Twill Mean Tearing Strength - Length 2/2 Z Twill 3/1 Z Twill Mean Tearing Strength - Width According to the test results, both warp and weft ways, tearing strength is getting increased from plain 2/2 S twill, 3/1 Z Twill, 2/2 SZ Twill, 2/2 Matt weave. When compare plain and twill weaves, Plain weave obtain the lowest tensile strength, which is around 16N. But 2/2 and 3/1 twills obtain 22N -24N tearing behavior. The main reason for this is the number of interlacements. Lesser the number of interlacements lesser the crimp will be. And the cover factor will be higher. So the bearing strength of the fabric will increase. Because bunch of yarns can move together as a bunch. So the applied force will be deviated among bunch of yarns. So the tensile and tearing strength will be higher. So here twill weave will have higher tear resistance than plain weave. When we consider the 2/2 matt weave, they face tearing force as yarn pairs. Thus it has a higher tearing strength. 4.0 Conclusion As per the research testing results, we can see that Matt weave has the comparatively high tensile and tearing strength. Since the fabric quality is affected by both tearing and tensile strengths, we can say matt has the better quality. And test results show that fabric properties are affected by their constructional parameters. 800 Words References Israt Jahan. (2017, Oct 21). Effect of Fabric Structure on the Mechanical Properties of. p. 7. Nasrin Ferdousa, Md. Sadiqur Rahmanb, Reashad Bin Kabir, Arif Eftekhar Ahmed. (2014, Dec 9). Structures, A Comparative Study on Tensile Strength of Different Weave. International Journal of Scientific Research Engineering & Technology (IJSRET), ISSN 2278, 7. Shakil Mahmud, Tarek Hossain Raju, Afjal Hossen. (2020). Effect of Weave Type Variation on Tensile and Tearing Strength of Woven. Technium Vol. 2, 6.