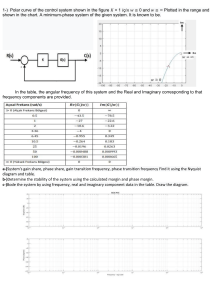
Frequency response analysis • Frequency response is the steady state output of a linear system to sinusoidal input • Even though these responses are of same frequency as that of input, they differ in amplitude and phase angle from the input • These differences are functions of frequency • Since input is sinusoidal substitute s=jω in the transfer function • Magnitude frequency response • Phase frequency response • Combination of the magnitude and phase response is called the frequency response frequency Phase plot Frequency domain specifications • • • • Gain margin Phase margin Resonant frequency Resonant peak Gain margin • It is the gain that can be varied before the system becomes just stable • The amount of additional open-loop gain, expressed in dB and measured at 180 degree of phase shift, required to make a closed-loop system unstable. Phase margin • The phase margin is the amount of additional open-loop phase shift required at unity gain to make the closed-loop system unstable. Standard second order system • Resonant Peak • Resonant frequency Gain margin and Phase margin from bode plot Minimum phase system • It is a system in which poles and zeros will not lie on the right side of s plane • The transfer function of the minimum phase system can be determined from the bode plot Polar plot