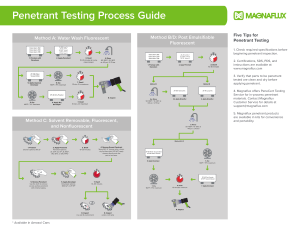
NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING (NDT) NDT • Is the process of inspecting, testing, or evaluating materials, components or assemblies for discontinuities or differences in characteristics without destroying the serviceability of the part or system Most Common NDT Methods • • • • • Visual Liquid Penetrant Magnetic X-ray Ultrasonic Visual Inspection Most basic and common inspection method. Tools include borescopes, magnifying glasses and inspection mirrors. Penetrant Testing • Penetrant Testing can be performed on magnetic and non-magnetic materials. • The basic principle of liquid penetrant testing is that when a very low viscosity (high fluid) liquid (penetrant) is applied to the surface, it will penetrate into fissures and voids open to the surfaces. Once the excess penetrant is removed and developer is applied the penetrant trapped in those void will flow back out creating an indication. Penetrant Testing Dye Penetrant Inspection Step 1. Pre-Cleaning Ensure surface is very Clean normally with the use of a solvent Dye Penetrant Inspection Step 2. Apply penetrant After the application of the penetrant, the penetrant is normally left on the components surface for approximately 15 minutes (dwell time). Dye Penetrant Inspection Step 3. Clean off penetrant After sufficient penetration time (dwell time) has be given the penetrant is removed, care must be taken not to wash any penetrant out off any defects present Dye Penetrant Inspection Step 4. Apply developer After the penetrant has be cleaned sufficiently a thin even layer of developer is applied. The developer acts as a contrast against the penetrant and allows for capillary action to take place Dye Penetrant Inspection Step 5. Inspection / development time Inspection should take place immediately after the developer has been applied any defects present will show as a bleed out during development time. After full inspection has been carried out post cleaning is generally required. Dye Penetrant Inspection Step 6. Post Cleaning Dye Penetrant Testing Bleed out viewed under white light Colour contrast Penetrant Magnetic Particle Testing The part is magnetized. Finely milled iron particles were applied to the specimen. These particles are attracted to magnetic flux leakage fields and will cluster to form an indication directly over the discontinuity. This indication can be visually detected under proper lighting conditions. Magnetic Particle Inspection Collection of ink particles due to leakage field Electro-magnet (yoke) DC or AC Prods DC or AC Radiographic Testing The part is placed between the radiation source and a piece of film. The part will stop some of the radiation. Thicker and more dense area will stop more of the radiation. X-ray film The film darkness (density) will vary with the amount of radiation reaching the film through the test object. = less exposure = more exposure Top view of developed film Radiographic Testing X – Rays Electrically generated Gamma Rays Generated by the decay of unstable atoms Radiographic Testing Source Radiation beam Radiographic film Image quality indicator Test specimen Ultrasonic Testing (Pulse-Echo) High frequency sound waves are introduced into a material and they are reflected back from surfaces or flaws. Reflected sound energy is displayed versus time, and inspector can visualize a cross section of the specimen showing the depth of features that reflect sound. f crack plate Crash of United Flight 232 Sioux City, Iowa, July 19, 1989 A defect that went undetected in an engine disk was responsible for the crash of United Flight 232.