Lecture Notes
advertisement

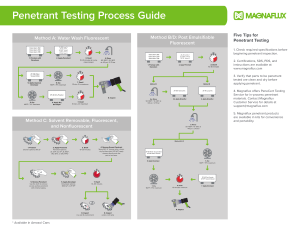
Lesson 10 Testing EG243 March 13, 2013 Lecture 10 Testing: -square and .505 round tensile specimens -”The Design and Methods of Construction of Welded Steel Merchant Vessels, 15 July 1946" book -Charpy impact specimens -Transverse and longitudinal shear test specimens - examples of AWS D1.1 showing coupon removal -examples of face, root, side bends -x-ray films and test assemblies - standards showing acceptable levels of porosity - film cassette with exposed film - Dye penetrant, cleaner, developer - PT specimen - MT equipment - MT crack specimens - UT equipment - UT test assembly - UT procedure Lecture: - Two types of testing. First consider Destructive Testing (Mechanical Testing). For welding, DT is used to qualify procedures and welders, in the laboratory. Common Destructive tests: - Page 576 Tensile: rectangular or .Page 575 .505 round: load/cross-sectional area = psi - Also on Page 576 ductility: elongation/gage on tensile specimen Final gauge length minus originalgauge lentgth divided by originl gauge length = % in 2 inches. - Page 591 hardness: resistance to penetration indicates wear-resistance and strength. (Directly related to tensile strength: ½ Brinell Hardness x 1000 = tensile psi.) - Page 577 Another test done on a tensile testing machine is the shear test. Two types: - transverse: max. force / (2 x width) . - longitudinal: max. force / length of ruptured weld - Page 576 – 7 fatigue: amount of stress, and number of stress cycles without failure and the stress used. - Page 583 impact test: Charpy specimens, ft-lbs. Absorbed from pendulum indicates toughness. Show broken Liberty Ships in book “The Design and Construction…” - page 582 (top): fillet break test: inspect broken weld faces. - Page 579 bends: root, face, side. Face toward gap, rRoot toward gap, side bend either side to the gap. - Nondestructive Testing: To examine welds in production where samples can't be removed. - Start Dye Penetrant (surface only) Lesson 10 Testing EG243 March 13, 2013 - precleaning and penetrant application. - Visual Testing is most common show: - Overlap forms stress raiser. - Porosity is often not visible on surface. - Undercut: show plastic weld examples - Crater cracks, caused by shrinkage, can be avoided by filling and reducing heat slowly. - Underfill. - Inadequate penetration: LOF in root - Lamination, Delamination, Lamellar Tears caused by stress across thickness of plate. Change joint design, make smaller passes to reduce stress. - Magnetic Particle - magnetic field created in workpiece by electromagnet or electric current is disrupted by discontinuities: -in MT this is revealed by attracting iron powder. - in Eddy Current testing, the strength of the field is measured - inspects surface and as much as 1/8" deep, but cannot locate flaws deep beneath the surface. - (show cracks) - X-Ray (Radiography,volumetric) - x-rays are blocked by metal, discontinuities allow more rays to pass through, film devlops black. - show Inclusions: nonmetallic materials, slag, silicates. - ( show Incomplete Fusion, or LOF) - Porosity: small amounts may be acceptable discontinuities, but more than allowed are “defects”.(MIL-STD 2035 in PT Procedure). - Not all inspected to same standard. Class I,II,III depends on type of service. - Ultrasonic (volumetric) - show diagram of use of trigonometry to map length and width of flaws. - Finish Dye Penetrant (surface only) - precleaning and penetrant application done at beginning of lecture - clean off penetrant. - apply developer. - inspect. Today’s lab, from the Course Schedule in the 3 ring binders. Booths 1-7 first demonstration. Booths 8 – 14 cut plates.