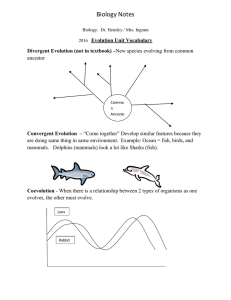
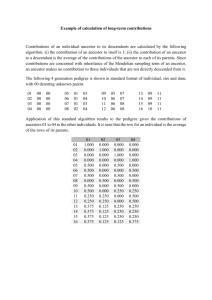
Evidence for Evolution 1. Fossil Record 2. Anatomoy 3. Embryology 4. Biochemistry Forces/Mechanisms of Evolution - Natural/artificial selection - Mutations/variations - Migrations/gene flow - Genetic drift Trends in Evolution - Coevolution - Convergent evolution - Adaptive radiation - Extinction: - Gradualism vs. Punctuated equilibrium - Speciation Anatomy Similar features that originated in a common ancestor, but now have different functions and/or external structures (common ancestry, different function now) Example: front limbs of human and bird: Features that serve identical functions and look somewhat alike but do not share a common ancestor (no common ancestor, but same function now) Example: wing of a butterfly and wing of a bird: Features that now seem to serve no useful function and are usually reduced in size, Structure was useful in an ancestor, but no longer serves original purpose- so it has changed, Example: human tailbone: Word Bank Homologous Structures Vestigal structures Analogous Structures Forces/Mechanisms of Evolution The study of shared features in young emrbyos suggest evolution from a common ancestor: When one extreme trait is picked over another (example: environment picking dark green frogs over light green) When a moderate or intermediate trait is selected (example: environment picking a medium green color instead of light green or dark green) When both of the extremes are chosen (example: environment picks light green and dark green and eliminates medium green) Word Bank Migration/Gene Flow Embryology Genetic Drift Directional selection Stabilizing selection Disruptive selection ______________ __________________ ____________________ Movement of individuals in and out of a population which introduces new traits: Random loss of alleles/variation throughout generations, due to “failed” mating A change of two or more organisms in close association with each other (two organisms changing according to one another): Animals developing similar feature due to environment and not common ancestor: Species split into seperate species from an original ancestor due to different environments: When all members of a species die off or no longer reproduce: Species slowly and steadily changes through small changes (slow evolution): Long periods of stability in a species are “punctuated” (interrupted) by periods of rapid evolution (fast evolution) Creation of new species, Occurs when two populations have bee reproductively isolated: Word Bank Speciation Coevolution Extinction Punctuated Equilibrium Convergent Evolution Gradualism Adaptive Radiation