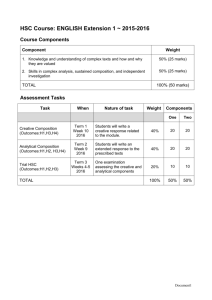
1. Save this to your PDHPE OneDrive folder. 2. Copy Q onto paper, set a stopwatch (1.8 mins/mark) and handwrite response. 3. Submit in Canvas, notify me when you have done so. - PDF / Word Document format only (so I can annotate in speedgrader). 4. Download annotated feedback from speedgrader and paste into this table under the Q. - Now you have a question bank for every DP in the syllabus, and you can attempt each Q again and seek more feedback. Also include your own practice questions sourced from past HSC papers. This will be extremely valuable for study and means you have an online version in case your paper copies are lost. Core 2: Factors Affecting Performance Students Learn about Practice Q’s (keep writing new syllabus dot points in as we progress) CQ1 DP1: Energy systems - Alactacid system (ATP/PC) - Lactic acid system - Aerobic system HSC 2020 PDHPE Section I, Q23a Q. An athlete ran in the 100-metre final at an Olympic Games. In the table below, identify the predominant energy system. (3 marks) Predominant energy system used by this athlete Alactacid system (ATP/PC) Source of fuel Creatine phosphate Energy system duration 10-12 seconds Cause of fatigue Depletion of CP Rate of recovery 2mins HSC 2017 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q25 Q. Compare TWO different energy systems by exploring their duration, sources of fuel and causes of fatigue. Use examples to support your answer. (7 marks) HSC 2014 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q27 Q. Compare the two anaerobic energy systems. (5 marks) DP2: Types of training and training methods - Aerobic, eg continuous, Fartlek, aerobic interval, circuit - Anaerobic, eg anaerobic interval - Flexibility, eg static, ballistic, PNF, dynamic - Strength, eg free/fixed weights, elastic, hydraulic DP3: Principles of training - Progressive overload - Specificity - Reversibility - Variety - Training thresholds - Warm up and cool down DP4: Physiological adaptations in response to training - Resting heart rate - Stroke volume and cardiac output - Oxygen uptake and lung capacity - Haemoglobin level - Muscle hypertrophy - Effect on fast/slow twitch muscle fibres CQ2 DP5: Motivation - Positive and negative - Intrinsic and extrinsic HSC 2020 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q24 Q. Explain how TWO flexibility training methods can improve performance of an athlete in ONE sport. Provide examples to support your answer. (5 marks) HSC 2011 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q24b Q. Describe how different strength-training methods affect an athlete’s performance. (4 marks) HSC PDHPE 2017 Exam, Section I, Q26 Q. Explain the physiological adaptations an individual develops in response to the different principles of training. Use examples to support your answer. (8 marks) HSC PDHPE 2012 Exam, Section I, Q27 Q. How can THREE principles of training be applied to improve strength? Provide examples. (6 marks) HSC PDHPE 2017 Exam, Section I, Q26 Q. Explain the physiological adaptations an individual develops in response to the different principles of training. Use examples to support your answer. (8 marks) HSC PDHPE 2013 Exam, Section I, Q25 Q. Describe the effect of stoke volume and cardiac output on aerobic performance. (3 marks) HSC 2015 PDHPE, Section I, Q26 Q. Explain how different types performance. (4 marks) of motivation can affect an athlete’s HSC 2021 PDHPE, Section I, Q23 Q. Describe TWO ways in which extrinsic motivation can affect an athlete’s performance? (4 marks) DP6: Anxiety and arousal - Trait and state anxiety - Sources of stress - Optimal arousal HSC 2018 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q25 Q. Explain why the optimum level of arousal varies for different sports (5 marks) HSC 2014 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q26 Q. How do anxiety and arousal differ in terms of their effect on athletic performance? (4 marks) DP7: Psychological strategies to enhance motivation and manage anxiety - Concentration/attention skills (focusing) - Mental rehearsal/visualisation/imagery - Relaxation techniques - Goal-setting CQ3 DP8: Nutritional requirements - Pre-performance, including carbohydrate loading - During performance - Post-performance HSC 2019 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q21 Q. Outline how goal setting can influence an athlete’s motivation level. Use examples to support your answer. (3 marks) HSC 2019 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q21 Q. Justify the psychological strategies used by athletes to enhance their motivation and to manage anxiety. (8 marks) HSC 2019 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q22 Q. Justify whether carbohydrate loading could improve performance for an athlete competing in a 100-metre running race. (4 marks) HSC 2014 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q25 Q. Outline the post-performance dietary considerations of an endurance athlete. (3 marks) DP9: Supplementation - Vitamins/minerals - Protein - Caffeine - Creatine products HSC 2017 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q24 Q. Using examples, explain how specific vitamins and/or minerals affect athletic performance (5 marks) HSC 2013 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q27 Q. What are the advantages and disadvantages of protein supplementation and creatine supplementation for improved athletic performance? (5 marks) DP10: Recovery strategies - Physiological strategies, eg cool down, hydration - Neural strategies, eg hydrotherapy, massage - Tissue damage strategies, eg cryotherapy - Psychological strategies, eg relaxation CQ4 DP11: use physiological and neural strategies during recovery. Use examples to support your answer (8 marks) HSC 2012 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q28 Q. Describe the different recovery strategies used by athletes to improve performance. Provide examples. (8 marks) HSC 2016 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q24a Q. Outline the stages of skill acquisition. (3 marks) Stages of skill acquisition - Cognitive - Associative - Autonomous DP12: HSC 2018 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q27 Q. Explain why marathon runners Characteristics of the learner, eg personality, heredity, confidence, prior experience, ability HSC 2021 PDHPE, Exam, Section II, Q30b Q. How can characteristics of the learner influence skill acquisition? Use examples to support your answer. (5 marks) HSC 2013 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q26 Q. Describe THREE characteristics of a learner that can influence his/her ability to learn a new skill. (4 marks) DP13: The learning environment - Nature of the skill (open, closed, gross, fine, discrete serial, continuous, self-paced, externally-paced) - The performance elements (decision-making, strategic and tactical development - Practice method (massed, distributed, whole, part) - Feedback (internal, external, concurrent, delayed, knowledge of results, knowledge of performance) HSC 2020 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q27 Q. Analyse how different types of feedback affect a learner’s progress through the stages of skill acquisition. Provide examples to support your answer. (8 marks) HSC 2016 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q24b Q. Outline, using specific examples, the types of feedback that are appropriate at each stage of skill acquisition. (4 marks) HSC 2015 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q28 Q. Why is it important for an athlete to develop the elements of performance? (8 marks) DP14: Assessment of skill and performance HSC 2018 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q26 Q. Evaluate how the characteristics of a skilled performer can be used to appraise elite performance. (7 marks) - - - Characteristics of skilled performers, eg kinaesthetic sense, anticipation, consistency, technique Objective and subjective performance measures Validity and reliability of tests Personal versus prescribed judging criteria HSC 2016 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q25 Q. Using examples, distinguish between valid tests and reliable tests of athletic performance. (5 marks) HSC 2015 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q27 Q. Why are both objective and subjective performance measures appropriate in the assessment of an athletic performance? (5 marks) HSC 2014 PDHPE, Exam, Section I, Q28 Q. How can the skill and performance attributes of athletes be validly and reliably appraised? (8 marks)