Acid-Base Mechanisms
advertisement

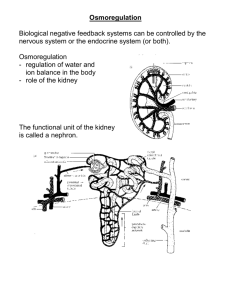
Name:___________________________ Acid-Base Mechanisms & ADH 1. What does ADH stand for? 2. Where is ADH produced? 3. How is the volume of ADH produced controlled? 4. How does ADH control the volume of water that is in the blood? 5. Explain, with the use of a diagram how ADH is produced by a negative feedback mechanism. Name:___________________________ 6. What does the term buffer mean? 7. What is the normal pH of the blood? 8. What does the term pH mean? 9. Why is it important that buffers are present in the human body? 10. Other than carbonic acid give the name of another amphoteric substance and label the basic and acidic ends. Name:___________________________ 11. What is a hydrogen ion? 12. How are hydrogen ions produced by the body? 13. What is the relationship between H+ concentration and pH? 14. What would be the H+ concentration of a substance with pH 5? 15. What is haemoglobin? Name:___________________________ 16. What is its role? 17. How does haemoglobin act as a buffer to CO2? 18. What is the structure of carbonic acid? 19. Explain the carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system and its importance. Name:___________________________ 20. How does haemoglobin control H+ concentration in the blood? 21. What happens to proteins if they are exposed to too high or too low pH? 22. Show the structure of a phosphate ion Name:___________________________ 23. How do phosphate ions act as a buffer to H+? 24. Which 2 organs in the body are the most important in acid-base balance? What do they do?