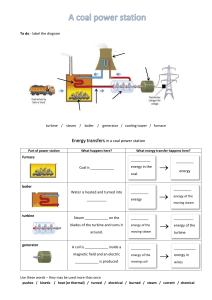
First, what is a powerplant? A power plant is an industrial facility that generates electricity from primary energy. Most power plants use one or more generators that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy in order to supply power to the electrical grid for society's electrical needs. The exception is solar power plants, which use photovoltaic cells (instead of a turbine) to generate this electricity. What are the types of powerplants? • Coal-fired power plant • Nuclear power plant • Hydroelectric power plant • Solar power plant • Geothermal power plant • Wind power plant Coal-fired power plant Coal fired power plants are a type of power plant that make use of the combustion of coal in order to generate electricity. Their use provides around 40% of the world's electricity and they are primarily used in developing countries. How it works? The workings of a coal fired power station are simple and straight forward. The animation above simplifies the process. Initially coal is pulverized (D) and burnt in a furnace (C). The heat energy released is used to heat water into super hot steam which is then used to turn turbines (B). The turbines drive the generators (A) which produce electricity. The steam is then condensed and recycled. The chimney labeled "F", known as a condensing tower, releases water vapor and is part of the recycling of steam. The chimney labeled "G" is attached to the furnace and releases carbon dioxide and ash. Advantages •Coal’s ability to supply power during peak power demand either as base power or as off-peak power is greatly valued as a power plant fuel. •depends on a lot of manpower to operate, so creates jobs •well-understood, non-threatening technology as compared to the nuclear alternative Disadvantages •Coal is a nonrenewable resource •Coal emits the largest amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) per kWH generated of all fossil fuels, and thus is the largest contributor to global warming •Coal mining can have serious environmental issues •Coal burning releases sulfur dioxide (SOx) and nitrous oxide (NOx) which cause acid rain, if not captured Nuclear power plant PowerPoint Presentation A Simple nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear Simple PowerPoint Presentation reactor. The steam is used to spin large Simple PowerPoint Presentation turbines that generate electricity. The steam is Simple Presentation used toPowerPoint spin large turbines that generate electricity. You can simply impress your audience and add a unique zing and appeal to your Presentations. Easy to change colors, photos and Text. You can simply impress your audience and add a unique zing and appeal to your Presentations. How it works? Nuclear power plants use nuclear fission to produce electricity. A nuclear power reactor uses uranium rods as nuclear fuel to generate heat that will be used to generate electricity. Carbon dioxide and water is then used to take the heat away to produce steam and generate electricity. Advantages •Unlike traditional fossil fuels like coal, nuclear power does not produce greenhouse gas emissions like methane and CO2. •Not intermittent Disadvantages •Despite all the safety measures in place these nuclear plants, different factors caused them to go into meltdown, which was devastating for the environment and for local inhabitants who had to flee the affected areas. •Cheap to run •Nuclear waste •Expensive to build Hydroelectric power plant Hydro power is electrical energy produced through the power of moving water. In modern technology, hydropower moves turbines that pass on their energy to a generator which then produces electric power. Hydropower is a type of renewable energy, and once the power plant is constructed it produces little to no waste. How it works? The dam raises the water level of the river to create falling water. Also controls the flow of water. The reservoir that is formed is, in effect, stored energy. The force of falling water pushing against the turbine's blades causes the turbine to spin. A water turbine is much like a windmill, except the energy is provided by falling water instead of wind. The turbine converts the kinetic energy of falling water into mechanical energy connected to the turbine by shafts and possibly gears so when the turbine spins it causes the generator to spin also converts the mechanical energy from the turbine into electric energy. Generators in hydropower plants work just like the generators in other types of power plants. The transmission lines conduct electricity from the hydropower plant to homes and business. Advantages Disadvantages •Hydropower is fueled by water, so it's a clean fuel source, meaning it won't pollute the air like power plants that burn fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas. •Hydropower is non-polluting, but does have environmental impacts. Hydropower facilities can affect land use, homes, and natural habitats in the dam area. Reservoirs may cover people’s homes, important natural areas, agricultural land, and archaeological sites. •Hydroelectric power is a domestic source of energy, allowing each state to produce their own energy without being reliant on international fuel sources. •The energy generated through hydropower relies on the water cycle, which is driven by the sun, making it a renewable power source, making it a more reliable and affordable source than fossil fuels that are rapidly being depleted. •Hydroelectricity is hydrology dependent. The system depends on precipitation levels, which can fluctuate from year to year, causing instability. •In some cases, hydroelectricity can disrupt wildlife habitat. Hydroelectric power plants can cause a loss or modification of fish habitat, and lead to the entrapment of fish and the restriction of their passages. Solar power plant A solar power plant is a type of facility that converts sunlight indirectly like solar thermal plants into electricity How it works? Basically, a heat transfer fluid is heated and circulated in the receiver and used to produce steam and that is converted into mechanical energy in a turbine which powers a generator to produce electricity Advantages • Solar power is pollution free and causes no greenhouse gases to be emitted after installation • Reduced dependence on foreign oil and fossil fuels Disadvantages •High initial costs for material and installation •Needs lots of space as efficiency is not 100% yet •Weather-Dependent • Efficiency is always improving so the same size solar that is available today will become more efficient tomorrow Geothermal power plant Geothermal power plants are used in order to generate electricity by the use of geothermal energy (the Earth's internal thermal energy). They essentially work the same as a coal or nuclear power plant, the main difference being the heat source. With geothermal, the Earth's heat replaces the boiler of a coal plant or the reactor of a nuclear plant. Modern Portfolio Designed How it works? Hot water is pumped from deep underground through a well under high pressure. When the water reaches the surface, the pressure is dropped, which causes the water to turn into steam. The steam spins a turbine, which is connected to a generator that produces electricity. The steam cools off in a cooling tower and condenses back to water. The cooled water is pumped back into the Earth to begin the process again. Types of Geothermal Powerplant Dry steam plants are the most common types of geothermal power plants, accounting for about half of the installed geothermal plants. They work by piping hot steam from underground reservoirs directly into turbines from geothermal reservoirs, which power the generators to provide electricity. After powering the turbines, the steam condenses into water and is piped back into the earth via the injection well. Flash steam plants differ from dry steam because they pump hot water, rather than steam, directly to the surface. These flash steam plants pump hot water at a high pressure from below the earth into a “flash tank” on the surface. The flash tank is at a much lower temperature, causing the fluid to quickly “flash” into steam. The steam produced powers the turbines. The steam is cooled and condenses into water, where it is pumped back into the ground through the injection well. In these binary cycle plants, the main difference is that the water or steam from below the earth never comes in direct contact with the turbines. Instead, water from geothermal reservoirs is pumped through a heat exchanger where it heats a second liquid— like isobutene (which boils at a lower temperature than water.) This second liquid is heated into steam, which powers the turbines that drives a generator. The hot water from the earth is recycled into the earth through the injection well, and the second liquid is recycled through the turbine and back into the heat exchanger where it can be used again. Advantages • Environmentally friendly compared to gas or oil furnaces (no combustion). Disadvantages •Electricity is still needed to operate heat pumps. • Not a significant source of pollution. •Geothermal energy using wells requires an incredible usage of water. • Geothermal energy is a renewable resource as long as the Earth exists. •Discharge into the Earth could include sulfur dioxide and silica (well pumps). • Not weather dependent like solar or wind power; geothermal heat pumps work year-round. Wind power plant Wind power generation means getting the electrical energy by converting wind energy into rotating energy of the blades and converting that rotating energy into electrical energy by the generator. Wind energy increases with the cube of the wind speed, therefore WTGs should be installed in the higher wind speed area. How it works? Wind blows across tall wind turbines.to turn huge turbine blades which spin generators to create electricity. A transformer increases the voltage to send electricity over distribution lines. Then local transformers reduce the voltage for you to use. Advantages • Wind Energy is Renewable and Sustainable Disadvantages •Unpredictable Energy Source •Noise Pollution • Renewable & clean source of energy • Low Operating Costs and Steadily Decreasing Overall Cost •Biological and Environmental Impacts