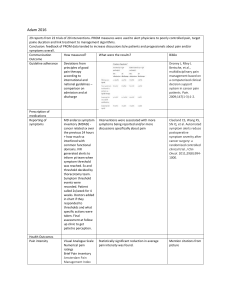
Adam 2016 29 reports from 22 trials of 20 interventions. PROM measures were used to alert physicians to poorly controlled pain, target paine ducation and link treatment to management algorithms. Conclusion: feedback of PROM data tended to increase discussions b/w patients and progessionals about pain and/or symptoms overall. Communication How measured? What were the results? Biblio Outcome Guideline adherance Deviations from Droney J, Riley J. principles of good Bertsche, et al., pain therapy multidisciplinary pain according to management based on international and a computerized clinical national guidelines – decision support comparison on system in cancer pain admission and at patients. Pain. discharge 2009;147(1-3):1-2. Prescription of medications Reporting of symptoms Health Outcomes Pain intensity MD anderso symptom inventory (MDASI) cancer related sx over the previous 24 hours + how much sx interfered with common functional domains. IVR generated alerts to inform pt team when symptom threshold was reached. Sx and threshold decided by thoracotomy team. Symptom threshold events were recorded. Patient called 2x/week for 4 weeks. Doctors added in chart if they responded to thresholds and what specific actions were taken. Final assessment at follow up clinic to get patietns perception. Interventions were associated with more symptoms being reported and/or more discussions specifically about pain Cleeland CS, Wang XS, Shi Q, et al. Automated symptom alerts reduce postoperative symptom severity after cancer surgery: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(8):9941000. Visual Analogue Scale Numerical pain ratings Brief Pain inventory Amsterdam Pain Management Index Statistically significant reduction in average pain intensity was found. Mention citations from picture Alsaleh Health outcomes Physical symptoms burden Communication effects Patient-provider communication Oncologists randomized to receive findings of completed questionnaires or not to receive. 510 pts. Self rated pain at baseline and then 4 weeks later. Improvement in pain rating and increase in analgesic was measured. Trowbridge R, Dugan W, Jay SJ, et al. Determining the effectiveness of a clinical-practice intervention in improving the control of pain in outpatients with cancer. Acad Med. 1997;72(9):798-800. DETMAR ET AL: Randomized cross over trial. 10. 214 pts. Half receive results of EORTC QLQ-C30 scale (PRO) and half conventional way without PRO. Washout period and crossed over. Detmar: better composite score on evaluation checklist Velikova: QoL scores were better in intervention than control (emotional well being) Detmar SB, Muller MJ, Schornagel JH, Wever LD, Aaronson NK. Healthrelated quality-of-life assessments and patientphysician communication: a randomized controlled trial [published correction appears in JAMA. 2003 Feb 26;289(8):987.]. JAMA. 2002;288(23):3027-3034. VELIKOVA ET AL: 3 arms. EORTC QLQ arm with feedback to physicians, EORTC QLQ arm without feedback to physicians, no questionnaire arm. Primary outcome was QoL and FACTG Patient and Clinician awareness of QOL Detmar RCT ^ Better physician awareness of patients QoL as assessed by agreement b/w physicians and patients rating of symptoms on the Dartmouth Primary Care Cooperative Information Velikova G, Booth L, Smith AB, et al. Measuring quality of life in routine oncology practice improves communication and patient well-being: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(4):714-724. Detmar SB, Muller MJ, Schornagel JH, Wever LD, Aaronson NK. Healthrelated quality-of-life assessments and patient- Functional Health Assessment (COOP) and the World Organisation Project of National Colleges and Academics (WONCA) charts Chen 2013 Health outcomes Monitoring of treatment response Positive impact of health outcomes – 13/15 studies Communication effects Patient-provider communication Detecting unrecognized problems Changes to patient management Etkind 2015 Health outcomes Improved psychological and emotional QOL Patient and Clinician awareness and involvement Communication outcomes Reporting of symptoms Patient-provider communication Changes to patient management Howell Health Outcomes physician communication: a randomized controlled trial [published correction appears in JAMA. 2003 Feb 26;289(8):987.]. JAMA. 2002;288(23):3027-3034. Helath realted QOL Early detection and monitoring of symptoms Communication effects Patient-provider communication Increased referral to psychosocial care Consultation time Kotronoulas Health Outcomes Physical symptom burden Communication effects Timing of referrals Discussion prompts Yang 2018 Health Outcomes Patient and Clinician awareness and involvement Physical symptom burden Communication effects Timing of referrals Interprofessional communication Discussion prompts