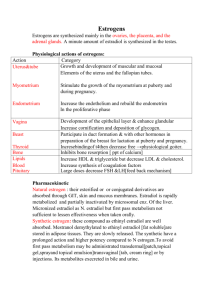
ESTROGEN HORMONE Group 5 By: Ahmed Saeed Hassan 2015/06088 Hossam Eldin Mohamed Saleh 2015/06989 Omneya Waleed Ahmed 20150/06823 Walaa Mosaad 2015/10299 INTRODUCTION What are Estrogens? -Estrogens are steroid compounds that are produced from the ovaries or adrenal glands in the form of estrone or estradiol that stimulate the development and maintainance of female characteristics and sexual reproduction ACTIONS On sex organs: -Estrogens helps in the growth of uterus, fallopian tubes and vagina at the age of puberty -Enhances the rhythmic contraction of the fallopian tubes and uterus -Estrogen suppress the activity of FSH, and stimulate the secretion of LH by direct action on pituitary gland Therapeutic Uses Contraception Hormone replacement therapy Osteoporosis Senile vaginitis CLASSIFICATION Natural: -Estradiol -Estriol -Estrone Synthetic: -Steroidal : mestranol, ethinylestradiol -Non-steroidal : diethylstilbesterol , hexesterol , dienestrol NATURAL ESTROGENS 1. Estradiol: known also 17 Beta - Estradiol -Princple estrogen in premenopausal women 2. Estrone: 1/3 the estrogenic potency of Estradiol -Primary circulating estrogen after menopause 3.Estriol: significantly less potent than estradiol -Present in significant amounts during pregnancy, because its principle estrogen produced by placenta. Synthetic Estrogen Prolame 17 beta amino estrogen (synthetic) that have amine substitution in place of the hydroxyl group at C-17 It has anticoagulant activity so patients with risk of venous thrombus embolism take it Moxestrol (surestryl) treat menopausal symptoms and menstrual disorders Taken orally metabolized by liver with short half life Synthesis Synthesis Receptors -Alpha receptor that are found in breasts , hypothalamus , endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscles -beta receptors that are found in brain ovaries and bones PHARMACOPHORE Estra-1,3,5-triene-3,17B-diol SAR Aromatic ring with C-3 oh is essential for activity The distance between 17 beta hydroxyl and C-3 oh is essential for activity and it must be hydrophobic rigid backbone Unsaturation of ring B decrease the activity Alkylation of the aromatic ring decrease the activity Steroidal structure is not essential for activity Insertion of OH group in positions (6, 7, 11) reduce the estrogenic activity Ester derivatives (acetates or benzoates) have prolonged action PHARMACOKINETICS ABSORPTION: -Synthetic estrogen well absorbed orally and transdermaly -Natural estrogen is inactivated due to first pass effect when administered orally DISTRIBUTION: -Natural estrogens are highly binding to plasma proteins -Estrogen drugs can pass through the palcenta to the fetus -It Can pass to testis to make some adverse effects if administered by males ( inhibit spermatogenesis ) PHARMACOKINETICS METABOLISM: - Estrogen Converted to esterone and vice versa in liver -Estrone (weak estrogen) converted to estriol by 17Bhydroxy dehydrogenation -phase 1 : conjugation by glucuronoic acid -Phase 2 : sulphonation PHARMACOKINETICS EXCRETION: -Mainly in urine -May be in bile Adverse Effects Most common estrogen therapy: -Nausea and breast tenderness -Post-menopausal uterine bleeding may occur Increase the risk of: -Myocardial infarction -Breast cancer and endometrial cancer Other effects -Headache and peripheral edema and hypertension Thank you for your time!