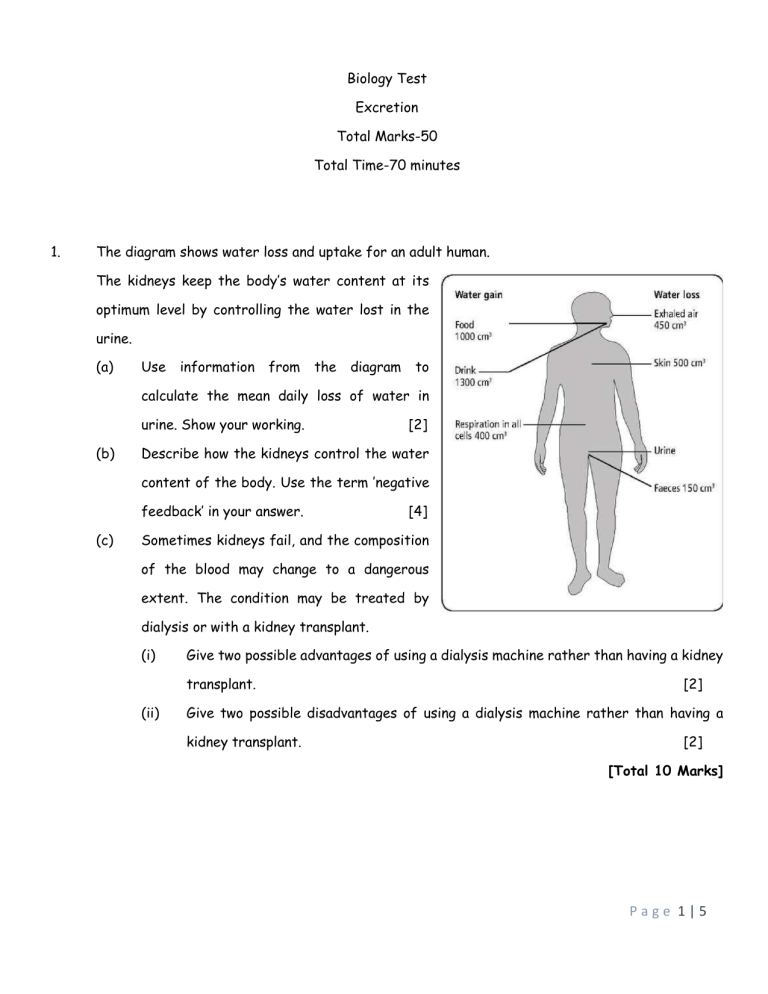
Biology Test Excretion Total Marks-50 Total Time-70 minutes 1. The diagram shows water loss and uptake for an adult human. The kidneys keep the body’s water content at its optimum level by controlling the water lost in the urine. (a) Use information from the diagram to calculate the mean daily loss of water in urine. Show your working. (b) [2] Describe how the kidneys control the water content of the body. Use the term ’negative feedback’ in your answer. (c) [4] Sometimes kidneys fail, and the composition of the blood may change to a dangerous extent. The condition may be treated by dialysis or with a kidney transplant. (i) Give two possible advantages of using a dialysis machine rather than having a kidney transplant. (ii) [2] Give two possible disadvantages of using a dialysis machine rather than having a kidney transplant. [2] [Total 10 Marks] Page 1|5 2. (a) (b) Define the following terms (i) excretion, (ii) egestion. [2] The kidney is an excretory organ. It produces urine that contains urea. (i) State where in the body urea is formed. (i) State what urea is formed from. [2] (c) The diagram on the right shows the urinary system and its blood supply. Mention the names of the labelled structures Q, R, S and T. (d) [4] Complete the table below to show which components of the blood are also part of the urine of a healthy person. Use ticks () and crosses (x). Two boxes have already been completed. Draw the table to answer your question. Component of blood [2] Present in urine Glucose Red blood cells Salts Urea Water White blood cells x [Total 10 Marks] Page 2|5 3. (a) The diagram shows the process of filtration in the kidney. Use information in the diagram and your own knowledge of how the kidney works to explain why: (i) protein molecules are not normally present in urine. [1] (ii) Glucose molecules are not normally present in urine. [3] (b) Write a short note on Aldosterone. [2] (c) A patient has kidney failure. Every few days the patient goes into hospital for dialysis treatment. The graph shows the concentration of urea in the patient’s blood over a period of two weeks. The concentration of urea in a healthy person’s blood is shown for comparison. (i) Suggest why the concentration of urea in the patient’s blood rises between dialysis treatments. [1] (ii) If the concentration of urea in the blood rises to 9 units, the patient may die. The dialysis machine reduces the concentration of urea in the patient’s blood to below the concentration in the blood of a healthy person. Suggest one advantage of this to the patient. (d) [1] One alternative to treatment with a dialysis machine is to have a kidney transplant. The donor kidney is similar tissue type to that of the patient. However, the transplanted kidney Page 3|5 may still be rejected by the patient’s immune system. State ONE other treatments which may help to prevent rejection of the transplanted kidney. [2] [Total 10 Marks] 4. The diagram shows a cross section of a kidney. (a) Identify the parts labelled A to D. [2] (b) State two different functions of this organ. [2] (c) State what you would expect the part labelled X to contain. (d) [1] State three differences in the composition of the blood entering and leaving this organ. [3] (e) Identify the structure to which the part labelled D leads to. (f) State how lungs are involved in excretion. [1] [1] [Total 10 Marks] 5. Look at the simple diagram of a nephron below. Page 4|5 (a) What are the names of the parts labelled X, Y and Z. [3] (b) Four places in the nephron and its blood supply are labelled A, B, C and D. Which of the following substances are found at each of these four places? (Water, urea, protein, glucose and salt). (c) (d) [4] What is the importance of the difference in diameter between the blood vessel A and the blood vessel that goes out of the structure X? [2] What do you mean by selective reabsorption? [1] Page 5|5