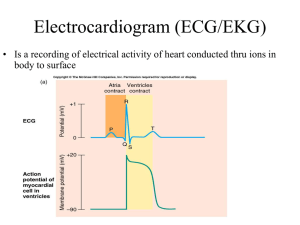
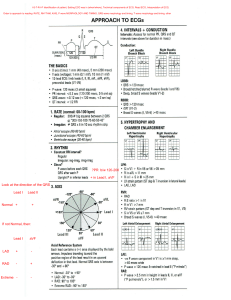
1 EKG Review Graph Paper 2 P wave represents atrial depolarization QRS represents ventricular depolarization and contraction. T wave represents ventricular repolarization U wave indicates the recovery of the Purkinje conduction fibers. This wave component may not be observable 3 EKG interpretation should be performed using a standard five step procedure: Rhythm Rate P Wave PR Interval QRS Interval 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Step 1. Is the Rhythm Regular or Irregular Small variations of up to 10% are considered equal. Step 2. What is the rate - Count the number of QRS complexes over a 6 second interval. Multiply by 10 to determine heart rate. The second method uses small boxes. Count the number of small boxes for a typical R-R interval. Divide this number into 1500 to determine heart rate. Step 3. P-wave Are they present? Do they occur regularly? Is there one P-wave for each QRS complex? Are the P-Waves smooth, rounded, and upright? Do all P-Waves have similar shapes? Step 4. PR Interval - Measure the interval from where the P wave begins until the beginning of the QRS complex Normal 0.12 to 0.20 seconds (3 to 5 small boxes) 4 Step 5. QRS Complex - Measure the QRS complex from the end of the PR interval to the end of the S wave Normally this interval is 0.10 seconds or less 1. Regular vs Irregular Rhythms Regular Rhythms 1. NSR 2. SB 3. ST 4. 1st Degree 5. 2nd Degree Type II 6. 3rd Degree 7. Junctional 8. Idioventricular 9. Aflutter Irregular Rhythms 1. Afib 2. Aflutter (can be both) 3. SA 4. WAP 5. 2nd Degree Type 1 2. Rate Slow <60 Normal 60-100 Fast >100 1. SB 2. Junctional 3. Idioventricular 4. Afib (atypical) 5. 3rd Degree 1. NSR 2. Acc. Junctional 3. Acc. Idioventricular 4. SA 5. WAP 6. Afib 7. Aflutter 8. 2nd Degree Type 1 1. ST 2. Junc Tachycardia 3. SVT 4. Afib with RVR 5. PAT 3. P-wave Present, Upright, Before QRS 1. NSR 2. SB 3. ST 4. Aflutter (lots of them) 5. 1st Degree AVB 6. 2nd Degree Type I 7. 2nd Degree Type II Absent, Inverted, Varies 1. Idioventricular 2. 3rd Degree 3. Afib 4. Junctional 5 8. Sinus Arrhythmia 9. Wandering Atrial Pacemaker 4. PR Interval PR <.20 (Immeasurable) 1. NSR 2. SB 3. ST 4. SA 5. WAP PR>.20 1. Afib 2. Aflutter 3. 2nd Degree Type II 4. 3rd Degree 5. Junctional/Idioventricular 1. 1st Degree 2. 2nd Degree Type I 5. QRS Less than .12 1. NSR 2. SB 3. ST Greater than .12 4. SA 5. WAP 6. Junc. Rhythms 1. Idioventricular 2. Left Bundle Branch Block 3. Right Bundle Branch Block Lethal Arrthythmias 1. Ventricular Tachycardia 2. Ventricular Fibrillation 3. Torsades De Pointes 6 Individual Cardiac Rhythms Components SB Regular Rate 40-60 P wave normal PR normal QRS normal SVT Regular Rate >150 P wave normal PR interval normal QRS normal NSR Regular Rate 60-100 P normal PR interval normal QRS normal Afib Irregular Rate: Atrial >400, Ventricular variable P wave absent or irractic PR interval not measurable QRS normal Sinus Arrhythmia Irregular Rate 60-100 (may increase) P wave normal PR interval normal QRS normal Wandering Atrial Pacemaker Irregular Rate Normal P wave changes shape (small) PR interval varies due to shape of P wave QRS normal Junctional Tachycardia Regular Rate 100-150 P wave hidden, inverted, or after QRS PR absent or short QRS Normal Accelerated Junctional Regular Rate 60-100 P wave hidden, inverted, or after QRS PR not measurable QRS Normal Accelerated Idioventricular Regular Rate 50-100 P wave absent PR not measureable QRS wide >.12 (looks like a PVC) First Degree Heart Block Regular Rate 60-100 P normal PR >.20 QRS normal 2nd Degree Type II Surprisingly Regular Rate Have to count atrial and Ventricular P wave normal, but too many before a QRS, not next to each other PR interval not measureable QRS Normal 3rd Degree Regular Rate Count Separately (Slow) P wave Normal shape and size, may appear within QRS complexes PR absent QRS normal or wide ST Regular Rate 100-150 P normal PR interval normal QRS normal Aflutter Regular or Irregular Rate: Atrial >350 Ventricular 60-100 P wave sawtooth, close together PR interval not measurable QRS normal Junctional Regular Rate 40-60 P wave hidden, inverted, or after QRS PR not measurable QRS Normal Idioventricular Regular Rate 30-40 P wave absent PR not measureable QRS wide >.12 (looks like a PVC) 2nd Degree Type I Irregular Rate typically 60-100 P wave normal PR interval progressively longer until QRS drops QRS normal