Unsegmented Worms, Flatworms, Roundworms Worksheet
advertisement

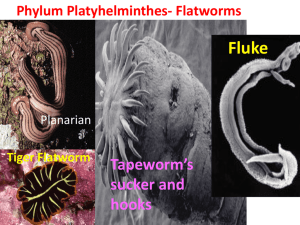
Sponges, Cnidarians, and Unsegmented Worms Section 4: Unsegmented Worms ____________________________________ have bodies that are not divided into special segments o Phylum ______________________________ Consists of simple animals called _________________ o Phylum _______________________ Consists of long, thin worms called ________________ Flatworms The members of the phylum Platyhelminthes are the simplest animals with _________________________________ Most members of this phylum exhibit enough ___________________________, or development of the anterior end, to have what we call a _______________ Many flatworms are no more than a few millimeters thick, although they may be up to 20 meters long Flatworms have more developed ____________________________ than either sponges or cnidarians Form and Function in Flatworms Flatworms feed in either of two very different ways Worms may be __________________________ that feed on tiny aquatic animals Free-living flatworms have a _______________________________ with one opening at the end of a muscular tube called a _________________ They use the pharynx to suck food into the gastrovascular cavity The gastrovascular cavity forms an intestine with many branches along the entire length of the worm In the intestines, _______________________ help break down the food into small particles These particles are taken inside the cells of the intestinal wall, where digestion is completed Like Cnidarians, flatworms expel undigested material through the _________________ Many other flatworms are ___________________________ that feed on blood, tissue fluids, or pieces of cells inside the body of their host In many parasitic flatworms, the digestive tract is simpler than in free-living forms _________________________, which live within the intestines of their host, do not have any digestive tract at all They have ____________________________________ with which they latch onto the intestinal wall of the host From this position, they can simply absorb the food that passes by – food that has already been broken down by the host’s digestive enzymes Flatworms lack any kind of specialized circulatory or respiratory system Freshwater flatworms such as planarians have structures called __________________________ that help them get rid of extra water Free-living flatworms have nervous systems that are much more developed than those of cnidarians and sponges They have a definite head in which a _________________________ is located One or more long nerve cords run from the brain down the length of the body on either side Many flatworms have one or more pairs of light-sensitive organs called ___________________, or eyespots The nervous system of free-living flatworms allows them to gather information from their environment – information that they use to locate food and to find dark hiding places Parasitic flatworms often do not have much of a nervous system Free-living flatworms usually use two means of locomotion at once o _____________________ on their epidermal cells help them glide through the water o ______________________________ controlled by the nervous system allow them to twist and turn so that they are able to react to environmental conditions Reproduction in free-living flatworms can be either sexual or asexual Most free-living flatworms are ______________________________ The eggs hatch within a few weeks Planarians The free-living flatworms belong to the class ____________________ Most familiar members of this class are planarians Turbellarians vary greatly in color, form, and size Although most Turbellarians are less that 1 cm in length, some giant land planarians, which are found in moist tropical areas, can attain lengths of more than 60 cm Flukes Class ________________________ contains parasitic flatworms known as flukes Most flukes are internal parasites that infect the blood and organs These flukes have complicated life cycles that involve at least two different ___________________________ Blood flukes are found primarily in Southeast Asia, North Africa, and other tropical areas ___________________ are the primary hosts of blood flukes Most flukes are hermaphrodites and undergo sexual reproduction in a manner similar to that of free-living flatworms Flukes produce many more eggs than free-living flatworms Blood flukes lay so many eggs that the tiny blood vessels of the host’s intestine break open The broken blood vessels leak both blood and eggs into the intestine The eggs are not digested by the host and thus become part of the _________________ In developed countries, where there are toilets and proper sewage systems, these eggs are usually destroyed in the sewage treatment process But in many undeveloped parts of the world, human wastes are simply tossed into streams or even used as fertilizer Once the fluke eggs get into the water, they hatch into _________________________________ When these larvae find a snail of the correct species, they burrow inside it and digest its tissues The snail is an _________________________________ for the fluke In the intermediate host, the flukes reproduce asexually The resulting new worms break out of the snail and swim around in the water If they find a human, the worms bore through the skin and eat their way to the blood vessels In the blood, the get carried around through the heart and lungs to the intestine, where they live as adults People infected with blood flukes get _________________________ They become weak and often die – either as a direct result of the fluke infection or because they cannot recover from other diseases in their weakened condition Tapeworms Members of the class _______________________ are long, flat parasitic worms that live a very simple life They have a head called a __________________ on which there are several suckers and a ring of hooks These structures attach to the intestinal walls of humans and other animals Adult human tapeworms can be up to 18 meters long Tapeworms almost never kill their host Behind the scolex of the tapeworm is a narrow neck region that is constantly dividing to form many __________________________, or sections, that make up most of the body of the tapeworm The youngest and smallest proglottids are at the anterior end of the tapeworm Male and female reproductive organs are contained in the proglottids If food or water contaminated with tapeworm eggs is consumed by cows, pigs, fish, or other intermediate hosts, the eggs enter the intermediate host and hatch into larvae These larvae grow for a time and then burrow into the muscle tissue of the intermediate host and form a dormant protective stage called a ______________ If a human eats raw or incompletely cooked meat containing these cysts, the larvae become active within the human host Once inside the intestine of a new host, they latch onto the intestinal wall and grow into __________________________ Roundworms Members of the phylum ________________________, which are known as roundworms, are among the simplest animals to have a digestive system with two openings – a mouth and an anus Food enters through the mouth, and undigested food leaves through the anus Roundworms may be the most numerous of all multicellular animals A single rotting apple can contain as many as ___________________ roundworms Form and Function in Roundworms Most roundworms are _________________________ All roundworms have a long tube-shaped digestive tract with openings at both ends Any material in the food that cannot be digested leaves through an opening called the _____________ Roundworms breathe and excrete their metabolic wastes through their body walls They have no ____________________________________ Roundworms have simple nervous systems They have several ganglia in the head region but no definite brain Roundworms reproduce ________________________ How Unsegmented Worms Fit into the World Do not have a lot of positive influence on humans Responsible for some of the most painful and horrific diseases known o ________________________ o ________________________ o ________________________