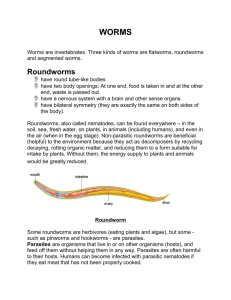
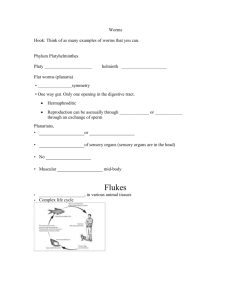
Flatworm and Roundworm Study Guide
advertisement

Unsegmented Worms Study Guide Test Date __________________________________ 1. A cuticle is a living (cellular) or nonliving (noncelluar) protective layer? (Circle one) 2. A tegument is a living (cellular) or nonliving (noncelluar) protective layer? (Circle one) 3. What type of symmetry do flatworms have? ______bilateral________________________________________ 4. The knob-­‐like head of tapeworms with hooks and suckers is called what? __scolex______________________ 5. The hermaphroditic reproductive structure in tapeworms is called what? ___proglottid___ 6. Adult blood flukes of the genus Schistostoma live, feed, and reproduce sexually in what host? _______humans_____________________________ 7. What is the intermediate host for the larva form of blood flukes? ___snail_____________________ 8. What type of roundworm is common in the United States and most often passed from child to child through touching contaminated objects and then putting hands in mouth? ____pinworms_____________________________________ 9. The _flame cells___________ in flatworms are part of the excretory system that removes nitrogen waste. 10. What type of digestive system do worms with a pharynx have? ____bidirectional_______________________ 11. Do roundworms or flatworms cause heartworms in dogs and cats? ______roundworms_______________ 12. How do worms breathe? _____through their skin________________________________________________________ 13. Which type of flatworm is free-­‐living rather than parasitic? _____planarian____________________________ 14. Which types of worms could humans contract by eating undercooked meat? (More than one type) tapeworms and trichinella 15. The reproductive process of planarians is called ____fragmentation___________________________________. Describe this process. The planarian splits in half. The head end grows a new tail and the tail end grows a new head (asexual reproduction). 16. When an organism has a concentration of nerve cells in the anterior region, we say this organism exhibits __cephalization_____________________________. The name for the simple brain in worms is _______ganglia__________________. 17. Which type of worm has a pharynx, flame cells, and eyespots? ___planarian___________________________ 18. The light sensitive eyespots in flatworms are called __ocelli______________________________. Phylum Flatworms Platyhelminthes Roundworms Nematoda Acoelom Pseudocoelom planarians, blood flukes, tapeworms Pinworms, trichinella, hookworms, heartworms Type of Body Cavity Examples 19. How are heartworms transmitted? ____through mosquitos biting animals____________________________ 20. What type of worm can humans get from eating undercooked pork? __Trichinella__________________ 21. Phylum ___Platyhelminthes_______, Class Turbllaria—Examples: planarians 22. Phylum ____Platyhelminthes__________________, Class Trematoda—Examples: flukes 23. Phylum ____Platyhelminthes________________________, Class Cestroda—Examples: tapeworms 24. Phylum Nematoda (roundworms) Examples: hookworms, pinworms, heart worms, Trichinella 25. Organisms that live on the outside of a host are called _____ecotoparasites________________________ while organisms that live inside a host are called ____endoparasites_________________________________. 26. How does food enter a tapeworm? Does it have a mouth? No mouth. Food is absorbed through the skin. 27. Does a tapeworm have a digestive system? Why or why not? No—the food absorbed from the host has already been digested. The tapeworm just gets the nutrients. 28. Do how many digestive openings do roundworms have? What type of digestive system would this be? Two—unidirectional digestive system Labeling. ocelli pharynx hooks head suckers proglottids