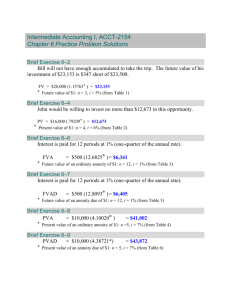
Time Value of money breakdown Some tips and constants in TVM that we need to be aware of: 1. Standard commission is charged at 2% of both the purchase and selling value (Commission will most likely be given to you anyways) (You must pay commission when you buy and when you sell) 2. The Face Value of ANY and ALL bonds in BU111 is $1000 3. In BU111, Bonds are always paid out semi-annually 4. Always draw time diagrams in order to ensure that you get the correct answer PROBLEMS ARE NEVER AS COMPLICATED AT THEY SEEM When solving any TVM question: V – Variables (Identify what needs to be solved) E – Equation (Identify what equation is needed to solve) N – Numbers (Plug numbers in appropriate place) T – Therefore (Always write a therefore statement to contextualize answer) Single Amount (Lump Sum): Putting money into an account once and letting it grow at a rate. Notation: - FVSA: Future Value Single Amount PVSA: Present Value Single Amount r: Rate n: Number of compounding periods (Calculated by multiplying years by # of times compounded per year) Future Value of a Single amount: Justin Moffatt Present Value of a Single amount: How to know whether to calculate present or future value??? Present Value: - Terms such as “Value Today”, “How much do I need today?”, “What is it worth today?” When referring to how much is needed in the bank in order to achieve X dollars later “How much money do I need to have in the bank today to have $50,000 in 6 months” Also referred to as “Discounting back” to the present day Practice drawing time diagrams in order to visualize!!!! Future Value: - Terms such as “Value Tomorrow”, “How much will I have 5 months from now?”, Refers to the expected value of your investment at a given rate and time. “If I put $50,000 in the bank today, how much money will it be worth 5 months from today” Referred to as “Accumulating forward” into the future Practice drawing time diagrams with Justin to help visualize!!!! Annuities: A sequence or periodic payments, usually equal, made at equal intervals of time Terminology: Payment Interval: Amount of time in between 2 consecutive payments Term of an Annuity: Time elapsed over the entire period of the annuity Simple Annuity: The frequency of payments is the same amount of time as the compounding frequency. Ordinary Annuity: Annuity where payments are made at the end of the payment period Annuity Due: Annuity where the payments are always made at the beginning of the payment frequency Justin Moffatt Notation: - FVOA: Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity PVOA: Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity PMT: Payment size r: rate n: number of compounding periods Future Value of an Ordinary Annuity: Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity: Remember! Since you’re calculating present value, the n value MUST be a negative because you are going backwards! Present Value of an Annuity Due: The extra (1+r) makes A LOT more sense when you draw a time diagram Always draw time diagrams to understand not only what is happening but WHY! Future Value of an Annuity Due: To understand whether an annuity is ordinary or an annuity due, ask yourself, “Are payments starting today? Or at the next payment period? (ANNUITY DUE’s START TODAY) How to know whether to use present or future value??? - Similar to Lump Sum! Present Value: Justin Moffatt - Look for terms such as “Value today”, “How much do I need in the bank today in order to make X monthly payments?” Questions where a loan is being paid off with periodic payments Loans, Mortgages, deducting from a sum periodically. etc Future Value: - Look again for terms such as “Value tomorrow” Questions that involve periodic investing (putting money away) ALWAYS mean future Saving up money! KEY TAKEAWAY: Are you saving money and growing an amount? Or are you shrinking an amount and deducting from it? Perpetuity: Annuities with a specific start date, but no defined term. (Payments are indefinite) If you don’t understand why this works, draw a time diagram Calculating an Effective Interest Rate: When do you need to do this: When the compounding periods DO NOT line up with the payment periods (Monthly payments compounded annually) - To fix this issue, we need to change the compounding rate to match the frequency of the payment periods Rnom = annual interest rate given M= number of compounding periods per year P= number of payments made per year *If you are given APR, simply divide APR by m as the APR is the relevant and no change needs to be made* Investment Calculations: - Calculating the return/yield that you will receive when investing in various assets. Justin Moffatt Capital Gains: The amount of “profit” that you gain after selling an asset Capital Gains = selling price – purchase price – relevant expenses General Yield: When calculating the yield of a stock, Capital gains is “What you made”, and the amount that you put into the investment is “What you paid” Bonds: A type of investing that involves the buying of the debt of a company, in return for a regular “coupon” as well as your initial investment returned to you at the end of the term. - Bond holders have priority over shareholders when a company goes bankrupt Bond Formatting: Approximate Yield of Bonds to maturity: Bond yield is calculated to the selling point, using all aspects of the bond. This is approximate because it does not take into account for TVM of the Bond Understanding Bonds: When trying to calculate the present value of a bond (purchase price), we need to break it into 2 parts. 1. The annuity (We need to find the present value of the coupons being paid out over the course of the term of the bond) Justin Moffatt 2. The single amount at the end of the term (since our initial face value of $1000 is being returned to us at the end of the term we need to also discount it back) The equation for this is: You might now be wondering “What is the n and r value when discounting the bond back to the present?” - R is going to be the yield that can be received on bonds of a similar risk (Will be provided in the question) N is going to be the number of years to maturity multiplied by 2 (Since bonds pay out twice annually) Buying On Margin: - The action of borrowing money from a broker in order to increase the amount that you can put into an investment A “Margin Requirement” is the % that the broker demands in order to provide you with money (Multiply the amount you are able to invest by the margin requirement in order to determine how much you can borrow from the broker) Example: Margin Requirement of 70%, you have $6,300 to invest personally. (If 6300 is 70% of the Current Market Value, what is 100%?) (0.70)CMV = 6300 CVM = $9000 - Therefore, you can borrow $2300 from the broker to invest Margin Call: If the value of your invest falls below the CMV, your broker will require you to pay the amount of money that will bring the investment back up to the margin requirement Mortgages: Is a long-term debt used to purchase real-estate, has a maximum amortization period of 25 years. Components of Mortgages: Justin Moffatt 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mortgage amount Amortization Period Based on interest rates, figure out the payments over amortization period Sign mortgage agreements locking in payment terms for up to 5 years When agreement expires, repeat process Calculating mortgages tips and tricks: - Subtract the down payment from the cost of the property in order to obtain the value of the loan that you will be paying off NOTE: mortgages are always Ordinary Annuities’ Mortgages are always monthly payments (r/12) To Calculate the amount of money owed at any point in the mortgage, simply use an n value of the difference between total length of the term and the date that you want the value at. - This means that if we want to know how much we have paid off at this point, we need to take the difference between the loan amount and the amount of money owed at the specified point. Net present Value: - Used to evaluate businesses and IRR (Internal rate of return) Finding out If an investment is worth it by using the present value of the payment and gains and comparing them. CONGRATS YOU SHOULD NOW BE ABLE TO DO TVM, IF YOU CAN’T WELL THAT’S UR PROBLEM LMAOO. JK JUST ASK ME QUESTIONS. Justin Moffatt