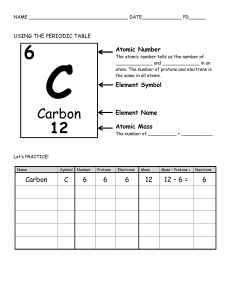
Essay 1 Chemistry Atomic Theory Atoms, the smallest units of an element that exists as stable and independent unit. Atoms are indivisible by regular chemical means, but it's possible to divide atoms using some specialized procedures. After a short introduction to Atoms, we can use its concept to explain the element and compound. An element is a substance consisting of only atoms that have the same number of protons. Elements are made up of one kind of atom, for example, carbon is only made from carbon atoms. Atoms are composed of two regions, these are the Nucleus and the Electron cloud. The nucleus is the middle part of the atom that has the mass and has two subatomic particles. Protons are positively charged and Neutrons are neutrally charged subatomic particles. These live compacted in the positively charged nucleus and contain most of the mass in an Atom. But, the negatively charged electrons take a lot of space outside the nucleus, even though they are small in mass. The subatomic particles in an Atom balance each other. For example, if there are 20 protons in an atom, then there will be 20 electrons to balance the charge of the atom. Also, the Electron cloud is the part outside the nucleus that has most of the space in the atom. The Electron cloud is the third subatomic particle, and inside it is the Electron, which is the subatomic particle negatively charged and has no mass. The atomic number in an atom indicates the number of protons. For example, Hydrogen’s atomic number is 1, which means that Hydrogen has only one proton. Such as, Carbon’s atomic number is 6, which means that Carbon has 6 protons. Similarly, the mass number indicates the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Hydrogen has one proton and must have two neurons, which means that it has a mass of 3. So, we have the equation: # of neutrons = mass # - atomic # (Number of neutrons equals mass number minus the atomic number). Likewise, Li has a mass number of 7 and an atomic number of 3, this means that it has 3 Protons, and Neutrons can be found: mass number – atomic number (7-3 = 4). Also, electrons are equal to the number of protons, so e- = p = atomic number. The Bohr Model of the atom shows how the particles are arranged.