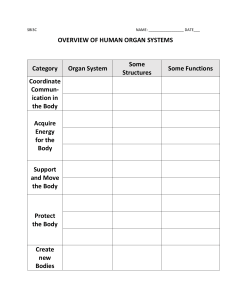
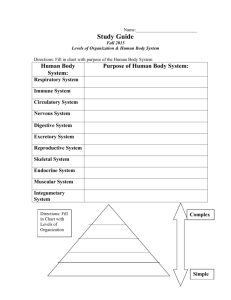
LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATION JOCELYN C. MOJICA Teacher I Prayer before Class Checking of Attendance At the end of the lesson, the learners are expected to: 1.Identify the different levels of biological organization 2.Describe each level of biological organization 3.Demonstrate and explain how each level is important RECALL Focusing specimens using a compound microscope What’s New? FIND ME! (Word Search) Words can go in any direction and share letters as well as cross over each other. There are ten (10) words to find. What’s New? FIND ME! (Word Search) A N S W E R S LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATION JOCELYN C. MOJICA Teacher I What I know? The Spectrum of Biological Organization Learning Task 1, (pp.17-18) BIOLOGY – the branch of science that deals with the study of life. To understand life, it must be studied from its basic unit to the most complex. Living things exhibit a UNIQUE and COMPLEX hierarchal organization. Living things are HIGHLY ORGANIZED and STRUCTURED. LEVELS OF BIOLOGICAL ORGANIZATION CELL – the simplest and lowest level – Considered as the fundamental structure of an organism – It is the basic unit of LIFE. – Smallest unit that can perform all activities associated with life like GROWTH, REPRODUCTION, EXCRETION and NUTRITION. Red blood cells Egg cell and sperm cells TISSUE – is a group of cells having a common structure and functions – Animal Tissues – Plant Tissues Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous Vascular ORGAN – is a group of tissues of the same structure and adapted to perform a specific function Nervous tissues grouped together form a BRAIN HEART Plants have organs, too. ORGAN SYSTEM – is a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function. ORGANISM – is an individual form of life – Organisms are made up of different organ systems that enable them to perform different functions necessary for living and survival. ORGANISMS POPULATION – a group consisting of members of the same species that live together in a given area at the same time. – A species is a group of organisms in which two members are capable of reproducing sexually. Examples of POPULATION A group of fishes in the ocean A group of teachers in school A group of cats at home A group of trees in a farm COMMUNITY – is an association of different populations of species living together at the same time and place. ECOSYSTEM – is a community of living organisms and the non-living components –Components of an Ecosystem: Biotic – living things (plants and animals) Abiotic – non-living things BIOMES – a group of similar ecosystems with the same type of physical environment BIOSPHERE – the part of the planet where life exists What is in? 1. The cell is the smallest unit of all living things. 2. There are particles smaller than cells. These are the organelles of the cells such as the nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, golgi bodies and others. 3. Molecules and atoms are much smaller than cells. Nonliving things are consists of atoms and molecules. Nonliving things do not have cells. 4. Not all living things have tissues, organs, and/or organ systems. These are the unicellular (uni- means one) organisms such as bacteria. What is it? LET’S CRISS-CROSS! Use the clues below to fill in the puzzle. Words can go across or down. Letters may be shared when the words intersect. Activity: LET’S CRISS-CROSS! ACROSS: 4. an individual that is capable of carrying out all processes of living things 7. non-living factors 11. a group of different tissues that form a singular unit and perform similar function 12. a group of organs working together to perform a specific function 14. a group of cells that perform a specific function 15. a group of similar ecosystems with the same type of physical environment DOWN: 1. organ responsible for the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the body 2. a group of organisms of the same kind living in the same area 3. organ responsible for the pumping of blood throughout the body 5. living things 6. portion of the earth where life exists 8. consists of all living things in a given area together with the nonliving things 9. a group of different populations of organisms living in the same area 10. an abiotic factor needed by living things 13. the smallest unit of all living things Activity: LET’S CRISS-CROSS! A N S W E R S What’s more? ANALOGY Let’s test your understanding of the levels of biological organization through analogies. You will be tasked to complete the following analogies. (Learning Task 4, p.19) Here is an example of analogy in English: CELL TISSUE ORGAN ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM : : : : : Letters Words Sentences Paragraphs Stories 1. Your school Cell : ___________________ Tissue : ___________________ Organ : ___________________ Organ System : __________________ Organism : __________________ 3. Our country, the Philippines Cell : ___________________ Tissue : ___________________ Organ : ___________________ Organ System : __________________ Organism : __________________ 2. Your municipality or city Cell : ___________________ Tissue : ___________________ Organ : ___________________ Organ System : __________________ Organism : __________________ 4. Make your own analogy: _______ Cell : ____________________ Tissue : ____________________ Organ : ____________________ Organ System : ___________________ Organism : ___________________ What I have learned DIFFERENTIATED TASKS ASSESSMENT INTEGRATIVE ASSESSMENT The class will be divided into three (3) groups and will be given differentiated tasks. These tasks will determine their understanding of the different levels of biological organization. The groups will be given 10mins to perform the task and then, 2 minutes each to present their outputs. The group will be given points based on a rubric. –Group 1: Role-playing/Dula-dulaan –Group 2: Chant or Jingle –Group 3: Graphic Organizer REFLECTION In your notebook, write your reflection about the lesson by completing the statements below. I understand that _______________________ I realize that ___________________________ Thank you!