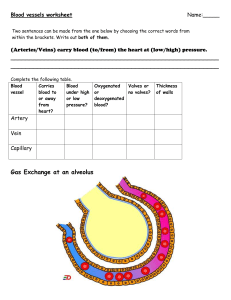
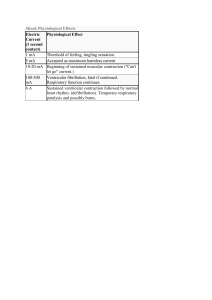
Heart 2 types of circuit – pulmonary circuit and systemic circuit 3 types of vessels – Arteries, veins, and capillaries 4 chambers of the heart – right and left atrium, right and left ventricle Atria on top and ventricles on bottom Wall of the heart – deepest part is called endocardium - Simple Squamous Myocardium – Dense tissue Layer inside heart is called visceral layer and part outside of the heart are called parietal layer. Pericarditis – caused by pathogens in pericardium Inflamed pericardial surfaces rub against each other causing cardiac tamponade. Cardiac skeleton – 4 dense bands of elastic tissue – helps to not make the blood flow back. interatrial Septum separates 2 atriums interventricular septum separates 2 ventricles Atrioventricular valves – Tricuspid and mitral valves – prevent backflow. Semilunar Valves – pulmonary valves go to lungs. (pulmon = lungs), Aortic valves goes to aorta and to the body. Superior vena cava – carries blood from the top part of the body Inferior Vena cava – carries blood from the bottom part of the body Right atrium - Foramen Ovale – huge hole that transfers blood, connects the two atria of fetal heart. Fossa Ovalis – closes after brith Tricuspid valves got 3 cups – prevent the backflow Mitral Valve got 2 cusps. Chordae Tendineae – Thread like bands of connective tissue Saclike expansions called aortic sinuses hold the extra blood that flows back in aorta Coronary artery disease CAD - partial or complete blockage of coronary artery Angina Pectoris – called chest pain – individual may feel uncomfortable at rest – symptom of CAD. results in myocardial infraction also called heart attack Heartbeat A single cardia contraction Pacemaker cells – auto rhythmic Nervous system doesn’t play a single role. Beating of the SA node is going to develop your sinus rhythm. SA node – 60 -100 action potential per minute – sets the heartbeat – opening K+ channels AV node – 40 – 60 action potential per minute SA nodes are the main pacemaker Pacemaker cells controls steps 1-3 Conducting cells controls steps 4 and 5 Impulse is delayed for 100 msec at AV node Strong ventricular contraction would close AV valve Purkinje fibers (Conducting fibers) distributes impulses to ventricular myocardium. Bradycardia – low heart rate – conduction deficit Tachycardia – faster heart rate – conduction deficit Ectopic pacemaker – an electrical signal note generated not where it should be. It messes up the timing of heart contraction rhythm. Premature atrial contraction – Paroxysmal Atrial Contraction – Ventricular Fibrillation – Desmosomes and gap junctions hold the cells together. Fast channels peak up sodium channel fast The plateau phase takes the calcium channels slow all the way down. Slow potassium channels lower everything down. Refractory period – nothing happens at this point – maintains heart rhythm Aerobic energy provides energy for contraction Normal heat beat rate – 75 beats per min Frank – Starling Principle As EDV increases, stroke volume increases