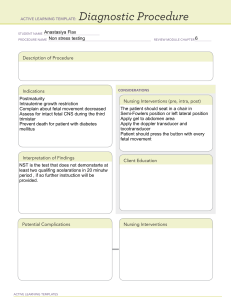
Exam 2 Study Guide Hormones Hormones What secretes this hormone? When is it secreted? When does it peak? Estrogen Ovary (follicle) Follicular and luteal phase - Uterine enlargement - Breast glandular hyperplasia - ↑ fallopian tube peristalsis - when estrogen reaches certain level → ↓ LH output - "Ovulatory mucus" to nourish sperm Leutenizing Hormone (LH) Anterior pituitary gland Follicular phase and peaks right before ovulation Affects final development and subsequent rupture of mature follicle Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Anterior pituitary gland Follicular phase and peaks right before ovulation Stimulates the ovary to produce five to 20 immature follicles Progesterone Corpus luteum After ovulation and peaks during luteal - Forms mucous plug - Breast glandular hyperplasia - Slows GI peristalsis - Prepares phase endometrium for implantation After implantation and peaks ~8-14 - Ensures the endometrium will be receptive to the implanting embryo - Maintains corpus luteum wks after conception until week 11 - During pregnancy test: detects presence/absence of hCG Hormone human Chorionic What does it do? Gonadotropin (hCG) Trophoblasts GnRH Hypothalamus Pulsates slowly during follicular phase and increases during luteal phase Induces release of LH and FSH to assist with ovulation Human Placental Lactogen (hPL) Placenta ~2 wks GA and rises slowly throughout to peak ~34 wks GA - Helps mediate fetal/maternal glucose metabolism during pregnancy (lactose) to ↓ maternal glu utilization & ↑ glu availability to fetus - Participates in breast development for lactation Hypothalamus During labor and breastfeeding Prostaglandins Oxytocin - ↑ follicular maturation - assist with ovulation - assists in transport of sperm - Stimulates labor and breastfeeding (contraction of womb and lactation) Summary of Menstrual Cycle Hormones 1. ↑ LH → follicle produces estrogen 2. As ↑ estrogen → inhibiting the output of LH → ovulation after LH surge damages estrogen-producing cells 3. Ovulation → ↓ estrogen 4. LH surge → corpus luteum → produces estrogen and progesterone 5. ↑ Estrogen and progesterone → suppresses LH output → promote degeneration of corpus luteum 6. Cessation of the corpus luteum → ↓ estrogen and progesterone output 7. ↓ ovarian hormones ends their negative effect on the secretion of LH 8. ↑ LH → menstrual cycle begins again Absence of fertilization → menstruation (on avg = 28-day cycle) Conception, Fetal Development, and Substance Abuse 1) Follicular Phase Goal: produce ovum for fertilization Length: variable 2) Ovulation 3) Luteal Phase Follicle rupture → corpus luteum → ↑ Occurs when ovum is released from follicle → fallopian tube → uterus progesterone (prepares endometrium for implantation) Hypothalamus: initiator of this phase (PG → LH/FSH) Proliferative Phase: ↑ estrogen = ↑ endometrial glands Typically takes place ~10-12 hrs after LH peak and ~24-36 hrs after estrogen peak Absence of fertilization: corpus luteum degenerates & ↓ ovarian hormone levels → ↓ estrogen & progesterone → endometrium Egg produced: ~14 days before menstruation involution Secretory Phase: blood vessel dilation = ↑ endometrial thickness Endometrium: ↑ thickness, vascularity, and glandular Prepares endometrium for implantation Fetal Development Overview Exam 2 Study Guide 🤰 Stages of Pregnancy: 1 🤰 Pregnacy averages: 10 lunar months, 40 weeks, 280 days (first day of LMP to birth) Pre-embryonic stage (0-2 wk) Embryonic Stage (2-8 wk) Fetal stage (8 wk - birth Fertilization usually occurs 14 days after LMP; actual gestation = 266 days Most born within ±14 days of EDD Conception Pre-Embryonic Stage: First 2 Weeks 1. ↑ estrogen → ↑ fallopian tube peristalsis 1. Cleavage: Rapid cell division 2. Prostaglandins in semen help transport sperm Blastocyst (inner cell mass) → embryonic disc + amnion 3. Sperm + ovum (in outer 1/3 off the ampulla) = diploid zygote Trophoblast (outer cell mass) → placenta + chorion 4. Zona pellucida forms: prevent entry of other sperm 2. Implantation: Blastocyst burrows into endometrium Nuclei of sperm and ovum unite Sex of zygote is determined at this time (fertilization) Occurs 7-10 days after fertilization Trophoblasts now secrete hCG Embryonic Stage: Week 2-8 3. Cellular Differentiation Tissues differentiate into essential organs Chorion + amnion → amniotic fluid Wks 3-4: heart, vertebrae, heart, eyes, arms begin to develop Primary germ layers give rise to all tissues: Wks 6-8: lung, ↑ RBC, digits develop, fetal circulation established 1. Ectoderm → CNS, special senses, skin, glands 2. Mesoderm → skeletal, urinary, circulatory, reproductive organs Functions of Placenta: Metabolic: glycogen, cholesterol, fatty acids 3. Endoderm → respiratory, liver, pancreas, digestive system Transport: diffusion, facilitated/active transport Endocrine: produce hormones vital to fetal survival (hCG, hPL, progesterone, estrogen) Functions of Amniotic Fluid: allows for mvmt, proper lung development, ↓ pressure on umbilical cord, constant temp around the baby, protect baby from injury Fetal Stage: Week 9-Birth Every organ system & structure is present; organ systems develop during this stage At 9 weeks: Weeks 12-16: Week 20: Week 24: Week 28: Week 32: Week 38: Every organ system & structure Fetal tones can be heard Quickening felt by all mothers Alveoli begin to form + Rapid brain development Rhythmic breathing Fetus is flexed Genitals well differentiated BAT appears are present 🖤 Active Fetal heartbeat heart by movements fetoscope surfactant production Fingerprints set movements ↑ body fat ↑ CNS function (quickening may be present) Fraternal Twins Identical Twins 2 ova + 2 sperm 1 ova + 1 sperm → split into two 2 chorion + 2 amnion 1 chorion + 2 amnion Earlier split = good b/c ↓ resources are shared Later split = bad b/c ↑ competition for resources Substance Abuse Factors Influencing Development: vulnerability timetable (exposure <9 wks are most damaging), Teratogens (physical agents, metabolic conditions, infection, drugs/chemicals), Medications (first trimester = greatest risk) Plan for L&D (pain meds shouldn't be withheld Goal: help mother recover from illicit drug abuse to optimize long-term health of self and baby (non-judgemental approach) Exam 2 Study Guide 2 Alcohol Use in Pregnancy Maternal Effects: malnutrition, BM suppression, ↑ infections, liver disease, WD/DTs Neonatal Effects: WD, fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD), long-term complications FASD: physical, behavioral, cognitive effects Long-term: delay in oral feeding, CNS dysfunction (most common), learning disabilities, impulsivity, cognitive/speech impairment S/S EtOH WD: hyperactivity, jitteriness, hyperreflexia, hypertonia, poor suck, seizures, poor sleep patterns, diaphoresis Nursing Implications: Educate elimination & detrimental effects of EtOH during pregnancy; find Tx program; no safe amt EtOH they can consume Tobacco Use in Pregnancy Maternal Effects: infertility, spontaneous abortion, IUGR/low birth wt, preterm birth Neonatal Effects: 3x SIDS risk that of non-smokers, chronic respiratory illness Nursing Implications: Consider nicotine replacement for those who can't quit; educate about smoking cessation & other coping strategies Heroin Use in Pregnancy Maternal Effects: poor nutrition, iron-deficiency anemia, abruptio placentae, PTL/PROM, IUGR/low birth wt, meconium staining, ↑STIs/HIV Neonatal Effects: WD, neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) S/S of NAS: restlessness, lack of habituation, shrill/high-pitched cry, irritability, seizures, V/D Nursing Implications: Tx = Methadone (blocks WD symptoms and cravings; crosses the placenta) Educate about effects; assess use of other substances; don't abruptly stop heroin; methadone maintenance program Infertility, Women's Health, Nutrition, & Special Populations Infertility Woman <35 yoa unable to conceive after >1 yr of attempting Woman >35 yoa unable to conceive after >6 mo of attempting Anything that prevents the egg to meet up with the sperm and fertilize the egg (Ex: scar tissue = pelvic inflammatory disease (PID; chlamydia, gonorrhea, endometriosis) Infertility Factors Male Category Factors 40% of cases (↓ sperm count/viability), Sperm blocked from release Possible Causes Female 40% cases (ovarian dysfunction, tubal/pelvic pathology) Prolonged periods of high heat, Over-/underwt, AIDS, chronic heavy EtOH, MJ, cocaine use, cancer Tx, STI scarring illnesses, PID/STIs, hormonal imbalances, smoking/EtOH Treatment Early 20s = peak fertility for women Lifestyle Δ's After 35 (especially 40) = ↓↓↓ fertility Ovulatory factors (basal body temp recording, induce ovulation via Clomid) Preconception Care Immune to preventable diseases? (update if not) Use of folic acid? PMHx: DM, thyroid disease, anemic PSHx: appendectomy, any abd. Sx Hormonal agents (impacts FSH, LH, Progesterone) Therapeutic insemination: intrauterine insemination (IUI) In vitro fertilization (IVF) Embryo donation/transfer Surrogacy & Adoption Gyn: LMP, regularity of menstrual periods, STIs, PID, endometriosis Work-Up Nursing Considerations 1. Emotions more difficult than testing/therapy Semen analysis (less invasive) Exam 2 Study Guide 3 Evaluation of ovarian function 2. Explain procedures, listen to concerns, answer Qs, support the family Cervical mucus adequacy for sperm receptivity 3. Provide accurate information about infertility and dispel myths Tubal patency Uterine structure evaluation Women's Health STIs Name Organism Chlamydia Symptoms Pregnancy Implications Notes Routine screening at 1st ABx for both partners, expedited Chlamydia d/c, urethritis (men/women), salpingitis, prenatal visit, ROM → vert partner treatment (EPT) in IL, trachomatis uterine bleeding; 50% men & 70% transmission → ophthalmia abstain from sex for 7 days asymptomatic neonatorum following Tx Neisseria Greenish-yellow d/c, dysuria, and gonorrhoeae frequency; 80% women asymptomatic Pelvic Chlamydia B/L sharp cramping pain in lower Inflammatory trachomatis, quadrants, >101 fever, chills, N/V, Disease (PID) Neisseria gonorrhoeae malaise, mucopurulent cervical or vaginal d/c Gonorrhea Treatment Impaired fertility, mucopurulent vagina Most common bacterial STI in the US, Screen: <25 yoa females and >25 yoa females at risk, all pregos ABx for both partners (EPT), As above Often occurs with Chlamydia abstain from sex until cured Inflammation of female upper post-infection → tubal damage → infertility or ectopic pregnancy ABx, hospitalization may be genital tract, Risk factors: multiple necessary, treat partner sex partners, h/o PID, sex at young age HSV-1 and HSV-2 Herpes (recurrent lifelong infection) Syphilis Treponema pallidum Primary outbreak with lesions, then Risk for SAB, PTL, C/S if dormant, recurrent active lesions present Congenital syphilis (IUGR, PT birth, stillbirth, CNS/intellectual disability, heart/lung/liver damage No cure, but treatment available: acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir (can be given in 3rd trimester) Screen VDRL or RPR blood test ABx Transmission: skin-to-skin contact with an infected site Transmission: transplacental Cervical Abnormalities Abnormal pap smear results → Bethesda System for specimen findings Atypical Squamous Cells (ASC) Surgical treatment: Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP): electric wire loop excises lesion Low-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion (LSIL) Cryosurgery: freezing → tissue necrosis High-grade Squamous IntraEpithelial Lesion (HSIL) Abnormal cytology → colposcopy (SSE with acid solution, abnormal cells visible, biopsy) Laser therapy Conization: cone biopsy Nutrition Considerations Maternal Weight Gain 1. General nutritional status before pregnancy Based on pre-pregnant BMI 2. Common discomforts of pregnancy (N/V) Avg wt gain distribution 3. Maternal age Obesity in pregnancy 4. Maternal parity 5. Not all foods have to be avoided (well varied, balanced) 6. Cravings, sensory Δ's, cultural variations 7. Pica, eating disorders, food safety 8. Nutrition impacts fetal well-being & birth outcome (PTD, low birthwt, macrosomia, development) Nutritional Requirements Name Value Calories Protein Fluids Folic Acid Iron +300 cal/day (pregnancy) +500 80 8-10 glasses (8 oz) of fluid 4-6 glasses of water 400-800 mcg/day (start 2-3 mo prior to pregnancy and 27 cal/day (BF) g/day Caffeine (diuretic effect) through pregnancy) mg/day Foods that can be eaten in pregnancy Foods to avoid in pregnancy 1. Swordfish, tilefish, mackerel, shark, ahi tuna (Risk: methylmercury) Exam 2 Study Guide 4 1. Cooked shellfish, canned fish, small ocean fish, farm-raised fish (salmon) 2. Cooked fish 2. Raw or undercooked fish like sushi or ceviche (Risk: bacteria or viruses) 3. Raw sprouts (Risk: bacteria can't be washed out) 4. Unpasteurized products, soft cheeses (Risk: bacteria may be present) 3. Pasteurized products, hard cheeses 5. Raw/undercooked meat, poultry, runny yolk (Risk: salmonella, E. coli) 4. Cooked eggs 6. Cold hot dogs, deli meat, refrigerated smoked seafood, deli salads (Risk: Listeria) 5. Heated or grilled deli meats, smoked seafoods, deli salads Special Populations Care of LGBTQI Families 1. Birth parents/adoptive families Ask pt how they prefer to be addressed (gender pronouns) → gender neutral terms if unsure 2. Cultural differences Involve partners in care per pt wishes 3. Differently abled families Caring demeanor and open-ended Q's as much as possible 4. LGBTQI families Consider fertility options: surrogacy and adoption 5. Adolescent families 6. Families >35 yoa Pregnancy Changes & Antepartum Assessment Pregnancy Changes Body Changes System Intervention Notes Cervix: mucous plug with progesterone stimulation of tissue, Goodell's sign (softening), Reproductive Chadwick's sign (bluish-purple discoloration) Vagina: ↑ vascularity, leukorrhea (whitish d/c) Cotton underwear/underpads, Ovaries: ovulation ceases Breasts: glandular hyperplasia + hypertrophy, tenderness, ↑ supportive bra (may need re-fit) estrogen/progesterone, darkened areolae, striae, colostrum (3rd trimester) N/V (d/t hCG levels), friable gums (d/t estrogen), heartburn (d/t relaxation of cardiac sphincter), Gastrointestinal ↓ GI motility, uterus displaces stomach, Hemorrhoids, constipation (d/t intestinal displacement, progesterone ↓ peristalsis, Fe+ is constipating), cholestasis of pregnancy BV +50% (1500 mL), physiologic anemia (↑ plasma volume > RBC), ↓ vascular resistance (to Cardiovascular accommodate for BV), ↑ fibrin/fibrinogen (↑ hypercoagulable state), ↑ CO, ↑ HR, edema, VV, hemorrhoids, supine hypotensive (vena caval) syndrome (postural hypotension) Musculoskeletal Genitourinary Respiratory Integumentary Endocrine Immune Pelvic joints relax → waddling gait, ↑ lumbodorsal curve → backache, round ligament pain (pelvic pain from stretching to support the uterus) ↑ frequency (d/t ↑ pressure of gravid uterus) → dehydration, ↑ GFR → ↑ glycosuria (d/t ↓ renal threshold for glu excretion) → DM, ↑ risk of UTIs Diclegis/Vit B6, soft toothbrush, ↑ fluids, fiber, mvmt, Tucks pads Elevate legs/hips/pelvis, support hose, avoid constipation, side- BV ↑ in 1st trimester & peaks at ~32 wks; +10-15 bpm HR lying position, sit breaks, Δ in 2nd trimester (fluctuates, position slowly should not be elevated) Good body posture/mechanics, Relaxin: helps to loosen up support garments, low-heeled shoes, counsel pt, heating pad joints → baby has more room to move Frequent voids, sufficient fluids (↓ in the evening), ↓ caffeine, Kegels ↑ O2 consumption (hyperventilation: faster/deeper), dyspnea (diaphragm pressure, endures elevate HOB, slow/deep until lightening), vascular congestion of nasal mucosa (stuffiness/epistaxis d/t ↑ estrogen) breaths, saline spray, humidifier Hyperpigmentation (linea nigra), striae, facial chloasma (darkening of skin around the face like use sunscreen, elevate legs, butterfly effect), varicose veins, spider veins support hose ↑ thyroid activity, ↑ insulin needs from pancreas (d/t hPL), latent deficiency → GDM, ↑ oxytocin & ADH (from hypothalamus/pituitary), ↑ ALD (from adrenal glands) Lightening: presses down on uterus to relieve pressure off the diaphragm Screen thyroid activity ↑ innate immunity, ↓ adaptive immunity (persisting x2 mo after delivery) Δ's in sleep pattern/disturbances (bladder & gravid uterus) → fatigue, "pregnancy brain" (↓ General Δ's Small/frequent meals, avoid fatty foods, ginger, antacids, attention, concentration, memory), maternal psychologic & emotional reactions (mood swings, ambivalence, acceptance), partner Δ's (feeling left out, emotional swings, Couvade Syndrome) Use pillows, promote relaxation, rest when possible (naps), provide anticipatory guidance and support for partner Fatigue 1st, more E 2nd, fatigue returns in 3rd trimester; Couvade: partner has symptoms like pregnant partner Antepartum Assessment Maternal & partner Hx, PMHx, PSHx, FHX, OB/gyn Hx, immunization record are collected Nägele's Rule: 1st day of LMP, subtract 3 mo, and add 7 days (only accurate if a woman has a regular 28 day cycle) Note: US is the most accurate to determine when the EDB will be (used in the 1st trimester) Measurement of fundal ht (symphysis pubis to fundus) Exam 2 Study Guide 5 20 wks = 20 cm = umbilicus +1 cm/wk until ~36 wks (lightening can occur at 36 wks) Screening: Initial Prenatal Labs 1. Pap Smear Bloodwork Tests: 1. ABO/Rh/Ab screen 2. HIV (Neg or Pos) 3. Rubella titer (Immune or Non-Immune) 4. HepB (Neg or Pos) 2. UA/Culture 3. Bloodwork 4. Glu testing for high risk 5. VDRL or RPR (NR or Reactive) for Syphilis 6. CBC Screening: Subsequent Prenatal Labs 1. GDM at 24-28 wks 2. RhoGAM evaluation at 28 wks (given for Rh- mothers) 3. GBS at 35-37 wks 📆 Visit Schedule: q4 wks in first 28 wks q2 wks until 36 wks q1 wk after 36 wks 4. Based on risk: Immunizations Ideally given prior to becoming pregnant Should be given: inactivated IM flu vaccine & Tdap booster (given in EVERY pregnancy → fetus benefits from Ab Should NOT be given: attenuated live viruses (MMR, varicella, chickenpox) Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) Warning signs: unexplained bruises/injuries, vague complaints, missed visits, noncompliant with Tx, h/o depression, substance abuse, suicide attempts "Yes" response: validate pt ("this is NOT your fault, no one deserves to be treated like this, help is available"; plan for safety) "No" response: document and screen again ☣ Complications: Maternal: HTN, pre-eclampsia, ROM, infection SAVE Model: SCREEN all pts for risk from violence Neonatal: preterm birth, IUGR ASK questions in a non-judgmental manner VALIDATE the pts experience EVALUATE, EDUCATE, & refer Antenatal Testing and EFM Antenatal Testing 1st Trimester: Viability confirmation: 2 levels, 48 hrs apart → should double IUP vs ectopic Establish GA Examine crown-rump length (most accurate at 6-12 wks) Transvaginal US Transabdominal US: requires full bladder (position = L lateral/tilt) 2nd Trimester: Cardiac motion Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): elevated = ↑ risk of neural tube defects; deficiency = ↑ risk of trisomy 21 or 18 Fetal # & presentation Amniocentesis: tests for chromosomal abnormalities, metabolic disease, NTD (amniotic AFP level), Rh assessment after exposure Placental position Cord & vessels Triple or Quad Screen: AFP, hCG, unconjugated estriol (and inhibin A) Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): tests for chromosomal/genetic abnormalities, enzyme deficiencies, metabolic disease Exam 2 Study Guide 6 Fetal anatomy Amniocentesis & CVS Indications: Advanced maternal age (>35 yoa) → ↑ risk for chromosomal abnormalities H/O neural tube defect Risks Management: Vaginal spotting, cramping Give support before, during, and after testing ROM Give RhoGAM PRN (if pregnant pt is Rh-) Other abnormal screening Chorioamnionitis: infection of the lining of the BOW Carrier for metabolic disease Spontaneous abortion 3rd Trimester: Pt should self-monitor for mvmt (should be consistent timing and amt per day) → tells you fetal CNS function & oxygenation Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI): normal = 5-25 cm using the 4 quadrant deepest pocket method; DM have ↑ risk of polyhydramnios Non-Stress Test (NST): assesses uteroplacental function (Reactive vs. Nonreactive) Reactive = 2+ accels in 20 mins, no, decels, normal baseline FHR with mod variability Nonreactive = no accels(or <2 accels in 40 mins), more testing needed Biophysical Profile (BPP): detects hypoxia (uteroplacental insufficiency) to guide early intervention 1. FHR acceleration (NST) 2. AFI Test Interpretation: 8+ = no intervention; <6 = possible mgmt (consider whole picture) 3. Fetal breathing 4. Fetal movements 5. Fetal tone (flexed or flaccid) If 1 or 2 are abnormal, the others don't really matter EFM 1. Contraction pattern (frequency & duration) 2. Baseline FHR (during "non-event" section b/t UC; # in 5 bpm increments) 3. Baseline FHR variability: fluctuations in HR from baseline (b/t UC and excludes accels/decels) → indicates CNS functioning Absent = 0 bpm Minimal = 0-5 bpm Moderate = 6-25 bpm Marked = 25+ bpm 4. Accelerations (present vs absent): ↑ FHR above baseline +15 bpm x15 seconds (but <2 mins) → indicates fetal well-being & adequate oxygenation 5. Decelerations: consider timing of ↓ FHR wrt UC Absent → good Early = head compression → fine Late = uteroplacental insufficiency → BAD Variable = cord compression → BAD Normal Labor Main factors of whether or not baby will be able to fit through pelvis & vagina safely: passageway, passenger, powers, position, psychosocial response 1) Passageway Bony Pelvis: Inlet (baby going into pelvis), outlet (baby coming out of pelvis), shape (gynecoid vs anthropoid are best) Soft Tissues: cervical dilation & effacement, vaginal canal & introitus distention Birth Course: uterus → pelvis → cervix → vagina → introitus 2) Passenger Exam 2 Study Guide 7 Fetal Head Fetal Attitude Largest D: Suboccipitobregmatic (9.5 cm) & Biparietal (9.25 cm) Relation of fetal body parts to one another (general flexion Frontal, parietal, occipital bones overlap during birth (molding) = good!) Fetal Lie Good: chin/knees/heels tucked, back curved, arms crossed Relation of fetal spinal column to mother (cephalocaudal axis) Bad: general extension Fetal Presentation Longitudinal (98%) = vertical or parallel to maternal spine (only way to get out of the pelvis by NSVD) Presenting part: body part that enters the pelvis first Cephalic = head down Normal = cephalic (vertex) & occiput presenting (head flexed) Breech = butt down Fetal Malpresentation Transverse (2%) = horizontal (will require C/S) Cephalic (brow & face) Shoulder presentation Breech (frank, incomplete/footling, complete) Clinical Implications of Fetal Malpresentation Name Cephalic (Brow) Presenting Part Forehead (extended head) Contributing Uterine anomaly, ↑ parity, ↓ birth wt, Causes pelvic shape Maternal Risk Prolonged labor, C/S, episiotomy Cephalic (Face) Face (hyperextended head) Same as brow Same as brow Edema/bruising to face, head, and Fetal Risk Birth injury Clinical None indicated if labor progressing; C/S recommended, NSVD possible in Therapy C/S if not some cases airway Breech Transverse Sacrum or feet Shoulder Previa, uterine anomaly, ↑ parity, multiples, prematurity Same as (footling), previous breech breech Prolonged labor, C/S C/S Cord prolapse, head entrapment, neuromuscular disorders External cephalic version, C/S, CAM Cord prolapse Same as breech 3) Powers of Labor Primary Force (Involuntary Work of Labor): UC, cervical Δ's, "laboring down" (pushing baby down w/o mom voluntarily pushing) Secondary Force (Voluntary Work of Labor): Pushing during 2nd Stage, coordinate with primary force 4) Position Relationship b/t the passageway and the fetus Fetal occiput relative to maternal landmarks Maternal position: ambulatory vs back-lying Cardinal mvmts: specific mvmts to allow ↓ diam to pass through pelvis Head extension & external rotation under mother's symphysis pubis Ex: ROA → maternal right, fetal occiput, maternal anterior Fetal Malposition Occiput posterior (OP) vs occiput anterior (OA): may be more common w/ smaller pelves OP: baby's occiput is facing posteriorly → NOT IDEAL OA: baby's occiput is facing anteriorly → IDEAL! Maternal Risks of OP: Intense pain in the small of back ("back labor") 🏥 Clinical Therapy of OP: Hands/Knees position to allow fetal rotation; Vaginal birth possible: spontaneous, forcepsassisted, forceps rotated, manual rotation; C/S possible Prolonged labor ↑ risk of assisted vaginal delivery, perineal laceration, C/S 5) Psychosocial 1. Birth experience factors (+/-): Locus of control, Pain or anxiety, Labor support (doulas), Previous experience Exam 2 Study Guide 8 2. Preconceived ideas or expectations about birth 3. Readiness 4. Cultural view 5. Birth plan = wish list (things might not go as expected) → provide support Labor Experience Maternal Response to Labor: CV: stressed by UC/pain/anxiety/pushing; ↑HR/BP during UC; ↓ BP with CLE (continuous labor epidural) Resp: ↑ O2 demand at labor onset GI: ↓ GI motility & gastric emptying → N/V Fluid/E- Balances Challenges: Sweating, IV fluids, and meds Labor Onset: exact cause is unknown Possible causes: ↑estrogen, ↓progesterone, ↑prostaglandins (myometrial gap junctions ↑), oxytocin receptors ↑ in the uterus Premonitory signs of labor: Initial cervical Δ's Bloody show (slimy blood) Braxton Hicks contractions Backache Sudden burst of energy (nesting) Lightening (mom can breathe again) ROM (1 in 4 women) NVD Is It Time? True Labor False Labor Progressive dilation/effacement (cervical Δ's) in response to... Lack of cervical Δ Regular contractions Irregular contractions (do not ↑ F/D/I) ↑ UC F/D/I (even with comfort measures) Contractions mainly in front of abd ↑ Intensity with ambulation Pain relieved w/ ambulation, position Δ, rest, hot bath/shower Pain usually starts in back → radiates to abd Nursing Care During Admission: 🏥 1. Maternal Assessment - VS & wt/wt gain - Prenatal records (PMHx, OB Hx, ↑ risk conditions) - Psychosocial - Labs 2. Establish (+) relationship & rapport Nursing Response: Education: s/s true labor Reassurance: false labor is common, difficult to distinguish from true labor Interventions: ↓ anxiety & discomfort; REST (labor will use all of E) 3. Labor Assessment: - UC - Membranes/BOW (+ R/O SROM) - Fetal movement - Vaginal bleeding - EFM - SVE 4. Notify Provider: SBAR & Plan of Care Stages & Phases of Labor First Stage: Dilation Third Stage: Placental Delivery Latent Phase (0-6 cm): UC q5-10 mins, x30-45 secs, ~5-9 hrs 5-30 min post delivery Active Phase (6-10 cm): UC q2-5 mins, x40-60 secs, ~4-6 hrs >30 mins = retained placenta → manual extraction Baby is still in the uterus; ends with 10 cm dilation Baby is out and ends with placenta out; provide newborn care if only Anticipatory guidance, pain mgmt, fluids, comfort measures, discourage pushing until fully dilated, bladder assessment nurse Signs: gush of blood, cord lengthening, bulge at perineum, fundal rise in abd Second Stage: Delivery Exam 2 Study Guide 9 UC q2-3 mins, x60-90 secs "Golden Hour": emotional time, complete assessments w/ baby, BF, attachment Ends with baby out of the uterus Fourth Stage: Recovery Bloody show, coach to bear down with UCs, remove catheter prior to pushing 1-4 hrs after birth Warm packs to perineum, encourage rest b/t contractions, ice chips Profound hormonal & hemodynamic shift Episiotomy not recommended for routine intervention (emergency now) EBL NSVD = 500 mL EBL C/S = 1000 mL Palpate fundus, assess bladder, and VS q1h → massage fundus if boggy Tremors are common, food & liquids, rest, transfer to postpartum unit Intrauterine pressure catheter (IUPC): UC intensity & resting tone Fetal scalp electrode (FSE): accurate FHR tracing Disadvantages: Contraindications: Must be s/p ROM & adequately dilated low-lying placenta Invasive: ↑ risk of uterine infection or perforation HIV+ HebB+ Exam 2 Study Guide 10