Investment Basics: Stocks, Bonds, and Portfolio Diversification
advertisement
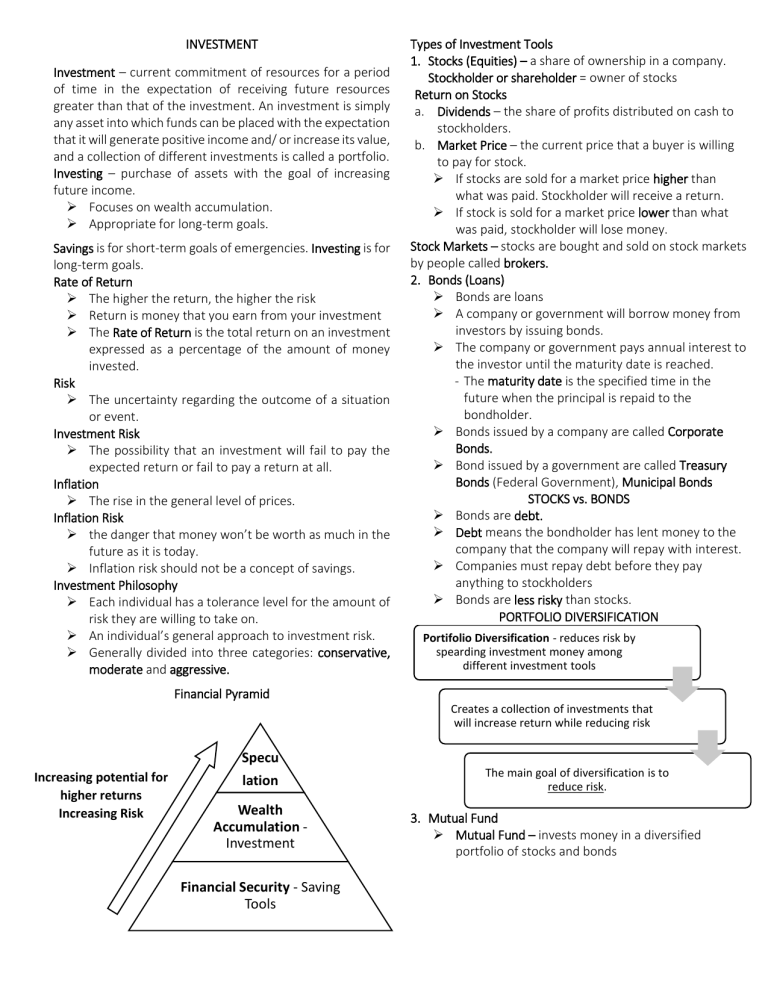
INVESTMENT Investment – current commitment of resources for a period of time in the expectation of receiving future resources greater than that of the investment. An investment is simply any asset into which funds can be placed with the expectation that it will generate positive income and/ or increase its value, and a collection of different investments is called a portfolio. Investing – purchase of assets with the goal of increasing future income. Focuses on wealth accumulation. Appropriate for long-term goals. Savings is for short-term goals of emergencies. Investing is for long-term goals. Rate of Return The higher the return, the higher the risk Return is money that you earn from your investment The Rate of Return is the total return on an investment expressed as a percentage of the amount of money invested. Risk The uncertainty regarding the outcome of a situation or event. Investment Risk The possibility that an investment will fail to pay the expected return or fail to pay a return at all. Inflation The rise in the general level of prices. Inflation Risk the danger that money won’t be worth as much in the future as it is today. Inflation risk should not be a concept of savings. Investment Philosophy Each individual has a tolerance level for the amount of risk they are willing to take on. An individual’s general approach to investment risk. Generally divided into three categories: conservative, moderate and aggressive. Types of Investment Tools 1. Stocks (Equities) – a share of ownership in a company. Stockholder or shareholder = owner of stocks Return on Stocks a. Dividends – the share of profits distributed on cash to stockholders. b. Market Price – the current price that a buyer is willing to pay for stock. If stocks are sold for a market price higher than what was paid. Stockholder will receive a return. If stock is sold for a market price lower than what was paid, stockholder will lose money. Stock Markets – stocks are bought and sold on stock markets by people called brokers. 2. Bonds (Loans) Bonds are loans A company or government will borrow money from investors by issuing bonds. The company or government pays annual interest to the investor until the maturity date is reached. - The maturity date is the specified time in the future when the principal is repaid to the bondholder. Bonds issued by a company are called Corporate Bonds. Bond issued by a government are called Treasury Bonds (Federal Government), Municipal Bonds STOCKS vs. BONDS Bonds are debt. Debt means the bondholder has lent money to the company that the company will repay with interest. Companies must repay debt before they pay anything to stockholders Bonds are less risky than stocks. PORTFOLIO DIVERSIFICATION Portifolio Diversification - reduces risk by spearding investment money among different investment tools Financial Pyramid Creates a collection of investments that will increase return while reducing risk Specu Increasing potential for higher returns Increasing Risk lation Wealth Accumulation Investment Financial Security - Saving Tools The main goal of diversification is to reduce risk. 3. Mutual Fund Mutual Fund – invests money in a diversified portfolio of stocks and bonds Reduces investment risk by helping people diversify their portfolio Saves investors time Fees can be high How do mutual funds work? Individuals buy shares The money is used to purchase stocks, bonds, and other investment Profits returned to shareholders monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually in the form of dividends. Pool their money with 2. Fund 1. Investors Manager Passed back to Invest in 4. Returns 3. Securities Generate s Market Indexes A market index is the value of a group of stocks or other investments. Market indexes are intended to represent an entire stock market and thus track the market’s changes over time. 4. Index Fund A mutual fund that was designed to reduce fees by investing in the stocks and bonds that make up an index. Offers high diversification with low fees 5. Real Estate Includes any residential or commercial property or land as well as the rights accompanying that land. A family home is not considered an investment asset. Can be risky and more consuming but has potential for large returns. 6. Speculative Investments Have the potential for significant fluctuations in return over a short period of time. Example: future options, commercial paper, collectibles Recommended for people with an aggressive investment philosophy and a high level of financial security. Buying and Selling Investments Investors must utilize a brokerage firm that acts as buying and selling agent for the investor (except for when buying real estate and certain speculative investments). The traditional broker, or full-service broker, in addition to executing clients’ transactions, offers investors a full array of brokerage services: providing investment advice and information, holding securities in street name, offering online brokerage services, and extending margin loans. Investors who wish merely to make transactions and are not interested in taking advantage of other services should consider either a premium or basic discount broker. Premium discount brokers focus primarily on making transactions for customers. They charge low commissions and provide limited free research information and investment advice. Basic discount brokers, also called online brokers or electronic brokers, are typically deep-discount brokers through whom investors can execute trades electronically online via a commercial service, on the Internet, or by phone. Investing Versus Speculating Investment – an asset that generates a return Income return – usually in the form of dividends interest payments Speculation – an asset whose value depends solely on supply and demand. Derivative securities- value derived from value other assets Option – right of owner to buy or sell an asset FORMULA: (𝐸𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 − 𝐵𝑒𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒) +𝐼𝑛𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒 𝑅𝑒𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑛 𝑹𝑶𝑹 = 𝐵𝑒𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 Profit = Initial Price – (Ending Price – Income Return) – Total commissions paid 𝑹𝒆𝒂𝒍 𝑹𝑶𝑹 = 1 + 𝑁𝑜𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑒 −1 1 + 𝐼𝑛𝑓𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑨𝒗𝒆𝒓𝒂𝒈𝒆 𝑹𝑶𝑹 = (𝐸𝑉 − 𝐵𝑉) + 𝐼𝑅 1 𝑥 𝐵𝑒𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑛𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑁







