Types of Investments
advertisement

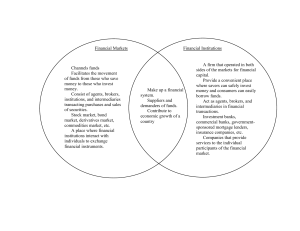
+ Investments + Purpose of Investments Investments constitute something that is purchased for future benefit (money, experience) Promotes economic growth and contributes to a nation’s wealth + Financial System Is a network of savers, investors, and financial institutions that work together to transfer savings to investors. + Financial Intermediaries Financial Intermediaries –are financial institutions that lend the funds that savers provide to borrows. Commercial Savings Credit Banks & Loans Unions Savings Mutual Banks Savings Banks + + Investing “Trade-Offs” Liquidity- Savings accounts are good for immediate cash, but pay a low interest rate Return- the money an investor receives over and above their initial investment Risk- Anything insured by the gov’t carries no risk compared to investments with high risks (but greater rewards), such as investing in the stock market + Mutual Fund and CD’s An investment company that pools money to invest in several different stocks on behalf of a group of investors. The fund is managed by a professional investment manager. (Includes Pension Funds- IRA’s) (A package O’ stocks) CD’s are common form of investment issued through banks for 2yrs. @ 4% interest + Bond An investment in a corporation or a government body through a loan. If you purchase a bond, you are loaning money with the expectation of interest compounded on your investment. Savings Bonds, Municipal Bonds, Corporate Bonds, Junk Bonds + What is a Stock? Ownership of shares in a corporation. Stockholders share a portion of the profit or loss incurred by the company.