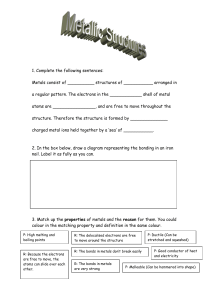
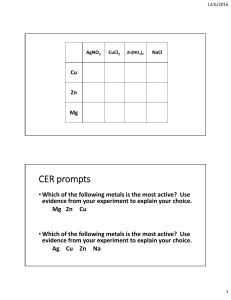
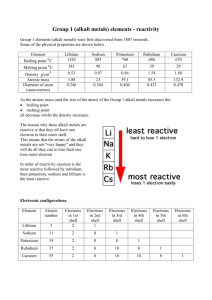
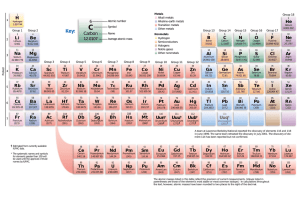
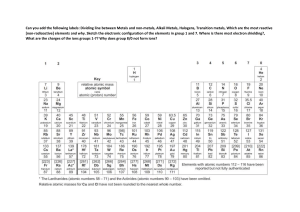
GROUP 1 – ALKALI METALS INTRODUCTION & DATA 5) The Group 1 elements have low densities for metals. Which Group 1 elements float on water? 1) Shade in Group 1 on the Periodic Table shown. ………………………………………………………………...………………………… 2) Give the name for Group 1. 6) What is the trend in melting points in Group 1? ……………………………………… ………………………………………………………………...………………………… 3) Complete the table about the Group 1 elements. name symbol atomic number relative atomic mass number of electrons in outer shell melting state at point room temperature (C) atomic radius (pm) density (g/dm3) CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF THE ELEMENTS lithium 7 181 123 0.53 7) a) When Group 1 metals react, what happens to the Group 1 metal atoms in terms of electrons? sodium 23 98 157 0.97 ………………………………..…………………………...………………………… potassium 39 63 203 0.86 rubidium 85 39 216 1.53 caesium 133 28 235 1.87 …………………………………..………………………...………………………… b) Where do these electrons go? ………………………………………………….. …………………………………..………………………...………………………… PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF THE ELEMENTS c) What type of compound is formed? ……………………………………………. 4) List some physical properties of the Group 1 metals. ………………………………………………………………...………………………… d) Explain why this happens when Group1 metals react in terms of electron structure. ………………………………………………………………...………………………… ………………………………………………………………...………………………… ………………………………………………………………...………………………… ………………………………………………………………...………………………… © www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 01-January-2016 ………………………………..…………………………...………………………… …………………………………..………………………...………………………… ………………………………..…………………………...………………………… …………………………………..………………………...………………………… Chemsheets GCSE 1028 8) a) Complete the table to show how the Group 1 metals react with oxygen, chlorine and water. Reaction with oxygen lithium sodium potassium Reaction with chlorine Reaction with water Observation Observation Observation Word equation Word equation Word equation Equation Equation Equation Observation Observation Observation Word equation Word equation Word equation Equation Equation Equation Observation Observation Observation Word equation Word equation Word equation Equation Equation Equation b) Describe how caesium reacts with water. ……………………………………………….....…………………………………………………………..………………………………………..….….. 9) a) What happens to the reactivity as you go down the group? ………………………………………………….....……………………………………………………..……………………………. b) Explain this trend in reactivity. Use these diagrams to help. X X X X ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… X XX XX X X XX X X X X X X X X X X X X X XX X XX XX lithium (2,1) sodium (2,8,1) potassium (2,8,8,1) © www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 01-January-2016 Chemsheets GCSE 1028