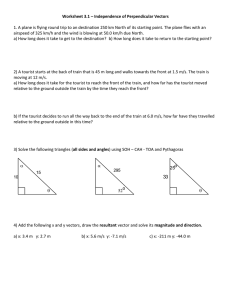
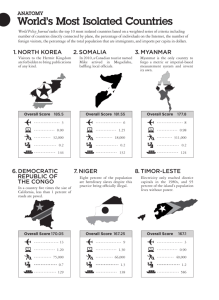
MACRO PERSPECTIVE OF TOURISM AND HOSPITALITY September 24, 2021 Meaning and Importance of Tourism Professors Hunziker and Krapf of Berne University, Switzerland defined tourism as “sum total of the phenomena and relationships arising from the travel and stay of non-residents, in so far as they do not lead tp permanent residence and are not connected to any earning activity.” The definition of the Tourism Society in Britain was: “Tourism is the temporary short-term movement of people to destinations outside the places where they normally live and work and their activities during their stay at these destinations.” The destination was reformulated by the tourism Society in Cardiff: “Tourism may be defined in terms of particularly activities selected by choice and undertaken outside the home environment.” Tourism refers to the activity of visitors (UNWTO IRTS 2008, 2.9). Meaning of Tourist In 1963, a United Nations Conference on International Travel and Tourism recommended a definition of a “visitor” as “any person visiting a country other than that of recommended a definition of a “visitor” as “any person visiting a country other than that of earning money. 2 Classifications of Visitors 1. Tourists: Temporary visitors staying at least 24 hours, whose purpose could be classified as: A. Leisure such as recreation, holiday, health, study, religion or sport or B. Business C. Family D. Mission E. Meeting 2. Excursionists: Temporary visitors staying less than 24 hours in the destination visited and not making an overnight, including cruise travelers in transit. Element of Travel Distance: It is the difference between local travel or traveling within a person community and non-local or traveling away from home. Length of stay at the destination: Tourist are temporary visitors staying at least one over night. Excursionist are temporary visitors who do not stay at least overnight in the country that they visit. Residence of the Traveler: For business and research purposes, it is important to know where people live. Purpose of travel a. Visiting friends and relatives b. Conventions, seminars, and meetings c. Business d. Outdoor recreation hunting, fishing, boating camping e. Entertainment - sightseeing, theater, sport f. Personal - family, medicinal, funeral, wedding. The Nature a Tour Domestic Tourism It is a travel taken exclusively within the national boundaries of the traveler’s country. International Tourism It involves the movement of people across international boundaries. It is more difficulty to travel outside one’s own country because of the language barriers, and the currency and documentation requirements such as passport and visas. Package Tour A package tour (also called as inclusive tour) is an arrangement in which transport and accommodation is bought by the tourist as an all-inclusive price and the price of the individual elements cannot be determined by the purchase himself. Independent Tour An independent tour is one in which the tourist buys these facilities separately, either making reservations in advance through a travel agent or en route during his tour. The Tourist Product It is a combination of what the tourist does at the destination and the services he uses during this stay. Characteristics of a Tourist Product: 1. It is a service 2. It is largely psychological in its attraction 3. It needs to vary in standard and quality over time 4. The supply of the product is fixed The Tourist Destination It is a geographical unit which the tourist visits and where he stays. It may be a village, a town, a city, a district, a region, an island, a country o a continent. The success of a tourist destination depends upon the interrelations of the three basic factors. 1. Attraction A. Site and Event attraction. A site attraction (e.g. a country, a city, a resort) is one which the destination itself has appeal while an event attraction (e.g. Festivals, sport, exhibition) is one which tourist are drawn to the destination solely because of what is taking place there. B. Natural and Man- made tourist Natural attractions include mountains, beaches, climatic features such as sunshine and pure air. Man-made attractions include buildings of historical or architectural interest such as Fort Santiago, holiday camps or theme parks such as Disneyland. 2. Amenities Includes accommodation, food, local transport and communications and entertainment at the site. 3. Accessibility It means having regular and convenience of transport in terms of time/distance to the destination from the originating country at a reasonable price. Tourist Services Passenger Passport Supplies principal tourist services. This provides the means to reach the destination as well as the movement at the destination. Districtions in transport are between public and private, domestic and international and among the various modes - land, sea, and air. Accommodation, Food and Beverage and Entertainment Hotels are vital concern to a large proportion of tourists. However, many stay with friends and relatives while others provide their own caravans and tents. Travel Agents and Tour Operator The travel agent is the distributor of the product while the tour operator is the manufacturer of the product. Others… Currency, information, shopping. documentation sightseeing and Characteristics of Tourism Tourism has special characteristics which make it different from other industries. 1. In tourism the product is not brought to the consumer. 2. The products of tourism are not used up; thus, they do not exhaust the country’s natural resources. 3. Tourism is a labor-intensive industry. 4. Tourism is people-oriented. 5. The tourist industry is seasonal. 6. The industry is dynamic. Importance of Tourism 1. Contribution to the balance of payments 2. Dispersion of development 3. Effect on general economic development 4. Employment opportunities 5. Social benefits 6. Cultural enrichment 7. Educational significance 8. A vital force for peace