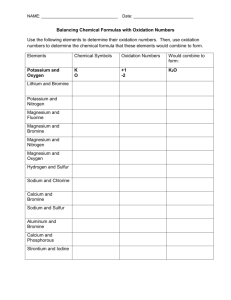
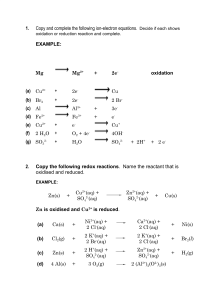
Needed for this lesson . • Class practical (1 set per group) • Two samples each of magnesium ribbon, iron wool, and copper for burning in Bunsen flame. •Blue glass to view magnesium through (2 per group). •Tongs, Bunsen, heatproof mat and safety specs. •Matches and wooden splints. Oxidation. Starter A. What has happened to the objects in the pictures and why this has happened? Starter B. What chemicals must be present for this to happen? Oxidation and reduction in a reaction • Make two sentences. • One of them will give you the first key definition for today’s lesson. Oxidation and reduction Oxidation is when oxygen is added Oxidation is ... to a chemical in a reaction. Reduction is when oxygen is removed Reduction is ... from a chemical in a reaction. What examples can you remember from last lesson where chemicals had oxygen added to them during a reaction? What happens when metals react with oxygen? 23/09/2021 • Predict the products formed in oxidation reactions. (Level 6) • Explain what happens to the mass of a metal when it is oxidised. (Level 5) • Describe what oxidation is. (Level 4) Oxidation reactions. ? Hydrogen reacts with oxygen to make water. H H H H + O O H H Hydrogen + 2 H2 O H O H + oxygen water O2 2 H2O The same atoms are present at the start and finish, they have just been rearranged. Oxidation reactions. Hydrocarbons reacts with oxygen to make water ? and carbon ?dioxide. H H C H + H O O O O O H H O H H O + C O Methane + oxygen water + carbon dioxide CH4 + 2 O2 2 H2O + CO2 Same atoms at the start and at the finish! Practical. Give yourselves numbers 1-4 • 1’s collect safety goggles. • 2’s a Bunsen burner, tongs and heatproof mat. • 3’s collect samples of the three test metals. • 4’s clear the work space and tuck stools away. Metal Observations Copper Iron REMEMBER! Health and Safety. Magnesium Product Formed Oxidation of metals. You will react magnesium, iron and copper with the oxygen in the air. 1. Use tongs. Hold a strip of magnesium into a Bunsen flame. Do not look directly at the strip. Observe the changes that occur. 2. Use tongs. Repeat with iron wool and copper. Record what you see in detail. Pay attention and record what happens to the appearance of each metal. Extension: can you figure out the products and write a word equation for each reaction? Oxidation of metals. Word equation for heating metals: “metal” + oxygen → “metal” oxide coppercopper + oxygen → copper oxide iron iron + oxygen → iron oxide magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide magnesium What happens when metals react with oxygen? 23/09/2021 • Predict the products formed in oxidation reactions. (Level 6) • Explain what happens to the mass of a metal when it is oxidised. (Level 5) • Describe what oxidation is. (Level 4) magnesium + Mg + oxygen O O Mg magnesium oxide Mg O O 2 Mg + O2 Mg 2MgO What happens to the number of atoms overall? What happens to the mass of the magnesium? magnesium + oxygen magnesium oxide • The reactants have the same type and number of atoms as the products do. • The oxygen atoms have bonded to the Mg O magnesium atoms. • Magnesium oxide is heavier than magnesium. copper Cu Cu 2 Cu + oxygen copper oxide + Cu O O O Cu + O2 O 2CuO Answer in your books. L4. What is being oxidised in the image above? L5. How and why does the mass of copper change? L6. Write a word equation to show this reaction. L7. Write a balanced symbol equation as well! What happens when metals react with oxygen? 23/09/2021 • Predict the products formed in oxidation reactions. (Level 6) • Explain what happens to the mass of a metal when it is oxidised. (Level 5) • Describe what oxidation is. (Level 4) Summarise in depth. When a bike rusts it becomes heavier. Discuss in your groups and use scientific ideas to explain why this is true.