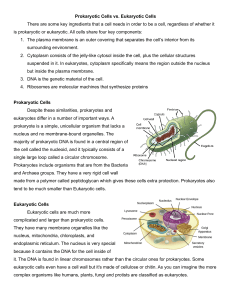
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells • The cell membrane and the DNA are universal to both plant and animal cells. • The term ”eukaryotic” came from the Greek word eu, which means “true” or “formed”, and karyon, meaning “nucleus”. • On the other hand, “prokaryote” originated from the Greek words karyon and pro. The latter means “before”. Eukaryotes • Can either be unicellular or multicellular. • Also known as true cells. • Have a well-organized internal condition • With membrane bound organelles • Bigger in comparison with prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotes • Has a nucleus which is not enveloped by a nuclear membrane called a nucleoid. • Neither the nucleus nor the internal organelles are membrane-bound. • Prokaryotic cell membrane is composed of phospholipids which serve as semipermeable barrier to the cell’s outside environment. • Plasmids are additional circular DNA molecules. • Some have cilia and flagella that enable them to move. • Prokaryotic cells are also smaller than eukaryotic cells. Cell Types in the Human Body