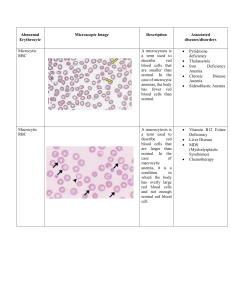
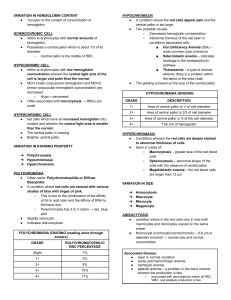
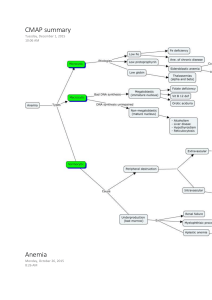
Abnormal Erythrocyte Microcytic RBC Macrocytic RBC Microscopic Image Description Associated diseases/disorders A microcytosis is a term used to describe red blood cells that are smaller than normal. In the case of microcytic anemias, the body has fewer red blood cells than normal. A macrocytosis is a term used to describe red blood cells that are larger than normal. In the case of macrocytic anemia, it is a condition in which the body has overly large red blood cells and not enough normal red blood cell. Pyridoxine deficiency Thalassemia Iron Deficiency Anemia Chronic Disease Anemia Sideroblastic Anemia Vitamin B12 Folate Deficiency Liver Disease MDS (Myelodysplastic Syndromes) Chemotherapy Spurr Cell RBC (Acanthocyte) Burr Cell RBC (Echinocyte) A spur cell anemia is an acquired hemolytic anemia associated with liver cirrhosis and is characterized by the presence of increased large red blood cells, which are covered with spike-like projections that vary in width, length, and distribution. Abetalipoproteinemia Liver Disease McLeod Blood Group Phenotype Post-Splenectomy A burr cells are red blood cells with short, evenly spaced spicules and preserved central pallor that is usually artifactual. This can be observed in uremia and liver disease Uremia Liver Disease Schistocyte Bite Cell RBC Elliptocyte A schistocyte is a fragmented part of a red blood cell. Schistocytes are typically irregularly shaped, jagged, and have two pointed ends. Bite cells are red blood cells that contain a semicircular indent on the edge of their membrane, giving the appearance of a bite being taken out of the cell A elliptocytes are elongated ovalshaped red blood cells. Very rare elliptocytes may be seen in normal blood smears. Elliptocytes may be increased in iron deficiency anemia where they are sometimes referred to as pencil cells and marrow infiltrative processes with teardrop cells. Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia Mechanical Valve Induced G6PD Deficiency (Glucose-6Phosphate Dehydrogenase) Unstable Hemoglobin Disorders Oxidative Drugs Hereditary Elliptocytosis Severe Deficiency Iron Spherocyte Stomatocyte Spherocytes are red blood cells that are sphereshaped rather than the usual round doughnut shape. Spherocytes are more fragile than normal red cells and their presence is accompanied by anemias of varying severity. Stomatocytes are red blood cells that, under a microscope, look like “kissing lips” or “coffee beans” rather than a biconcave disc with a clear center. Hereditary Spherocytosis Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Hereditary Stomatocytosis Liver Disease Target RBC Cell Codocytes, also known as target cells, are red blood cells that have the appearance of a shooting target with a bullseye. Thalassemia Hemoglobinopathies Post-Splenectomy Liver Disease Artifact Sickle RBC Cell An inherited disease in which the red blood cells have an abnormal crescent shape, block small blood vessels, and do not last as long as normal red blood cells. Hemoglobin SS Disease Hemoglobin SC Disease Hemoglobin SD Disease S-beta Thalassemia Teardrop cells are frequently associated with infiltration of the bone marrow by fibrosis, granulomatous inflammation, or hematopoietic or metastatic neoplasms. Teardrop RBC Myelofibrosis Underlying Marrow Process/Infiltrate Hemoglobin C Crystals Red Cell Agglutinate Rouleaux Hemoglobin C crystals are dense rectangular structures composed of precipitated hemoglobin C. Target cells form when there is an excess of membrane in relation to cytosol. A red cell agglutination or autoagglutination is a phenomenon in which red blood cells clump together, forming aggregates. It is caused by the surface of the red cells being coated with antibodies. Rouleaux are clumps of red blood cells that look like stacked plates. They usually form as a result of abnormal quantities of certain proteins (immunoglobulin, fibrinogen) in the blood. Rouleaux are a non-specific indication of the presence of a pathology. Hemoglobin Disease Hemoglobin Disease SC C Cold Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria IgM Associated Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Chronic Liver Disease Malignant Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Chronic Inflammatory Disease