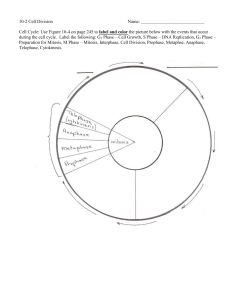
The Great Divide 05/04 Why Would a Cell Divide? As cells absorb nutrients and get larger, the ______ of the cell increases faster than the _______ ____ This means that a cell can no longer _________ and __________________ fast enough to support its demands (volume) So what shall a cell do? DIVIDE !!!! Why Would a Cell Divide? Besides growth a cell would also divide for: R_________ or R__________ C________ Different cells divide at different rates: Most mammalian cells = ______ hours Some bacterial cells = _______ minutes Getting Older… All cells are only allowed to complete a certain number of divisions Then they die (_________________________) How does cell division change over a lifetime? Childhood = Adulthood = The Later Years = Cell Cycle Tidbits How long is one cell cycle? Depends on the cell- skin cells = ~__ hours, nerve cells = ______ after maturity, cancer cells = _______ Remember: every cell only has a certain # of divisions it can undergo, then it dies = _________ (programmed cell death) The Cell Cycle Stages of the Cell Cycle There are two stages to a cells life. ___________ (growth & replication of DNA) ____________ (division of cell into 2 daughter cells) Cell spends about __% of the time in interphase Interphase Divided into 3 phases: ____________ = small cell is absorbing nutrients, growing & doing its job. ____________ = cell is continuing to grow & duplicates its DNA. ____________ = cell keeps growing & doing its job. Mitosis: A Closer Look DNA is all twisted up into a Chromosome. During S phase the Chromosomes are copied. 2 complete identical sets of chromosomes are formed. They are connected in the middle by a ___________. A single copied chromosome is called a __________. The Mitotic Phase Divided into 4 stages of Mitosis: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase (+) PLUS Cytokinesis Prophase Chromatids ________ becoming ________. Nuclear membrane _________ The _________(an organelle that makes microtubules) appears and _________ to opposite sides. ______________ start to form between them Metaphase Chromosomes _______ on the _______________ __________ _________ are attached to spindle fibers Anaphase Spindle fibers _______ Centromeres ______ Sister chromatids are _____ ______from each other ________________ Telophase The chromosomes ________________ _______ ___________ reform around the 2 new nuclei. Cytokinesis The cytoplasm is distributed equally between the 2 new cells In animals, a ___________ forms from __________ In plants, a ____ ________ forms from ___________ Animal Plant What Mitosis Actually Looks Like Interphase Metaphase Prophase Anaphase Telophase http://www.sci.sdsu.edu/multimedia/mitosis/mitosis_gif2.html http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/bio1int.htm What Happens After Mitosis? The cell returns to ________ Chromosomes ______ back into ________ The cycle repeats itself over & over… At What Stage Are Our Cells At In The Cell Cycle? Different cells can be in different stages Interphase Mitosis: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis The Guarantee The product of mitosis is _______ The daughter cells are _______ to each other & to the mother cell Why is this so important? Mother cell Identical daughter cells The Daughter Cells In humans, the 2 daughter cells will have ____ chromosomes (___ pairs) Each chromosome is said to have ____ _____ gene sequence Identical daughter cells The Beauty of Asexual Reproduction Mitosis is a form of ______ ___________ New individuals are produced by 1 parent & thus, are identical to their parent Mother cell Runners produces by strawberries Identical Budding by hydra & yeast daughter cells Cuttings from plants