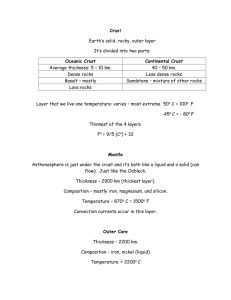
Journey to the Center of the Earth Guided Notes Review ● is a measure of how tightly packed the particles are in a substance ○ Substances that are less dense than water will ● is the transfer of thermal energy through fluids like liquids and gases ○ Cool dense liquid , while hot less dense liquid Earth’s Layers ● ○ Very rigid (hard) and composed of ○ Like the skin of an apple ○ Very thin compared to the other layers - about km thick ○ Divided into two types: and ■ ● Thickness: 30-75 km ● Composition: rigid rock, granite ■ ● Thickness: 5-10 km ● Composition: rigid rock, basalt ● ○ Solid and rocky layer ○ Almost 3,000 km thick ○ Thickest layer of the Earth ○ Made up of two portions: and ■ Upper Mantle ● Lithosphere ○ Thickness: about 100 km ○ Composition: rigid, brittle rock ○ It is divided into that slowly move the Earth’s crust ○ It consists of all the crust and the part of the mantle ● ○ ○ ○ ○ Thickness: 70-350 km Composition: less rigid, plastic-like molten rock Located under the At the uppermost part of the Asthenosphere, the Lithosphere is not attached causing the plates to ■ ● ● ● ● ■ ● Thickness: 2200 km Composition: rigid rock Temperatures can reach up to degrees Celsius The layer is due to pressure of the rocks above it Convection Currents ● Created by and differences in the fluid ● Expanded, heated rocks, being less dense, while colder, denser rocks ● Causes the crust’s plates to move Core ○ Made up of and alloys ○ Extreme ○ Divided into two parts: and ■ ● Thickness: 2300 km ● Composition: metal (liquid iron and nickel) ● Only layer ● of the Earth generated when the iron metal moves around ■ ● Dense and solid due to great at the center of the Earth ● Thickness: 1200 km ● Composition: rigid, solid metal of mostly iron and some ● Higher temperatures up to