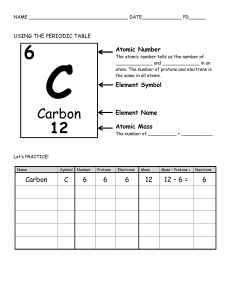
STUDY GUIDE-Atoms Quiz MATTER: 1. All matter is made of ________________________ 2. Matter is anything that has ____________ or takes up __________________ 3. Matter comes in four forms: _____________________________________________________________ 4. List two examples of things are matter and two that are not. ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1. What are the charges and location of the each of the subatomic particles? Subatomic Particle Charge Location 2. Which two subatomic particles have the most mass? ___________________________________________ 3. Which subatomic particle defines the element? _____________________________ 4. How do you determine the number of protons in the nucleus? _________________________________ 5. How do you determine the number of electrons in the shells? _________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. How do you determine the number of neutrons? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What does the atomic mass tell you? __________________________________________________________ 8. The atomic number tells what information? ___________________________________________________ 9. An atom likes to bond with other atoms if _____________________________________________________ ELEMENTS 1. An element is made of how many types of atoms? _______________________ 2. Elements are identified by the number of ____________________ they have. 3. Copper is made only of what type of atoms? ___________________________________________________ 4. Atoms generally have what electric charge? _________________________ 5. Why doesn’t an atom have a charge? _______________________________________________________________ 6. What if an atom has an abnormal number of electrons? Is it still the same element? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What if an atom has an abnormal number of neutrons? Is it still the same element? ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What is the smallest piece of an element? ______________________________ 9. How many naturally occurring elements are in the universe? ____ 10. If they are not naturally occuring they are __________________ 11. How is the periodic table arranged? _______________________________________________________________ 12. What is the most common (or abundant) element in the universe? ____________________________ 13. What is the correct way to write an element’s symbol? ________________________________________ 14. Why are some elements symbols different than their name? Honors: (Add to academic) 1. What is density? 2. How are mass and volume related? 3. List items that are more or less dense. 4. Why do substances change state? 5. What processes do substances go through when they change state? 6. Which particles make up a proton? Neutron? 7. What is an ion? 8. Calculate the number of P, N, E of atoms that are not electrically balanced. 9. What is an isotope? 10. Calculate the number of P, N, E of atoms that are isotopes? 11. Be able to make Bohr Models for ions and isotopes. 12. What does it mean when an element is radioactive? 13. What parts of the periodic table are reactive (alkali metals) or not reactive (nobel gasses)? STUDY GUIDE-Atoms Quiz (Answers) MATTER: 1. All matter is made of ATOMS 2. Matter is anything that has MASS or takes up SPACE 3. Matter comes in four forms: SOLID, LIQUID, GAS, PLASMA 4. List two examples of things are matter and two that are not. ATOMIC STRUCTURE 1. What are the charges and location of the each of the subatomic particles? Subatomic Particle Charge Location PROTON POSITIVE NUCLEUS NEUTRON NEUTRAL NUCLEUS ELECTRON NEGATIVE ELECTRON CLOUD 2. Which two subatomic particles have the most mass? PROTONS AND NEUTRONS 3. Which subatomic particle defines the element? PROTONS 4. How do you determine the number of protons in the nucleus? ATOMIC NUMBER 5. How do you determine the number of electrons in the shells? ATOMIC NUMBER BECAUSE THE NUMBER OF PROTONS IS BALANCED WITH THE NUMBER OF ELECTRONS 6. How do you determine the number of neutrons? SUBTRACT ATOMIC MASS AND ATOMIC NUMBER. 7. What does the atomic mass tell you? THE NUMBER OF THINGS IN THE NUCLEUS 8. The atomic number tells what information? THE NUMBER OF PROTONS IN THE NUCLEUS 9. An atom likes to bond with other atoms IF ITS OUTER ELECTRON SHELL IS NOT FILLED ELEMENTS 1. An element is made of how many types of atoms? ONE 2. Elements are identified by the number of PROTONS they have. 3. Copper is made only of what type of atoms? COPPER 4. Atoms generally have what electric charge? NONE/ NEUTROL B/C PROTONS= ELECTRONS 5. Why doesn’t an atom have a charge? PROTONS + = ELECTRONS 6. What if an atom has an abnormal number of electrons? Is it still the same element? YES, IT IS STILL THE SAME ELEMENT B/C THE PROTON DETERMINES THE TYPE OF ELEMENT. 7. What if an atom has an abnormal number of neutrons? Is it still the same element? YES, IT IS STILL THE SAME ELEMENT B/C THE PROTON DETERMINES THE TYPE OF ELEMENT. 8. What is the smallest piece of an element? ATOM 9. How many naturally occurring elements are in the universe? 92 10. If they are not naturally occuring they are SYNTHETIC 11. How is the periodic table arranged? BY INCREASING ATOMIC NUMBER 12. What is the most common (or abundant) element in the universe? HYDROGEN 13. What is the correct way to write an element’s symbol? CAPITAL THEN LOWER CASE 14. Why are some elements symbols different than their name? THEY ARE IN LATIN