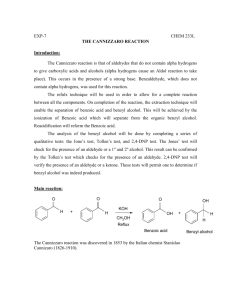
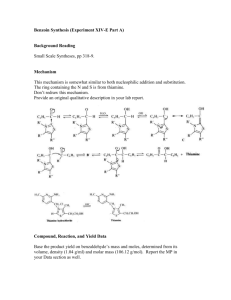
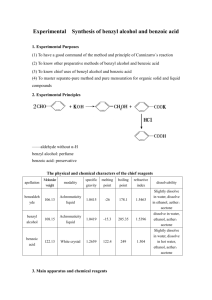
Practical 1 CANNIZARO REACTION: AUTO-OXIDATION-REDUCTION OF AROMATIC ALDEHYDES INTRODUCTION The dilute base added to aldehydes or ketones leads to the formation of β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketones by aldol condensation. When the aldehyde or ketone has no hydrogens in the α position, aldol condensation does not take place but rather undergoes auto-oxidationreduction (disproportionation) in the presence of strong bases to give equimolar mixture of the alcohol and the corresponding acid (the latter in salt form). For example, benzaldehyde produces benzyl alcohol and sodium benzoate in the presence of sodium hydroxide. Formaldehyde also yields the Cannizaro reaction, like aliphatic aldehydes (such as trimethylacetaldehyde) containing no α hydrogens, and aromatic derivatives such as benzaldehyde. MATERIALS Equipment: 250-ml Erlenmeyer flask, 250-ml beakers, stopper (rubber bung), separatory funnel, stirring rod, graduated cylinder, rotary evaporator, beakers, vacuum filtration apparatuses, vacuum distillation apparatuses Chemicals Benzaldehyde 10 ml NaOH 9g Page 1 of 3 CH2Cl2 50 ml NaHSO3 10% 40 ml Na2CO3 10% 20 ml Na2SO4 / or any drying agents HCl for precipitation Distilled water PROCEDURE 1. In a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask, place 10 ml of benzaldehyde and 9 g of NaOH (dissolved in 5 ml water). Cover securely with a stopper (septum), and shake vigorously for 20 min by hand, until a solid product and a colorless liquid simultaneously appear. 2. After the reaction, add enough water to dissolve the solid formed (sodium benzoate), but not too much water. 3. Transfer the solution to a separatory funnel. Wash the Erlenmeyer flask with a few ml of CH2Cl2 to drag any solid residues left in the flask and add the washing to the separatory funnel. 4. Extract the solution with CH2Cl2 (3 x 15 ml). To determine which layer is organic and which one is aqueous, check their densities. Save both phases, aqueous layer will be acidified in procedure no. 7. 5. Collect the organic extracts and wash with NaHSO3 10% (2 x 20 ml) and with Na2CO3 10% (1 x 20 ml). 6. Dry over Na2SO4, filter, and evaporate in a rotary evaporator or over the hood to remove the solvent. If there is enough time will do vacuum distillation to purify the benzyl alcohol (colorless liquid slightly soluble in water). 7. Acidify the aqueous alkaline layer from the first extraction (from procedure no. 4) with HCl in order to precipitate benzoic acid as a white mass. Cool the mixture, filter under vacuum, and wash with distilled water. Benzoic acid is a white crystalline solid, slightly soluble in water (0.2 g/100 g at 20 °C, 2.2 g/100 g at 75 °C). Recrystallize from distilled water to achieve purity, estimated yield of benzoic acid is 80%. Page 2 of 3 POST-LAB REPORT: Submit a report about this practical before the due date. POST LAB QUESTIONS: Answer the following and attach your answers to your report. 1. Draw the reaction mechanism of your practical leading to benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid. (6 marks) 2. When o-phthalaldehyde is treated with base, o-(hydroxymethyl)benzoic acid is formed. Draw the mechanism of this reaction. (6 marks) Page 3 of 3