Uploaded by
Karthikeyan Balasubramanian
Welding Processes & Techniques: A Technical Overview
advertisement

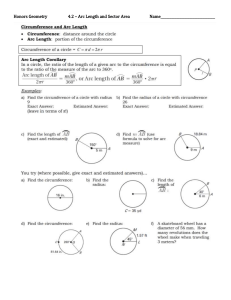
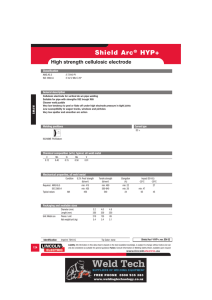
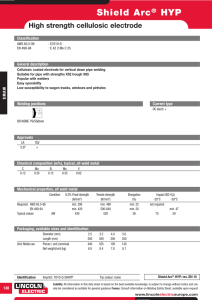
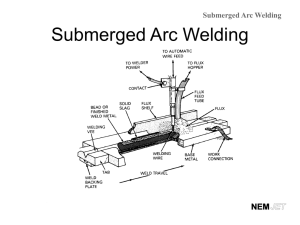
WELDING By hammering nuggets of gold or silver into rods, forming the rods into circles or segments of a circle,and then forging the ends together to form a continuous ring. This earliest welding process is called forge welding. Temporary joint was first –rivetted joint which is weight increased Welding is permanent joint needed in second world war It is a process in which localized permanent joint can be produced by with or w/out application 0f heat, or pressure. ADVANTAGES 1. Permanent joint…….. 2. Strength………. 3. Any position…………. 4. Similar/Dissimilar…… .As we reqd .We get exact mech strength of raw material in weld part also .We can build in any shape by weld .Same material also with other material LIMITATIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. Setup cost-….. Machine cost Technician- ……… skill required HAZ---------Mech property can be changed Cracks…………. Defects To be avoided by taking preventive measures WELDING………CLASSIFICATION…………… A . . .SOLID STATE……Diffusion,U/Sonic,Forge,Friction,Explosive B. LIQUID STATE……Based on heat production, There are three types 1.ARC……MMAW,Fcaw,SAW,Shielded Gas (TIG,MIG,PAW) 2. Resistance……………...Spot, Seam, Projection welds 3. Chemical Reaction………Gas welding, Thermit weld C. SOLID/LIQUID STATE…………………….Soldering, Brazing. Here Base metal is solid and filler metal is fused into liquid state ARC welding Welding circuit Open Circuit Voltage ---------60v to 110v Always current is zero Closed Circuit Voltage -------18v to 55v (or) Arc Voltage (Short circuit voltage) Always current is as per setting Voltage is increased by increasing the Arc length, Max 55v by increasing the arc length (La=0.5d to 1.5d) where d is the dia of electrode. Arc is cutoff, if increased beyond 1.5d distance . HOW THE ARC IS PRODUCED: Due to high potential Difference Electrons in cathode are pushed to transfer towards bottom of electrode when electrode is –ve charged. These Electrons break the air molecules and air decomposes into +ve ions and –ve ions.ie called plasma stage(good conductor of electricity).charged particles in air.To continue this arc arc length is maintained. +ve ions melt faster than Electrons hence 2/3 of heat is at +ve side. As ac current is passed in circuit (DCSP+DCRP alternatively) uniform heat generation is obtained. METHOD OF STRIKING ARC: TYPES OF POLARITIES IN DC MACHINE Cathode is Negative charged having electrons of small mass hence getting 1/3 of heat Anode is positive charge having positive ions of high mass hence getting 2/3 of heat If we use consumable electrode we select DCRP (DCEP) for Non-Consumable electrode we select DCSP (DCEN). DCEN DCEP For high thickness of workpiece For less thickness of workpiece For high melting point material For low3 melting point material Metal deposition rate is less Metal deposition rate is high—Kg/Hr For Low speed application For high speed application ELECTRODE ANGLE ARC BLOW: Specially occurred in DC welding M/C. The clash of Magnetic field which was already present in work piece with present Magnetic field of Short circuit within electrode and work piece…..Hence arc always goes towards the Strength of Magnetic field at centre of work piece….Hence Spatter occurs by deflecting the arc.. Arc blow can be controlled mainly by following 4 methods…. WELDING TECHNIQUES:.(ADVANCED WELDING TECHNIQUE). Key point is to maintain constant Arc length. If arc length is changed the Welding parameter is changed by Current. When Voltage(arc length) varies , Current (Heat)also varies asper Ohms law.(V=IR) 1. Manual arc welding--Two motion (Speed and Feed) are controlled by man 2. Automatic arc welding--Both are controlled by machine. 3. Semi-automatic arc welding—one motion (speed) is controlled by man. Type of welding Machines: Based on step-down Transformer. 1. Constant current…Drooping Characteristics…(Parabolic curve)Downward bend curve have small changes in current….Due to hand shake arc length varies in turn voltage varies…so this is suitable for manual weld. 2. Constant Voltage….small change in voltage will give high change in current…so machine will keep arc length constant will not affect current….hence suitable for Automatic machines OTHER FEATURE OF WELDING M/C TO BE ASSESSED ON PURCHASE FOR USE: 1. Short circuit current… Max current can be allowed at rated condition..Arc voltage is the function of arc length 2. (D)-Duty cycle… Arc is ON w/out overheating the elements of welding machine…%of time=Arc on time/(arc on time+Idle time)….I2D=constant…In india we follow 5 min i.e 3 min arc on, 2 min Idle will give 60% duty cycle. TYPES OF JOINTS: WELDING TERMS Permitted Reinforcement of weld is T/10 where T is the thickness of parent metal. ARC LENGTH LONG ARC NORMAL ARC CHARACTERISTICS OF ARC SHORT ARC WELDING POSITIONS FOR PLATE WELD 1F AND 1G 2F ANF 2G 3F AND 3G 4F AND 4G WELDING POSITIONS FOR PIPE WELD 1G AND 2G POSITION 5G AND 6G POSITION TACK WELD: WELDING PROCESS FUNCTIONS OF FLUX DURING WELDING FLUX COATING MATERIAL TO PROTECT THE WELD STRENGTH: DESIGNATION OF ELECTRODE: BIS( Bureau of Indian Standard)used only in India. E122 413 P E…..Extrusion..Type of manufacturing of Electrode 1….Type of flux coating…..1-High cellulose, 2-High Titanium(TiO )--Rutile 2…Position of Electrode….0-F,H,V-u+d,O 2 1-F,H,V-u+d 2- V-u+d 2…Polarity of Electrode…..1—DCSP (DCEN).. 2—DCSP—v90 413…Strength of Electrode….4—Tensile strength 1—Yield strength 3--% of Elongation P….Specific Information ( Deep penetration) DESIGNATION OF ELECTRODE: ASPER ISO—International Organisation for Standardisation. ER 4312HJX E…Extrusion (Manufacture type) R..Type of Flux used….A—Acidic, B—Basic, C—Cellulose, R—Rutile. 43..Mechanical properties of joint…4—Yield strength and Ultimate tensile strength 3--% of Elongation 12..Performance characteristics of coverings.. 1—Welding position 2—Welding current and voltage settings H..Special characteristics….H—Hydrogen controlled electrodes J—Iron powdered electrodes-(110-129%)Deposition recovery X—Radiographic quality of weld. DESIGNATION OF ELECTRODE: ASPER E6013 E………….Electrode. 60………..Tensile strength in 1000psi. 1………….Welding position in all position (1-3) 3………….Flux coating of Titania potassium(0-8) AWS WELD DEFECTS AND ITS CAUSES CAUSES OF DEFECTS UNDERCUT 1. HIGH CURRENT, 2. SHORT ARC, 3. TOO SPEED, 4. INCORRECT ANGLE OF ELECTRODE, 5. HIGH HEAT ON JOB OVERLAP: 1. LESS CURRENT 2. SLOW SPEED, 3.LONG ARC, 4.OVER SIZE OF ELECTRODE BLOW HOLE and POROSITY 1. DUST,OIL,GREASE ON JOB, 2. HIGH SULPHUR ON JOB 3. FAST COOLING OF WELD 4. EDGE PREPARATION NOT DONE 5. WETNESS ON METAL SPATTERS 1. HIGH CURRENT, 2. LONG ARC, 3.WRONG POLARITY 4.ARC BLOW 5.FLUX DAMAGED ON ROD EDGE OF PLATE MELTED OFF:(lap&coner) 1. OVERSIZE ELECTRODE 2. HIGH CURRENT 3. WRONG WEAVING OF ELECTRODE. IMAGE OF DEFECTS CRACKS 1. LOCALISED STRESS 2. FAST COOLING OF WELD 3. HIGH SULPHUR ON METAL 4. W/O PRE &POST HEAT OF METAL, 5. LESS DUCTILITY OF METAL, 6.WRONG SELECTION OF ELECTRODE, 7.WRONG TECHNIQUE USED. INCOMPLETE PENETRATION 1.TOO SPEED, 2.KEY HOLE NOT MAINTAINED IN ROOTRUN, 3.LESS CURRENT, 4.OVERSIZE ELECTRODE, 5.ANGLE OF ELECTRODE INCORRECT, 6.INSUFFICIENT ROOT GAP. SLAG INCLUSION 1.WRONG EDGE REPARATION, 2.DAMAGED ELECTRODE, 3.HIGH CURRENT, 4.LONG ARC, 5.WRONG WELD TECHNIQUE, 6. CHIPPING OF SLAG NOT DONE ON SUBSEQUENT PASS OVERSIZED WELD/EXCESSIVE REINFORCEMENT 1. OVER WELD NOT NEEDED FOR ECONOMIC,TIME,PRODUCTION PURPOSE. 2. INCREASED WEIGHT. EXCESSIVE CONCAVE/INSUFFICIENT THROAT THICKNESS 1.UNDER SIZED ELECTRODE, 2.TOO SPEED WELDING, 3.WRONG WEAVING OF ELECTRODE, 4.NO CONSTANT SPEED.