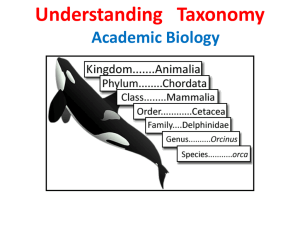
Understanding Taxonomy Academic Biology The 6 Kingdoms Organisms are placed into kingdoms based on their type of cells, their ability to make food and the number of cells in their bodies Prokaryotes organisms whose cells lack a nucleus Nucleus—dense area in a cell that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instructions that direct the cell’s activities. Nucleic acids are scattered throughout the cell. Bacteria. Ecological Importance of Prokaryotes • • • • • Decomposition Nitrogen fixation Mutualistic relationships Parasitic relationships Commercial uses Treponema pallidum, a spiral-shaped bacteria which causes Syphilis in humans Eukaryotes organisms with cells that contain nuclei. Their chemical instructions are in the nucleus. Introduction to Phylogenetic Kingdoms • Monera (Eubacteria and Archaebacteria) Prokaryotes. • Protistia – Eukaryotes, diverse, not fungi, plants, or animals • Fungi – Eukaryotes, multicellular (except yeasts) • Plantae – Eukaryotes, multicellular, nonmotile, autotrophic, cell wall containing cellulose • Animalia – Eukaryotes, multicellular, motile, heterotrophic, no cell wall Kingdoms and Domains The three-domain system Bacteria Archaea Eukarya The six-kingdom system Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia The traditional five-kingdom system Monera Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Kingdom Monera The traditional five-kingdom system Monera The six-kingdom system Eubacteria Archaea The Kingdom Monera Eubacteria • • • • Common name: Bacteria Unicellular prokaryotes Have cell wall Basic shapes are cocci, bacilli, spirilla Streptococcus mutans (can cause endocarditis and dental caries) Bacillus anthracis (spores can live in soil for years) Eubacteria a. Can be found in yogurt b. Unicellular bacteria c. Autotrophic or heterotrophic d. Most are helpful, some cause things like strep throat Bacteria which causes strep throat Kingdom Archaebacteria means “ancient bacteria” a. Unicellular bacteria b. Autotrophic or heterotrophic c. Live in places without O2 (ocean floor, salty water, hot springs, and your intestines!) d. Prokaryotes The Kingdom Protista Slime molds b. Autotrophic or heterotrophic c. Most unicellular d. Some multicellular, sea weed e. Eukaryotes A classification problem • Some move with flagella, pseudopods or cilia • Animal-like, plant-like and funguslike groups Entamoeba histolytica Ecological Importance • Important foundation in food chain. • Produce a lot of Oxygen • Decomposition • Symbiotic relationships – Mutualistic – Parasitic • Medicinal and Industrial Uses Euglena is both autotrophic and heterotrophic The Kingdom Fungi Mushrooms, molds and mildew b. Most are Multicellular eukaryotes c. Yeast is unicellular eukaryotes d. Most found on land, a few in fresh water e. Heterotrophs—feed on decaying organisms Puffball Drops of rain trigger the release of spores Pholiota spp Degrades wood very quickly Ecological Importance • Decomposers • Symbiotic – Parasitic • On plants • On animals – Mutualistic • Lichens • Mycorrhizae Epidermop hyton floccosum, fungi causing athlete’s foot The Kingdom Plantae Dandelions, mosses, tomatoes b. Multicellular eukaryotes c. Autotrophs d. Some produce flowers some do not. e. Can be small or grow tall like a sequoia tree Sunflowers in Fargo, North Dakota Major Groups of Plants • Three traditional groupings: – Bryophytes—nonvascular plants – Tracheophytes — vascular, – Seed plants • Gymnosperms • Angiosperms Ginkgo biloba Ginkgos are often very long-lived. Some specimens are thought to be more than 3,500 years old. Importance of Plants to Humans • Food source – Wheat, grains, fruits, vegetables • Medicine – Aspirin, cancer treatments, stimulants • Industry – Agriculture, wood products, cotton Sugarcane The Kingdom Animalia Dogs, fleas, rabbits, Human, turtles mosquitoes… • Multicellular eukaryotes. • Heterotrophs Baby Chicks Invertebrates and Vertebrates • Invertebrates – 97% of the Animal Kingdom – Absence of backbone – Includes sponges, cnidarians, mollusks, worms, arthropods, and echinoderms • Vertebrates – Internal skeleton (bone or cartilage) – Includes fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals Asian ladybeetle Harmonia axyridis Notice the “false” white eye markings behind the head. Invertebrate Animals • • • • • • Sponges Cnidarians Worms Mollusks Arthropods Echinoderms Colony of sponges Chambered Nautilus Invertebrate Animals • • • • • • Sponges Cnidarians Worms Mollusks Arthropods Echinoderms Hymenoptera Dialictus zephrum Txodes scapularis Deer tick Vertebrate Animals • Chordates • Fish – Agnatha (jawless fish/lamprey) – Chondrichthyes (sharks, skates, rays) – Osteichthyes (bass, tuna, salmon) • • • • Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Ardea herodias Great Grey Heron Name 6 Kingdoms Name 6 Kingdoms The six-kingdom system Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia What is a prokaryote? Prokaryotes organisms whose cells lack a nucleus Nucleus—dense area in a cell that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instructions that direct the cell’s activities. Nucleic acids are scattered throughout the cell. Bacteria. Which 2 kingdoms only have prokaryotes? Kingdom Monera The traditional five-kingdom system Monera The six-kingdom system Eubacteria Archaea Which kingdoms include only heterotrophic organisms? Which kingdoms include only heterotrophic organisms? • Fungi and animalia