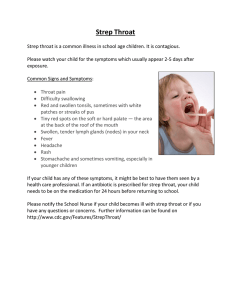
Soap Note #1 Strep Pharyngitis CHIEF COMPLAINT: Sore throat Fever HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS (HPI): A 19-year old male presents w/a 3day history of sore throat, red and swollen tonsils with white patches. Pt c/o painful swallowing with associated fever. He states it becomes worse at night and while drinking or eating. He reports pain 7/10 and no other home treatment other than Motrin. He is otherwise healthy and is a freshman in college. Use mnemonic “OLD CARTS” to clarify the attributes of each system: O = Gradual started about 3 days ago L = Throat D = 3 days and continuous C = Red and swollen tonsils, white patches and painful swallowing A = Motrin makes it better, drinking liquids and eating makes it worse R = Fever T = Worse at night and continuous throughout the day S = 7/10 Home Treatment: Motrin PAST MEDICAL HISTORY: Childhood Illnesses: Strep throat, ear infection Past Medical History: None Surgical History: Tympanostomy tube, 2009’ Hospitalizations/Accidents/Injuries: None Transfusions: None Reproductive/ Gynecologic History; Sexual History: Sexual history: Number of sexual partners- two Sexual orientation –female partner History of sexual transmitted infections- None Safe sex behaviors- Condoms History of sexual dysfunction-None Psychiatric History: None Medication History: Motrin 600mg every 6 hours as needed Allergies: Bee stings If allergic, what type of reaction do they have- Redness and swelling Immunizations/Health Maintenance: Heath Maintenance: Eye exam- 4/2010 Results: 20/40 bilateral Dental exam-7/2017 Results: Normal Immunizations up to date Travel History: None Family History: Father- 47 years old alive, hx of Diabetes and allergies to PCN Mother- 40 years old alive, hx of Hyperlipidemia and Gout, NKA Sister -16 years old alive, hx of Anxiety, NKA Sister- 10 years old alive, no medical hx and NKA Psychosocial History: Marital status/relationships- girlfriend Employment status- unemployed Substance abuse – smokes ½ pack every other day, no treatment Diet is normal Sleep pattern is normal Exercise- 4x a week REVIEW OF SYSTEMS (ROS) – General: (+) fever, (+) decrease appetite, (+) pain (-) chills, (-) malaise, (-) fatigue, (-) night sweats, (-) weakness, (-) unintentional weight loss Neurological: (-) Fainting, (-) dizziness, (-) seizures, (-) numbness, (-) tingling, (-) paresthesias, (-) weakness, (-) speech disorders, (-) tremors, (-) headaches, (-) imbalance, (-) loss of balance or coordination, (-) mood or temperament changes, (-) memory changes, (-) LOC. Head: (-) Lumps, (-) asymmetry, (-) trauma, (-) syncope, (-) headache, (-) dizziness. Eyes: (-) Pain, (-) redness, (-) itching, (-) burning, (-) discharge, (-) swelling, (-) excessive tearing, (-) blurring of vision, (-) diplopia, (-) spots, (-) photophobia, (-) changes in vision or visual fields, (-) glasses/corrective lenses/contact lens Ears: (-) Pain, (-) discharge, (-) infections, (-) tinnitus, (-) changes in hearing, (-) injury, (-) hearing aid, Nose/Sinuses: (-) Epistaxis, (-) obstruction, (-) airflow, (-) discharge, (-) olfactory changes, (-) postnasal drip, (-) sinus pain. Mouth/Throat: (+) sore throat, (+) difficulty chewing or swallowing, (-) Bleeding gums, (-) sores in mouth, (-) toothache, (-) changes in taste, (-) dentures, (-) hoarseness, (-) voice changes. Neck/Nodes: (+) swollen glands, (-) Pain, (-) stiffness, (-) masses, (-) swelling, (+) swollen glands. Breast/Axilla: (-) Lumps, (-) discharge, pain, (-) tenderness, (-) dimpling, (-) contour changes, (-) nipple changes. Respiratory: (-) Cough, (-) sputum production, (-) hemoptysis, (-) chest pain, (-) shortness of breath, (-) wheezing Cardiovascular: (-) Chest pain or tightness, (-) palpitations, (-) dyspnea, (-) murmur, (-) edema, (-) paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, (-) known heart murmur, (-) edema, (-) phlebitis, (-) calf pain, (-) intermittent claudication, (-) varicose veins Gastrointestinal: (+) dysphagia (-) Anorexia, (-) nausea, (-) vomiting, (-) indigestion, (-) belching, (-) heartburn, (-) hematemesis, (-) abdominal pain, (-) food intolerance, (-) diarrhea, (-) constipation, (-) change in bowel habits, (-) bloody or tarry stools, (-) pain or rectal itching, (-) rectal bleeding. GU: (Genitourinary): (-) Frequency, (-) urgency, (-) burning, (-) dysuria, (-) hematuria, (-) nocturia, (-) incontinence, (-) change in color or odor, (-) (-) dribbling, (-) retention, (-) oliguria. (-) ADL: Urinary pattern Male Genital: (-) Weak urine stream, (-) discharge from penis, (-) lesions, (-) testicular pain or swelling, (-) lumps on testicles Musculoskeletal: (-) Pains in joints, (-) swelling, (-) heat, (-) redness, (-) stiffness, (-) muscle weakness, (-) muscle aching or pain, (-) back pain or injury, (-) limitation in movement or ROM. Integument: (+) moles, (+) birthmarks, (+) Hygiene patterns, (+) sun exposure, (+) use of sunscreen (SPF70), (-) Rashes, (-) lesions, (-) itching, (-) dryness, (-) changes in color or texture, (-) changes in hair distribution or texture, (-) nail changes. Lymphatics: (+) lymph node enlargement or tenderness Endocrine: (-) Temperature intolerance or sensitivity to heat or cold, (-) polyuria, (-) polydipsia, (-) glycosuria, (-) weight changes, (-) voice changes, (-) change in glove or shoe size, (-) fatigue. Hematopoietic: (-) Bleeding tendencies, (-) bruising Psychiatric: (-) Suicidal ideation, (-) depression, (-) history of mental illness. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION General: Well developed, well nourished. No acute distress Vital Signs: 111/65, 70, 15, 97.9, Weight 135, BMI 23 HEAD: NCAT NEURO: Cranial Nerves CN I, Olfactory: Tested with common scents – normal CN II: Visual Acuity: Snellen chart 20/40 OS, 20/40 OD 20/40 OU. Near vision is normal. Color discrimination (Ishihara) is normal CN III: Oculomotor Nerve: Instruct the patient to follow the penlight or ophthalmoscope with their eyes without moving their head- normal CN IV: Trochlear Nerve: Instruct the patient to follow the penlight or ophthalmoscope with their eyes without moving their head-normal CN V: Trigeminal Nerve: using a pinprick to test facial sensation and by brushing a wisp of cotton against the lower or lateral cornea to evaluate the corneal reflex-normal CN VI: Abducens: Instruct the patient to follow the penlight or ophthalmoscope with their eyes without moving their head-normal CN VII: Facial: Asymmetry of facial movements is often more obvious during spontaneous conversation, especially when the patient smiles or, if obtunded, grimaces at a noxious stimulus; Hyperacusis, indicating weakness of the stapedius muscle, may be detected with a vibrating tuning fork held next to the ear-normal CN VIII: Vestibulocochlear, acoustic, auditory: Hearing is first tested in each ear by whispering something while occluding the opposite ear. Testing for Nystagmus may be rotary, vertical, or horizontal and may occur spontaneously, with gaze, or with head motion-normal CN IX: Glossopharyngeal: Check for gag reflex by asking the patient to say “ah” or using a tongue blade-normal CN X: Vagus: Check for gag reflex by asking the patient to say “ah” or using a tongue blade-normal CN XI: Spinal Accessory: For the sternocleidomastoid, the patient is asked to turn the head against resistance supplied by the examiner’s hand while the examiner palpates the active muscle (opposite the turned head). For the upper trapezius, the patient is asked to elevate the shoulders against resistance supplied by the examiner-normal CN XII: Hypoglossal: valuated by asking the patient to extend the tongue and inspecting it for atrophy, fasciculation, and weakness (deviation is toward the side of a lesion)-normal Cerebellar: Romberg is negative Finger to Nose is normal Heel-to-shin test is normal Motor: Strength 5/5 in all extremities Pronator drift is not appreciated Sensory: Light touch, deep touch, pinprick: normal DTR: List each reflex tested and result Patellar reflex 2+ bilaterally Biceps reflex 2+ bilaterally Eyes: PERRLA, EOMI. Periorbital structures are normal – no swelling, erythema. Fundoscopic exam reveals healthy vessels, sharp disc margins. No papilledema. Macula appears normal Visual Acuity: OD_ 20/40, OS: 20/40, OU 20/40 EARS: external ears are symmetrical. There is no swelling, redness or tenderness. Mild cerumen bilateral canal. No drainage, swelling, debris, fb TM: pearly. Normal light reflex, No erythema, fluid levels. Nose: External nose is normal – no swelling, tenderness. Nares are patient. Nasal mucosa is pink and moist. No polyps, drainage, swelling Throat: Good dentition. + White patches. The airway is patent. The uvula is midline, mild exudate with + erythema. Tonsils are swollen and red. Neck: Supple, full painless ROM. Negative meningism, -nuchal rigidity; Kernigs and Brudzinski signs are negative. There is no appreciable adenopathy. The thyroid gland is normal in size and is without nodules. +Swelling and tender lymph nodes. Chest: Symmetrical expansion, no crepitus, no tenderness. Lungs: Clear to auscultation with equal breath sounds Cardiac: S1, S1 are normal. There is no rub, murmur or gallop. Normal rate and rhythm Abdomen: The abdomen is soft, non-tender and nondistended. The liver and spleen are non-tender and of normal size. There is no hernia. GU: - S/S Musc/Skel: Full, painless ROM. No swelling, erythema, tenderness Integ: Pink, warm dry. No pallor, jaundice. There are no rashes or lesion ASSESSMENT (DIAGNOSIS) Assessment =Strep Pharyngitis List 2 differential diagnosis 1. Infectious mononucleosis 2. Tonsillitis PLAN Strep Pharyngitis Reduce symptom severity and duration Prevent acute complications such as; otitis media, rheumatic fever, peritonsillar abscess and prevention of spread to others. A physical exam will be done along with a rapid antigen test on your throat, if negative and still suspects strep a throat culture might be done. Treatment includes Penicillin V 500 mg TID for 10days, Ibuprofen and Tylenol to relieve pain and reduce fever. Patient education: 1. Keep your hands clean: cover your mouth when you cough or sneeze and don’t share personal items 2. Gargling with salt water: ¼ tsp of table salt in 8 ounces of warm water 3. Rest, drink fluids and eat soft foods No referrals needed at this time If left untreated or does not resolve follow up with PMD in 7 days. If recurrent infections occur an extended or different antibiotic may be prescribed. Infectious Mononucleosis Physical exam of throat and lymph nodes Check labs (chemistry, monospot and heterophile antibody) Treatment is based on clinical s/s, comfort measures such rest, OTC Tylenol or Motrin for body aches, fever or headaches. Patient Education: 1. Avoid participation in any contact sports for 3-4wks after onset of s/s to prevent trauma 2. Avoid close to close contact with infected individuals 3. Practice excellent hygienic practices 4. Avoids sharing utensils, toothbrushes and drinking glasses 5. S/S usually improve within one to two weeks Referrals depends on if there are any complications such as rupture of spleen, pericarditis, myocarditis, encephalitis. In that case; hematologists, cardiologist, neurologist and surgeon would be referred if needed. Follow up as needed or any concerns Tonsillitis Seek medical help if your child has a sore throat for more than two days, trouble or painful swallowing, weak, starts drooling or trouble breathing Physical exam of throat, neck and lymph nodes Rapid strep test or throat culture Treatment is based on the cause such a virus, then there is no treatment. If its bacterial such as strep then antibiotics will be needed. Patient Education 1. Continue full course of antibiotics 2. Get plenty of rest 3. Drink plenty of fluids 4. Soft foods 5. Warm liquids or cold foods such as popsicles to soothe throat 6. Avoid cigarette smoking or around it to irritate the throat 7. Use humidifier 8. Gargle with saltwater 9. Use lozenge 10. Taking over the counter pain reliever such as acetaminophen Referrals depends on the severity of the illness, if needed tonsillectomy Follow up as needed or if any concerns Rationale #1: My rationale for choosing Strep Pharyngitis is because he c/o throat pain, painful swallowing and fever. He had positive swollen lymph nodes and had strep throat as child multiple times. Rationale #2: My rationale for choosing Infectious Mononucleosis is because the patient c/o fever, sore throat and there are positive swollen lymph nodes noted, which are prominent in Mono. Rationale # 3: My rationale for choosing tonsillitis is because the patient complained of sore throat with red swollen tonsils. He also c/o fever with white patches on his tonsils and difficulty swallowing when he eats or drinks. His c/o are similar to what the symptoms of tonsillitis are. Reference: Aronson, M., & Auwaerter, P. (2018). Infectious mononucleosis. In J. Mitty (Ed.), UpToDate. Retrieved September 16, 2018, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/infectious-mononucleosis?search=infectious %20mononucleosis&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=de fault&display_rank=1 Busaba, N., & Doron, S. (2018). Tonsillectomy in adults: Indications. In L. Kunins (Ed.), UpToDate. Retrieved September 16, 2018, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/tonsillectomy-in-adults-indications? search=tonsillitis&source=search_result&selectedTitle=2~57&usage_type=defaul t&display_rank=2 Pichichero, M., (2018). Treatment and prevention of streptococcal pharyngitis. In S. Bond (Ed.), UpToDate. Retrieved September 16, 2018, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/treatment-and-prevention-of-streptococcalpharyngitis?search=strep %20pharyngitis&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~96&usage_type=default &display_rank=1#H2187629545