Scarlet Fever
advertisement

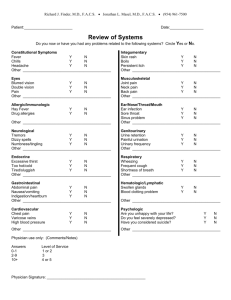
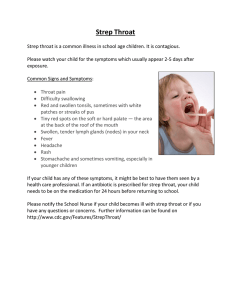
Infectious illness caused by a group A streptococcus (GAS) bacterium that affects the lower respiratory system Develops from strep throat Also known as "scarlatina" Agent: Streptococcus pyogenes Gram staining: positive (+) Morphology: chained cocci (circles) Endospores: none Toxins › Streptolysin O › Streptolysin S › Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A (and C) aerobic non-motile Outbreak: › Most recent was on 2008-2009 › Lasted a period of 42 weeks › Reported almost 400 cases by the Health Protection Agency Most commonly seen on: › 5-12 y/o children › late winter › early summer Direct contact with mucus from nose Fluid from nose Infected saliva Begins with a rash that shows red bumps The rash lasts about 2-7 days After the rash is gone the skin on the tip of the fingers and toes peel. A flush face with a pale area around the face. A red and sore throat that can have white or yellow patches . Fevers of 101 degrees or higher. Swollen glands in the neck. Check for the rash Swab the back of the throat Check the tongue and tonsils Use of antibiotics such as: › Penicillin › Erythromycin › Ibuprofen for symptom relief Avoid the use aspirin in children younger than 16 Wash your hands often and Avoid sharing › › › › eating utensils Linens Towels other personal items. There is no vaccine to prevent strep throat or scarlet fever. Children with scarlet fever or strep throat should stay home at least for 24 hours after starting antibiotics. http://kidshealth.org/parent/infections/bacterial_viral/scarlet _fever.html http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dbmd/diseaseinfo/scarletfever_ g.htm http://scienceblogs.com/aetiology/2011/07/06/scarlet-feverin-hong-kong/ http://www.cdc.gov/features/scarletfever/ http://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/article-1146944/Casesscarlet-fever-reach-highest-level-decade.html http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/s/scarlet_fever/stats.htm