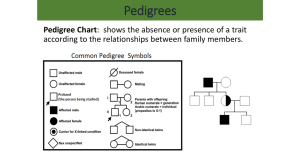
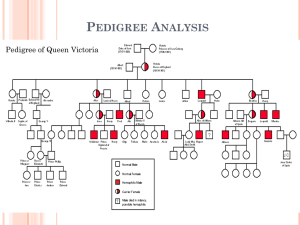
Genetic Disorder Chart CP Biology Disorder Autosomal or Sex-linked Dominant, Recessive or Codominant Description of Symptoms Albinism autosomal recessive Albinism is a rare group of genetic disorders that cause the skin, hair, or eyes to have little or no color. Cystic Fibrosis Autosomal Recissive Defective blood clotting factor VIII recessive on the X chromosome Galactosemia autosomal recessive Galactosemia refers to a group of inherited disorders that impair the body's ability to process and produce energy from a sugar called galactose. Phenylketonuria (PKU) Autosomal Recessive Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Tay-Sachs disease Autosomal Recessive The body lacks hexosaminidase A Achondroplasia Autosomal Dominant Achondroplasia is a disorder of bone growth that prevents the changing of cartilage Huntington’s disease Autosmal Dominant Production of an inhibitor of brain cell metabolism Hypercholesterolema Autosomal Dominant Hypercholesterolemia is the term used to refer to a high blood cholesterol level. Sickle Cell disease Autosomal Recissive Abnormal hemoglobin molecule Colorblindness sex-linked recessive olor blindness is inherited as a recessive trait on the X chromosome. This is known in genetics as X-linked recessive inheritance. Hemophilia Sex-linked Recissive Defective blood clotting factor VIII recessive on the X chromosome Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Sex-linked Recessive Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy that primarily affects boys. Down Syndrome autosomal Recissive Down syndrome is a condition in which a child is born with an extra copy of their 21st chromosome Turners Syndrome sex-linked neither Usually due to a paternal error in sex chromosome transmission. Klinefelters Syndrome Sex-linked Neither Extra X chromosome in males