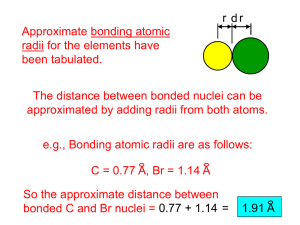
UNIT 2_MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS_SHORTQUESTIONS and TRUE and FALSE_With Answers MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1.1 The __________ quantum number defines the shape of an orbital. A) spin B) magnetic C) principal D) azimuthal E) psi 1.2 There are __________ orbitals in the third shell. A) 25 B) 4 C) 9 D) 16 E) 1 1.3 The __________ subshell contains only one orbital. A) 5d B) 6f C) 4s D) 3d E) 1p 1.4 There are __________ orbitals in the second shell. A) 1 B) 2 C) 4 D) 8 E) 9 1.5 The azimuthal quantum number is 3 in __________ orbitals. A) s B) p C) d D) f E) a 1.6 The n = 1 shell contains __________ p orbitals. All the other shells contain __________ p orbitals. A) 3, 6 B) 0, 3 C) 6, 2 D) 3, 3 E) 0, 6 1.7 __________-orbitals are spherically symmetrical. A) s B) p C) d D) f E) g 1.8 Each p-subshell can accommodate a maximum of __________ electrons. A) 6 B) 2 C) 10 D) 3 E) 5 1.9 The electron configuration of a ground-state Ag atom is __________. A) [Ar]4s2 4d9 B) [Kr]5s14d10 C) [Kr]5s23d9 D) [Ar]4s14d10 E) [Kr]5s2 4d10 1.10 The ground state electron configuration for Zn is __________. A) [Kr]4s23d10 B) [Ar]4s23d10 C) [Ar]4s13d10 D) [Ar]3s23d10 E) [Kr]3s23d10 1.11 There are __________ unpaired electrons in a ground state phosphorus atom. A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 E) 4 1.12 Which is the correct ground-state electron configuration for silver __________ ? A) [Kr]5s2 4d9 B) [Kr]5s14d10 C) [Kr]5s2 4d10 D) [Xe]5s2 4d9 E) [Xe]5s14d10 1.13 What is the correct ground-state electron configuration for molybdenum __________? A) [Kr]5s14d10 B) [Kr]5s2 4d4 C) [Kr]5s14d5 D) [Kr]5s2 4d5 E) [Kr]5s2 4d9 1.14 All of the __________ have a valence shell electron configuration ns1 . A) noble gases B) halogens C) chalcogens D) alkali metals E) alkaline earth metals 1.15 In a px orbital, the subscript x denotes the __________ of the electron. A) energy B) spin of the electrons C) probability of the shell D) size of the orbital E) axis along which the orbital is aligned 1.16 116) Which electron configuration represents a violation of the Pauli exclusion principle? 1.17 Which one of the following orbitals can hold two electrons? A) 2px B) 3s C) 4dxy D) all of the above E) none of the above 1.18 The ground state electron configuration of Fe is __________. A) 1s2 2s23s23p63d6 B) 1s2 2s2 2p63s23p63d6 4s2 C) 1s2 2s2 2p63s23p6 4s2 D) 1s2 2s2 2p63s23p6 4s2 4d6 E) 1s2 2s23s23p10 1.19 The ground state electron configuration of Ga is __________. A) 1s2 2s23s23p63d10 4s2 4p1 B) 1s2 2s2 2p63s23p6 4s2 4d10 4p1 C) 1s2 2s2 2p63s23p63d10 4s2 4p1 D) 1s2 2s2 2p63s23p63d10 4s2 4d1 E) [Ar]4s23d11 1.20 The ground-state electron configuration of the element __________ is [Kr]5s14d5. A) Nb B) Mo C) Cr D) Mn E) Tc 1.21 Which one of the following configurations depicts an excited oxygen atom? A) 1s2 2s2 2p2 B) 1s2 2s2 2p23s2 C) 1s2 2s2 2p1 D) 1s2 2s2 2p4 E) [He]2s2 2p4 1.22 __________ is credited with developing the concept of atomic numbers. A) Dmitri Mendeleev B) Lothar Meyer C) Henry Moseley D) Ernest Rutherford E) Michael Faraday 1.23 Elements in the modern version of the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing __________. A) oxidation number B) atomic mass C) average atomic mass D) atomic number E) number of isotopes 1.24 The first ionization energies of the elements __________ as you go from left to right across a period of the 1.25 periodic table, and __________ as you go from the bottom to the top of a group in the table. A) increase, increase B) increase, decrease C) decrease, increase D) decrease, decrease E) are completely unpredictable 1.26 The __________ have the most negative electron affinities. A) alkaline earth metals B) alkali metals C) halogens D) transition metals E) chalcogens 1.27 In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first ionization energy __________. A) decreases, decreasingly, increases B) increases, increasingly, decreases C) increases, increasingly, increases D) decreases, increasingly, increases E) decreases, increasingly, decreases 1.28 Metals can be __________ at room temperature. A) liquid only B) solid only C) solid or liquid D) solid, liquid, or gas E) liquid or gas 1.29 Most of the elements on the periodic table are __________. A) gases B) nonmetals C) metalloids D) liquids E) metals 1.30 Na reacts with element X to form an ionic compound with the formula Na3X . Ca will react with X to form __________. A) CaX2 B) CaX C) Ca2X3 D) Ca3X2 E) Ca3X 1.31 The element(s) __________ could be used to produce a red or crimson color in fireworks. A) Mg or Ba B) Sr C) Ca, Sr, or Li D) Ba E) Na or K 1.32 Oxides of the active metals combine with water to form __________. A) metal hydroxides B) metal hydrides C) hydrogen gas D) oxygen gas E) water and a salt 1.33 Oxides of the active metals combine with acid to form __________. A) Hydrogen gas B) metal hydrides C) water and a salt D) oxygen gas E) metal hydroxides 1.34 An alkaline earth metal forms a compound with oxygen with the formula __________. (The symbol M represents any one of the alkaline earth metals.) A) MO B) M2O C) MO2 D) M2O2 E) MO3 1.35 Element X reacts with chlorine to form a compound with the formula XCl2 . The oxide of element X is basic. Element X is __________. A) Rb B) Ca C) Al D) P E) H 1.36 In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties? A) O, S, Se B) N, O, F C) Na, Mg, K D) S, Se, Si E) Ne, Na, Mg 1.37 Which element would be expected to have chemical and physical properties closest to those of fluorine? A) S B) Fe C) Ne D) O E) Cl 1.38 Atomic radius generally increases as we move __________. A) down a group and from right to left across a period B) up a group and from left to right across a period C) down a group and from left to right across a period D) up a group and from right to left across a period E) down a group; the period position has no effect 1.39 Of the following, which gives the correct order for atomic radius for Mg, Na, P, Si and Ar? A) Mg > Na > P > Si > Ar B) Ar > Si > P > Na > Mg C) Si > P > Ar > Na > Mg D) Na > Mg > Si > P > Ar E) Ar > P > Si > Mg > Na 1.40 Screening by the valence electrons in atoms is __________. A) less efficient than that by core electrons B) more efficient than that by core electrons C) essentially identical to that by core electrons D) responsible for a general increase in atomic radius going across a period E) both more efficient than that by core electrons and responsible for a general increase in atomic radius going across a period 1.41 The atomic radius of main-group elements generally increases down a group because __________. A) effective nuclear charge increases down a group B) effective nuclear charge decreases down a group C) effective nuclear charge zigzags down a group D) the principal quantum number of the valence orbitals increases E) both effective nuclear charge increases down a group and the principal quantum number of the valence orbitals increases 1.42 Which one of the following atoms has the largest radius? A) O B) F C) S D) Cl E) Ne 1.43 Which one of the following atoms has the largest radius? A) Sr B) Ca C) K D) Rb E) Y 1.44 Which one of the following has the smallest radius? A) Na B) Cl C) Fe D) P E) Br 1.45 Which one of the following atoms has the largest radius? A) I B) Co C) Ba D) Sr E) Ca 1.46 Which one of the following elements has the largest atomic radius? A) Se B) As C) S D) Sb E) Te 1.47 Which one of the following elements has the largest atomic radius? A) O B) F C) Al D) P E) B 1.48 Which of the following correctly lists the five atoms in order of increasing size (smallest to largest)? A) F < K < Ge < Br < Rb B) F < Ge < Br < K < Rb C) F < K < Br < Ge < Rb D) F < Br < Ge < K < Rb E) F < Br < Ge < Rb < K 1.49 Of the choices below, which gives the order for first ionization energies? A) Cl > S > Al > Ar > Si B) Ar > Cl > S > Si > Al C) Al > Si > S > Cl > Ar D) Cl > S > Al > Si > Ar E) S > Si > Cl > Al > Ar 1.50 Of the following atoms, which has the largest first ionization energy? A) Br B) O C) C D) P E) I 1.51 Which equation correctly represents the first ionization of aluminum? A) Al- (g) → Al (g) + eB) Al (g) → Al- (g) + eC) Al (g) + e- → Al- (g) D) Al (g) → Al+ (g) + eE) Al+ (g) + e- → Al (g) 1.52 Which ion below has the largest radius? A) ClB) K+ C) BrD) F E) Na+ 1.53 The ion with the smallest diameter is __________. A) BrB) ClC) I D)F E) O21.54 Of the following elements, __________ has the most negative electron affinity. A) Na B) Li C) Be D) N E) F 1.55 Of the following elements, __________ has the most negative electron affinity. A) S B) Cl C) Se D) Br E) I 1.56 Of the following elements, __________ has the most negative electron affinity. A) P B) Al C) Si D) Cl E) B 1.57 Chlorine is much more apt to exist as an anion than is sodium. This is because __________. A) chlorine is bigger than sodium B) chlorine has a greater ionization energy than sodium does C) chlorine has a greater electron affinity than sodium does D) chlorine is a gas and sodium is a solid E) chlorine is more metallic than sodium 1.58 Sodium is much more apt to exist as a cation than is chlorine. This is because __________. A) chlorine is a gas and sodium is a solid B) chlorine has a greater electron affinity than sodium does C) chlorine is bigger than sodium D) chlorine has a greater ionization energy than sodium does E) chlorine is more metallic than sodium 1.59 Which equation correctly represents the electron affinity of calcium? A) Ca (g) + e- → Ca- (g) B) Ca (g) → Ca+ (g) + eC) Ca (g) → Ca- (g) + eD) Ca- (g) → Ca (g) + eE) Ca+ (g) + e- → Ca (g) 2- SHORT QUESTIONS 2.1 List seven nonmetals that exist as diatomic molecules in their elemental forms. 2.2 What are the elements called that are located between the metals and non-metalsa? 2.3 Which metal is a liquid at room temperature? 2.4 [Xe]6s2 is the electron configuration for __________? 2.5 All of the group VIA elements are solids except __________? 2.6 As successive electrons are removed from an element, the ionization energy __________. 2.7 Which noble gas has the highest first ionization energy? 2.8 When electrons are removed from a lithium atom they are removed first from which orbital __________? 2.9 An added electron to the element bromine goes into which orbital __________? True/False 3.1 Electron affinity measures how easy an atom gains an electron. 3.2 The effective nuclear charge acting on an electron is larger than the actual nuclear charge. 3.3 The atomic radius of iodine is one-half the distance separating the iodine nuclei. 3.4 A group of ions all containing the same number of electrons constitute an isoelectronic series. 3.5 Cadmium preferentially binds to carbonic anhydrase, displacing zinc.