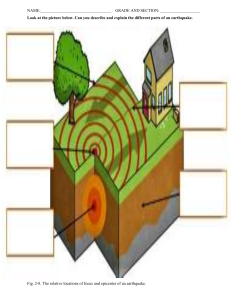
NAME: Elgen Mae G. Puebla Section: NST001 - C01 DISASTER PREPAREDNESS ACTIVITY Objective 1: Identify dangerous zones and safe areas during earthquakes Activity 1. You will be ask the following questions: a. What would you do if an earthquake occurred at this moment? b. Where would you go? The most important thing to do during an earthquake is to remain CALM. Make no moves or take no action without thinking about the possible consequences. Do not run outside or to other rooms during shaking; instead go find a table near your place for you are much safer when you are under from it. After counting 60 seconds or if shaking ends, go outside to an open area without any buildings, streetlights or any utility wires. If you are INDOORS -- STAY THERE! Get under a desk or table and hang on to it (Drop, Cover, and Hold on!) or move into a hallway or against an inside wall GET OUT of the kitchen, which is a dangerous place (things can fall on you). STAY CLEAR of windows, fireplaces, and heavy furniture or appliances. DON'T run downstairs or rush outside while the building is shaking or while there is danger of falling and hurting yourself or being hit by falling glass or debris. 2. Below is the K-W-L chart. This K-W-L chart is about earthquake safety. Under the ‘K’ write what you KNOW about earthquake safety. When you are finished, under the ‘W’ write what you WANT to know. KNOW What do you know? WANT What do you want to know? (BEFORE AN EARTHQUAKE) 1. Remove potential earthquake hazards in the home and workplace. 2. Supplies of food and water, flashlight, a first-aid kit and a battery-operated radio should be set aside for use in emergencies. 3. One or more family members should have a working knowledge of first-aid measures. 4. All family members How strong does an earthquake have to be to do damage? LEARNED What have you learned? Earthquake cannot be predicted, so as an individual we must know the safety precautionary measures whenever an earthquake occurs. It is better to know should know what to do to avoid injury and panic. They should know how to turn off the electricity, water and gas. Do and don'ts during earthquake? (DURING AN EARTHQUAKE) 1. The most important thing to do during an earthquake is to remain CALM. 2. Make no moves or take no action without thinking about the possible consequences. 3. If you are inside stay there. Stand in a doorway or crouch under a desk or table, away from windows or glass fixtures. 4. If you are outside, stay there. Stay away from objects such as light poles, buildings, trees and telephone and electric wires, which could fall and injure you. 5. If you are in an automobile, drive away from underpasses/overpasses, and stop in the safest place possible and stay there. What are the safety measures to be followed during an earthquake? the possible hazards in our home or community for us to be aware of the possible risk that might happen in the future. The probability that hazard interacts with vulnerability to different consequences is called risk. (AFTER AN EARTHQUAKE) 1. After an earthquake check for injuries in your family and in the neighborhood. 2. Evacuate the building as soon as the shaking stops. 3. Check for safety-hazards gas, water sewage breaks; downed power lines and electrical short circuits, damaged and weakened buildings and foundations, fires and fire hazards. 4. Turn off appropriate utilities. 5. Do not use the telephone except in extreme emergency. 6. Wear shoes and protective clothing, for example, hard hats and gloves, to avoid injuries while clearing debris. 7. Keep battery-operated radios and listen for emergency bulletins. 8. If electrical power is off for any length of time use the foods in your refrigerator and freezer before they spoil. Canned and dry foods should be saved for last. 9. Co-operate with all public safety and relief organizations. 10. Be prepared for additional earthquake shocks. Awareness in hazard How can we and its risk is a save our lives valuable input in the in earthquake? preparedness stage where the capability of the at-risk community or school or anywhere must know by the individuals. How can you be prepared for an earthquake? 3. You will have a group discussion about what items would be potential hazards during an earthquake and most earthquake-related injuries. After the discussions, you will answer the following questions. A.) What are some other hazards that you know of? Asbestos, Ergonomical hazards Slips, trips, and falls Fire, Noise Forklifts Confined spaces Lockout/tagout Electrical – Extension cords, Chemicals, Falls, Fires, Carbon monoxide, Choking, Cuts, Poisoning, Strangling, Drowning and Burn B.) What are some hazards in this classroom at home? Mechanical – shearing, cutting punctures etc. o Physical – manual handling, slips, trips and falls etc. o Chemical – acids, corrosive agents and harmful substances. o Environmental – weather, noise, heat etc. o Biological – Weil’s disease, Leptospirosis, Legionella etc. Organizational – work pressures, bullying, management instruction o o o o Falls o Fires Carbon monoxide Choking o o Cuts o Poisoning o Strangling o Drowning o Burns 4. You will analyze the following photographs which areas are safe and which areas are dangerous. Color it with green if it is a safe area and red if it is dangerous. Picture 2 Picture 4 5. To deepen your understanding regarding safe areas during earthquakes, look at the illustration below and color the areas that are safe in green and hazards in red.