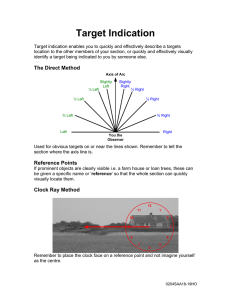
Neurological Disorders of Voice Adduction or Abduction Problems Hypoadducti • Myasthenia gravis on • Parkinsonism • Peripheral nerve paresis/paralysis • Shy-Drager • Supranuclear palsy Hyperadducti on • Adductor spasmatic dysphonia • Huntington’s disease • Pseudobulbar palsy Phonatory Instability Short Term ( jitter & shimmer) • Most neurological disorders Long Term (tremor) • Essential tremor • Parkinsonism • ALS/MND Phonatory Incoordination/Voiced-Voiceless Distinction Abductor Spasmodic Dysphonia Mixed Disorders Miscellaneous Disorders • Cerebellar ataxia • Multiple sclerosis • Tourette syndrome Parkinson’s Disease • Perceptually • Monopitch • Breathiness • Roughness • Reduced loudness • Visually • VF may appear normal or bowed • Laryngeal tremor • Abnormal phase closure + phase symmetry • Management • Lee Silverman Voice Treatment • Myasthenia Perceptually Gravis • Breathy/weak • Muscle weakness on prolonged sounds • Other: stridor, reduced vocal loudness, monotone voice, hypernasality + tremor • Visually • Fluctuating impairment of VF motility (reduction in phase closure + vibratory amplitude) • Management • Pharmacological treatments to improve muscles’ ability to contract • Perceptually Unilateral Vocal Fold • Aphonia through Paralysis to normal voicing • Breathy, rough, strained • Visually • Affected VF weakened or bowed • Passive vibration due to flow of exhaled air but does NOT match normal VF • Management • Wait and see (6-9 months) • Behavioural voice therapy • Surgery = medialisation of VF, reinnervation to RLN • Bilateral Perceptually Vocal Fold • Normal voicing Paralysis through to severe breathiness/ aphonia • Inspiratory stridor if in adducted position • Visually • VF floppy or bowed • Arytenoid cartilage on both sides does not abduct or adduct • Management • Wait and see (6-9 months) if no airway obstruction • Tracheostomy if airway obstructed • Surgery = lateralisation of VF to widen glottis • Perceptually • Weak + breathy (Abductor SD) Spasmodic Dysphonia • Strain (Adductor SD) • Voice stoppages during sustained vowel production and connected speech • Delayed onset of voicing • Visually • Abductor SD = moves VFs in open position when should be closed • Adductor SD = moved VFs in closed position when should be open • Management • Botox injected ALS/MND • Perceptually • Weak voice, roughness, strained, hypernasality • Visually • Incomplete vocal fold closure • Management • No effective treatment • AAC devices