1.1b Equipment B
advertisement

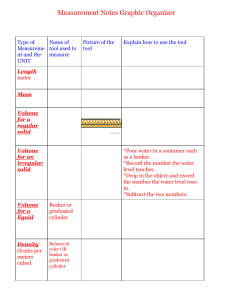
Unit 1 eMAPS Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B Equipment B You will need to get out of your seat at times to find the names, locations and sizes of the equipment shown. Refer back to Equipment A when necessary 1. a) The piece of equipment to the left is a ____________________ ______________________. b) What sizes of this equipment are available in our classroom? (Look on the shelves under the back counter on BOTH the left hand and right hand sides) c) What do you think this piece of equipment is used for? (Make your best guess ; circle all that apply) (A) holding liquids (B) heating liquids (C) measuring liquids (D) making solutions of a precise and accurate volume (E) mixing liquids (F) providing a location for a reaction to occur (G) holding solids d) When using the ________________________ _____________________ shown above, you would measure to the _________ position to get the correct number of sig figs. (A) 10’s 2. A (B) 1’s (C) 1 ’s 10 (D) 1 ’s 100 ________________________ _____________________ gets its name because it is a _______________________ that has GRADUATIONS (markings that show give the shape particular volume measurements). Unit 1 eMAPS 3. a) Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B ______________________ ________________s are relatively good at measuring liquids accurately and precisely. That is because their ________________________ (markings that show the volume measurements) have been ____________________ carefully. In other words, someone took the time to make sure that the 1 mL mark actually corresponds to 1 mL, that the 2 mL mark corresponds to 2 mL etc. (Refer back to Equipment A if you can’t remember the word.) 4. a) However, a ______________________ ________________ is generally not as precise as a ______________________ or a __________________ . This is because _ _____________________ ____________________s are WIDER. If a piece of glassware is NARROWER, adding a small volume of liquid will cause the liquid level level to rise A b) LOT: If a piece of glassware is WIDER, adding a small volume of liquid will cause the liquid level to rise only A LITTLE: So…if 3 people use the narrow cylinder to measure out 8 mL, the actual volumes they get are more likely to be very, very close to 8 mL, since by adding an extra drop, it would no longer look like 8 mL and they would reject that sample. Therefore their actual volumes will be closer together. When results are closer together that makes them more _______________________. Unit 1 eMAPS 4. c) Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B If the three people used the wider cylinder, one measurement might be a couple drops less than 8 mL (say 7.9 mL) and another a couple drops more than 8 mL (say 8.1 mL) but the water level would look almost exactly the same. So the 3 results would be further from each other, making the measurements less __________________. d) In general things glassware that is narrower / wider is better for measuring, because they will make the results more REPRODUCIBLE (i.e. the results will be more _______________). 5. This piece of equipment, that was used in question 4 is called a/n ____________________ ____________________. We use it to deliver small amounts of liquid. 6. The ________________________ ________________________ has no _gr______________________ (measurement markings) so it is only used to deliver approximate volumes of liquid. 7. In equipment A we saw VOLUMETRIC __________________________s. Glassware that has only 1 measurement marking is described as being ______________________________. 8. a) What is the name of this piece of equipment? ____________________________ ______________ b) How many measurement markings does it have on it? ___________________ This is why the flask is called ______________________. If it had many measurement markings it would be called ______________________. Unit 1 eMAPS 8. c) d) Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B What size _______________________ _____________ is available in our classroom? _________________________ ___________________s are used to exclusively to make solutions. Their extremely NARROW neck makes them awkward to use for other purposes. But…the NARROW neck means that you can make a solution of a volume that is very ______________________. _______________________ ________________s have also been very well ________________________ so that their measurement mark is very, very close to the actual volume. This is what makes volumetric flasks very ____________________. 9. a) What is the name of this piece of equipment? ________________________ ____________ ______________________ Zero adjustment knob Zero mark Pan hanger b) Since It has ____________ beams, this is why it is called a _______________________ beam give the number balance. If it had only 3 beams it would be called a _________________ _________ ____________________. Unit 1 eMAPS 9. c) Section 1.1 Equipment Before you begin to use the 1.1.b Equipment B __________________________ ___________ ____________________ , you must ZERO it. Here are the steps to zeroing the balance: ① Make sure the _________ _________________ TOP / BOTTOM hook. is hung from the circle correct response ② Make sure the four ___________________ are all set to ____________________. give the number i.e. Slide them all the way to the LEFT / RIGHT , circle correct response as shown in the picture. ③ Make the __________________ line up with the ____________ ____________ by using the ____________ ` ___________________________ ____________ Turn the zero knob CLOCKWISE / COUNTER-CLOCKWISE , to make the pointer move DOWN. Turn the zero knob pointer move UP. CLOCKWISE / COUNTER-CLOCKWISE , to make the Unit 1 eMAPS 9. d) Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B Go get a _____________________ ___________ __________________ from the cart at the back of the room. On your own, or in a group of 2 or 3, correctly zero the balance. If you work in a group, you MUST make sure EACH PERSON could do the correct steps…there will be a HANDS-ON PRACTICAL QUIZ on this skill! Have Ms. Spence come over and check your zeroing. Get her signature here: e) Use your balance and/or the following picture to determine what the smallest division (graduation) is on the _____________________ _________ ___________________ The smallest division is… (A) 1 g (B) 0.1 g (C) 0.01 g (D) 0.001 g … therefore your measurements should be recorded to the ________ position (A) 1 g f) (B) 0.1 g (C) 0.01 g (D) 0.001 g Go and get a 250 mL beaker. Use the sliders to find the mass of the beaker. NOTE: The sliders must “CLICK” into position! (except the smallest one) Record the mass here: (remember, measurements must have units!) mass of 250 mL beaker = How many sig figs are in your measurement? __________ Have Ms. Spence check your measurement and sign here: Unit 1 eMAPS 9. g) Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B Keep your beaker…you will need it for question 10. If you have to save it for next class label it with masking tape (on the small table at the front) with your name on it. Put it on a side counter where you can find it easily. Before you put the balance away, hang the PAN HANGER ON THE BOTTOM HOOK, and give the ZERO KNOB A FEW TURNS. This will un-zero the balance making it ready for the next person to practice zeroing. h) Put the balance away on the cart. Alternate the direction of the balances so that they can all fit on the cart. YES! 10. a) b) c) NO! Go and get an _______________________ _______________________ from the counter at the front left of the room. Carry it IN ITS BOX to your desk. Turn on the _____________________ ____________________. • Check to see that the unit displayed is grams (g). If it is not, call Ms. Spence over to help. • Check to see that the display reads 0.00 . If it does not, press the button that says “ZERO” or “TARE”. Measure the mass of the beaker that you kept from question 9. Record the measurement here, using 9(f) as a model for how to record your result. How many sig figs are in your measurement? ___________ Have Ms. Spence sign here to make sure you are recording your measurements correctly. d) Compare your measurements from 10(c) and 9(f). Which balance gives you MORE SIGNIFICANT FIGURES? e) Which balance will give you results that are more PRECISE? Unit 1 eMAPS 10. f) Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B If you answered the ____________________________________ balance for 10(e) you are correct! Ex. Say the mass of the beaker was actually 120.00000 g A measurement of 120.00 could be 120.01 g or 119.99 g 1 because the 0.01 ( 100 ’s) digit is uncertain. Therefore, different measurements for the beaker on the _____________________ ________________ 𝟏𝟏 can be off by 𝟏𝟏𝟏𝟏𝟏𝟏 of a gram. A measurement of 120.000 could be 120.001 g or 1 119.999 g because the 0.001 ( 1000’s) digit is uncertain. Therefore, different measurements for the beaker on the _____________________ ____________ ________________ 1 can be off by only 1000 of a gram. This makes results from the _____________________ ____________ ________________ more reproducible (more likely to be closer to each other) and hence more accurate / precise . circle the correct answer g) In general, devices that measure to MORE DECIMAL PLACES are MORE _______________ because repeated measurements from those devices will be closer to each other than measurements from a device with fewer decimal places. h) With the beaker on the balance, press the TARE / ZERO button. What happens to the mass reading? This will allow you to measure the mass of something IN the beaker, without having to subtract the mass of the beaker. h) Take the beaker OFF the balance and place it on the desk. Add water to the beaker until it reaches the 100 mL line. Be sure the beaker is ON THE DESK Be sure you read the volume at the BOTTOM OF THE MENISCUS Be sure your EYE is LEVEL with the bottom of the meniscus See picture on next page Unit 1 eMAPS Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B 10. h) i) Move the beaker back onto the balance. Record the mass of the water here: Have you recorded your mass correctly? Check back with 10(c) and 9(f). How many sig figs are in your measurement? __________ Have Ms. Spence sign here to make sure you are recording your measurements correctly. j) The density of water at 21°C (room temperature) is 0.998 grams per millilitre or 0.998 g 1 mL We can write the density of water upside down: 1 mL 0.998 g Plug your mass of water into the following UNIT CONVERSION calculation: ___________ g × 1 mL 0.998 g = _____________ mL Notice how the grams cancel out in the unit conversion calculation. One of the main skills in the next unit of study will be unit conversion. Unit 1 eMAPS k) Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B Finding volume of a liquid by measuring its mass and finding its density is one of the most accurate ways of finding volume. So we will assume your volume from 10 (j) is very close to the true value (i.e. the calculated volume is very ________________________). In 10 (h) you measured out 100 mL of water. Your measuring tool was the beaker. Use your result from 10 (j) as the “true” volume of water. How accurate was the beaker? l) In general beakers are NOT very accurate. Give TWO reasons why they are not. ① _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ② _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 11. Extra Practice reading a quadruple beam balance a) (i) mass: _____________________________ (ii) number of decimal places __________ (iii) number of sig figs __________ (iv) circle the uncertain digit in your measurement Unit 1 eMAPS Section 1.1 Equipment 1.1.b Equipment B 11. b) (i) mass: _____________________________ (ii) number of decimal places __________ (iii) number of sig figs __________ (iv) circle the uncertain digit in your measurement 11. c) 40 (i) mass: ______________ (iii) number of sig figs __________ 12. Label each of the pieces of equipment: 200 (ii) number of decimal places __________ (iv) circle the uncertain digit