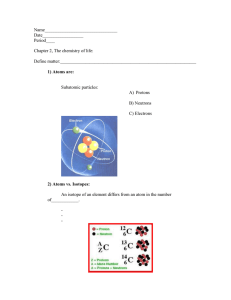
Covalent Bonds • Covalent bonds form between two non-metals. Groups 14-17 on the Periodic Table • Covalent bonds are formed when atoms SHARE electrons. • Both atoms need to gain electrons to become stable, so they share the electrons they have. • Atoms can share more than one pair of electrons to create double and triple bonds. Covalent Bonds Each Hydrogen atom wants to gain one electron to achieve stability. Covalent Bonds Chlorine Molecule It is a single bonding pair so it is called a single covalent bond. The compound is now called a molecule. Cl Cl Cl2 Covalent Bonds How will oxygen bond? Covalent Bonds Two bonding pairs, making a double bond. The double bond can be shown as two dashes O O O2 Covalent Bonds • Elements can share up to three pairs of electrons. electrons). (6 total Single Bond (2e) Double Bond (4e) Triple Bond (6e) Covalent Bonds WORK GROUP!! Draw a diagram to show the bonding in : Iodine I2 Oxygen O2 Nitrogen N2 Chlorine Cl2 Sulfur S8 Phosphorus P4 Ionic Bonds • Ionic bonds are formed between metals and nonmetals. • Ionic bonds are formed between oppositely charged atoms (ions). • Ionic bonds are formed by the transfer of electrons. • One atom loses (gives away) electrons. • One atom gains (receives) electrons. Ionic Bonds Atoms with 4 or less valence electrons want to LOSE (give away) their valence electrons. [Groups 1, 2, 13, 14] Atoms with 4 or more valence electrons want to GAIN (receive) more electrons to satisfy their octet. [Groups 14, 15, 16, 17] Ionic vs. Covalent Bonds Ionic Bonds • Form when electrons are transferred between atoms. • Form between a metal and a non-metal. Covalent Bonds • Form when electrons are shared between atoms. • Form between two non-metals.