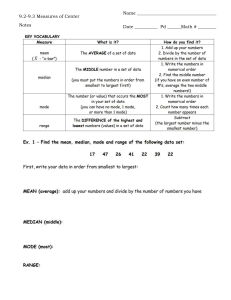
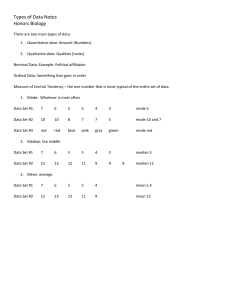
Measures of Central Tendency New Symbols and Terminology • The symbol S is the Greek letter “S” and is called sigma • This symbol means to sum (add) • You will see it used in notations such as SX. This is pronounced as the “sum of X” and means to find the sum of the X scores • x̅ (X-bar) is the symbol for the mean • Beginning with this module, we will be using common statistical formulas. In them, we use X as the generic symbol for a score. When a formula says to do something to X, it means to do it to all of the scores you are calling X. 3-2 Central Tendency • Measures of central tendency answer the question: • “Are the scores generally high scores or generally low scores?” 3-3 What is Central Tendency? • A measure of central tendency is a statistic summarizing the location of a distribution on a variable • It indicates where the center of the distribution tends to be located 3-4 The Mode • The mode is the score having the highest frequency in the data • The mode is used to describe central tendency when the scores reflect a nominal scale of measurement 3-5 Unimodal Distributions When a polygon has one hump (such as on the normal curve) the distribution is called unimodal. 3-6 Bimodal Distributions When a distribution has two scores tied for the most frequently occurring score, it is called bimodal. 3-7 The Median • The median is the score at the 50th percentile • The median is used to summarize ordinal or highly skewed interval or ratio scores 3-8 Determining the Median • When data are normally distributed, the median is the same score as the mode. • The symbol for the median is Mdn. • Use the median for ordinal data or when you have interval or ratio scores in a very skewed distribution. 3-9 Determining the Median When data are normally distributed, the median is the same score as the mode. When data are not normally distributed: 1. 2. 3. 4. Arrange the scores from lowest to highest. Determine N. If N is an odd number, the median is the score in the middle position. If N is an even number, the median is the average of the two scores in the middle. 3 - 10 The Mean • The mean is the score located at the exact mathematical center of a distribution • The mean is used to summarize interval or ratio data in situations when the distribution is symmetrical and unimodal 3 - 11 Computing a Sample Mean The formula for the sample mean is SX X N 3 - 12 Comparing the Mean, Median, and Mode On a perfect normal distribution, all three measures of central tendency are located at the same score. 3 - 13 Central Tendency and Skewed Distributions 3 - 14