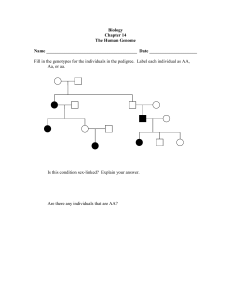
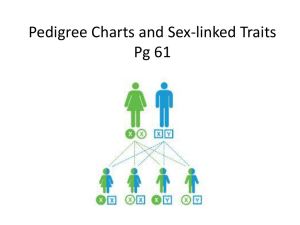
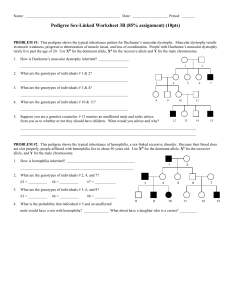
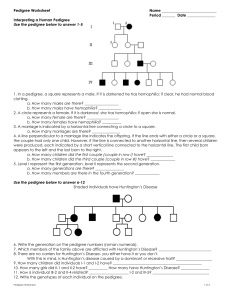
NAME ____________________ HONORS BIO: COMPLEX INHERITANCE & HUMAN HEREDITY REVIEW SHEET 1. Know all the vocabulary associated with this chapter. 2. For the following, define each and give examples: Incomplete dominance, co-dominance, polygenic traits, traits controlled by multiple alleles, epistasis, pleiotropy 7. What are the two sex chromosomes? Describe the shape of each. 8. What is the probability of having a female offspring? Show a cross in a Punnett square illustrating this. 9. What is sex linkage? Give examples of sex-linked traits. 10. What are karyotypes? What do they show? 11. Explain non-disjunction. During what stage of meiosis can it occur? Name some disorders caused by this. 12. What is another name for trisomy 21? Describe some of their characteristics. 13. Name and describe the three types of genetic screening tests? 14. Pedigree Problem on back… GENETICS PROBLEMS: Be able to follow the steps for solving genetic problems and apply it to sex-linked problems and blood type problems. FOLLOW THE SET-UP FOR SOLVING GENETICS PROBLEMS. 1. Colorblindness is recessive over normal vision. A colorblind man marries a heterozygous normal female. If they have two girls, how many are expected to be colorblind? If they have one son, what could he be? 2. A man with O blood marries a woman heterozygous for B blood. What are the possible types of blood that their offspring could have? PEDIGREE PROBLEMS The pedigree below traces the inheritance of alkaptonuria, a biochemical disorder. Affected individuals, indicated here by the filled-in circles and squares, are unable to break down a substance called alkapton, which colors the urine and stains body tissues. Does alkaptonuria appear to be caused by a dominant or recessive allele? Fill in the genotypes of the individuals whose genotypes you know. What genotypes are possible for each of the other individuals?