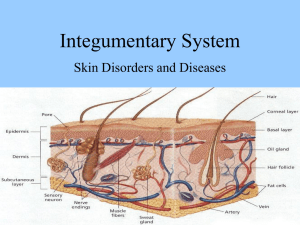
Al Asmarya Islamic University Faculty of Pharmacy Clinical biochemistry Lectured by : ESMAEIL B. MUSA 1/30/2021 1 Liver function tests • Introduction • The liver plays a major role in protein, carbohydrate and lipid homeostasis • The metabolic pathways of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, amino acid synthesis and degradation, and the processes of oxidative phosphorylation are all carried out in the hepatocytes, which are well endowed with mitochondria • It is responsible for the synthesis of albumin and many other plasma proteins, as well as most of the coagulation factors 1/30/2021 2 • It synthesizes bile acids, major constituents of bile, and is the key organ for detoxification, metabolism and inactivation of drugs and the metabolism and excretion of many endogenous compounds, including cholesterol, amino acids, steroid and other hormones • It also protects the body against potential carcinogens 1/30/2021 3 • Liver disease is relatively common, and the measurements of serum levels of bilirubin, hepatic enzymes and albumin, as well as the prothrombin time (PT), provide simple tests to determine whether disease is present and give some guidance as to its nature • Structure of the liver • Only about 80% of the cells in the liver are hepatocytes • The functional unit of the liver lobules, each lobule is primarily composed of a central vein (CV), the portal triad consists of a portal vein, biliary duct and hepatic artery • Hepatocyte cords are separated by sinusoids that carry blood from the portal triads to the central vein • Hepatocytes secrete bile salts into the bile canaliculi that lead to the bile duct 1/30/2021 4 • Stellate cells are in the space of Disse between the hepatocyte cords and sinusoids • Kupffer cells, which are the specialized macrophages of the liver, that form part of the reticulo‐endothelial system, the epithelial cells that line the bile ducts are called Cholangiocytes 1/30/2021 5 • Liver function tests • Most laboratories perform a standard tests which are useful for: 1. Obstruction to the biliary tract 2. Acute hepatocellular damage 3. Chronic liver disease CLASSIFICATION OF LIVER FUNCTION TESTS A. Tests of the liver’s capacity to transport organic anions and to metabolize drugs: (Serum bilirubin, urine bilirubin, urobilinogen) 1/30/2021 6 B. Tests that detect injury to hepatocytes [serum enzyme tests]: (Aminotransferases, alkaline phosphatase, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, 5-nucleotidase, leucine aminopeptidase) C. Tests of the Liver’s biosynthetic capacity: (Serum proteins, albumin, prealbumin, serum ceruloplasmin, procollagen III peptide, a 1 antitrypsin, α-feto protein, prothrombin time) 1/30/2021 7 A. Tests of the liver’s capacity to transport organic anions and to metabolize drugs • Bilirubin production and metabolism • Bilirubin is derived from haem, an iron-containing protoporphyrin mainly found in haemoglobin, from other haem proteins such as myoglobin and the cytochromes • Iron is removed from the haem molecule, and the porphyrin ring is opened to form bilirubin • An adult normally produces about 450 μmol of bilirubin daily • It is insoluble in water and is transported in plasma almost totally bound to albumin 1/30/2021 8 • It is taken up by liver cells and conjugated to form mono- and diglucuronides, which are much more soluble in water than unconjugated bilirubin • The conjugated bilirubin is excreted into the bile • Normal bile contains bilirubin monoglucuronide as 25% and the diglucuronide as 75% of the total, accompanied by traces of unconjugated bilirubin • The main functional constituents of the bile are the bile salts, which are involved in fat digestion and absorption from the small intestine 1/30/2021 9 • Serum bile acid concentrations are more sensitive indices of hepatic transport function than are total bilirubin measurements • In the terminal ileum and colon the bilirubin conjugates are attacked by bacteria to form a group of compounds that are known collectively as stercobilinogen, most of which are excreted in faeces • Some are absorbed and eventually re-excreted from the body by way of bile (the enterohepatic circulation) • Small amounts of these tetrapyrroles are found in urine in which they are known as urobilinogen • When the biliary tract becomes blocked, bilirubin is not excreted and serum concentrations rise and the patient becomes jaundiced 1/30/2021 10 1/30/2021 11 1/30/2021 12 1. SERUM BILIRUBIN • Bilirubin is altered by exposure to light so serum and plasma samples must be kept in dark before measurements are made • When the liver function tests are abnormal and the serum bilirubin levels more than17μmol/L suggest underlying liver disease Types of bilirubin 1. Total bilirubin: This is measured as the amount, which reacts in 30 minutes after addition of alcohol • Normal range is 0.2-0.9 mg/dl (2-15μmol/L) • It is slightly higher by 3-4 μmol/L in males as compared to females, which helps to diagnose Gilbert syndrome in males easily 1/30/2021 13 2. Direct Bilirubin : This is the water-soluble fraction • Measured by the reaction with diazotized sulfanilic acid in 1 minute and this gives estimation of conjugated bilirubin • Normal range 0.3mg/dl( 5.1μmol/L) 3. Indirect bilirubin: it is calculated by the difference of the total and direct bilirubin and is a measure of unconjugated fraction of bilirubin A newer highly accurate method of estimation involves alkaline methanolysis of bilirubin followed by chloroform extraction of bilirubin methyl esters and later separation of these esters by chromatography and spectrophotometric determination at 430 nm 1/30/2021 14 i. Diagnostic value of bilirubin levels : • Bilirubin in body is a careful balance between production and removal of the pigment in body Hyperbilirubinemia: It results from overproduction / impaired uptake, conjugation or excretion / regurgitation of unconjugated or conjugated bilirubin from hepatocytes to bile ducts • Increased unconjugated bilirubin: This results from overproduction/impaired uptake, no conjugation • Increased conjugated bilirubin: Impaired intrahepatic excretion / regurgitation of conjugated bilirubin from hepatocytes of bile ducts 1/30/2021 15 ii. Prognostic value of bilirubin levels • Bilirubin may be of prognostic value in conditions like hepatic failure where deep jaundice is associated with increased mortality Hyperbilirubinemia and Hemolysis • Bilirubin itself is not soluble in water and is bound to albumin and thus does not appear in urine • Hemolysis with overproduction of bilirubin and concomitant reduced GFR cause decreased excretion and can lead to high bilirubin levels • Bilirubin levels in excess of 25 mg/dl may be seen in hemolysis in association with liver disease 1/30/2021 16 1/30/2021 17 1/30/2021 18 1/30/2021 19 2. URINE BILIRUBIN • Normal blood test range from 0 to 0.3 mg/dL in adults • Unconjugated bilirubin is tightly bound to albumin and not filtered by the glomerulus and thus not present in urine • Measurable amounts of conjugated bilirubin in serum are found only in hepatobiliary disease • The presence of urine bilirubin indicates hepatobiliary disease 1/30/2021 20 3. UROBILINOGEN • Normal range: 0.5-4mg is excreted in urine of 24 hours • It is markedly increased in hemolysis • In cholestatic jaundice urobilinogen disappears from urine • Urobilinogen gives a purple reaction to Ehrlich’s aldehyde reagent • Freshly voided urine should be used Cause of increased urobilinogen • It can be increased in case of hemolysis and hemorrhage in tissue Cause of decreased urobilinogen • Obstructive jaundice and reduction of intestinal bacterial flora 1/30/2021 21 B. Tests that detect injury to hepatocytes( serum enzyme tests 1. Enzymes that detect hepatocellular damage – aminotransferases • The aminotransferases (formerly transaminases)are the most frequently utilized and specific indicators of hepatocellular damage • These enzymes are AST and ALT • ALT is primarily localized to the liver but the AST is present in a wide variety of tissues like the heart, skeletal muscle, kidney, brain and liver • Whereas the AST is present in both the mitochondria and cytosol of hepatocytes, ALT is localized to the cytosol 1/30/2021 22 Mild , moderate and severe elevations of aminotransferases 1. Severe ( > 20 times, 1000 U/L) • The highest elevations occur in severe viral hepatitis, drug or toxin induced hepatic necrosis and circulatory shock 2. Moderate (3-20 times) • The AST and ALT are moderately elevated in (acute, neonatal, chronic, autoimmune, drug induced, alcoholic) hepatitis and acute biliary tract obstructions • The ALT is usually more frequently increased as compared to AST except in chronic liver disease 1/30/2021 23 3. Mild (1-3 times) • These elevations are usually seen in sepsis induced neonatal hepatitis, extrahepatic biliary atresia (EHBA), fatty liver, cirrhosis, non alcoholic steato hepatitis(NASH), drug toxicity, myositis, Duchenne muscular dystrophy and even after vigorous exercise 2. Enzymes that detect cholestasis a) ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE (ALP) • Highest levels of alkaline phosphatase occur in cholestatic disorders • Elevations occur as a result of both intrahepatic and extrahepatic obstruction to bile flow • Alkaline phosphatase levels are likely to be very high in EHBA 1/30/2021 24 • Mildly elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase may be seen in cirrhosis and hepatitis of congestive cardiac failure • Low levels of alkaline phosphatase occur in hypothyroidism, pernicious anemia, zinc deficiency and congenital hypophosphatasia • Drugs like cimetidine, frusemide, phenobarbitone and phenytoin may increase levels of alkaline phosphatase b) γ-GLUTAMYL TRANSPEPTIDASE (GGT) • GGT is a membrane bound glycoprotein which catalyzes the transfer of γ-glutamyl group to other peptides, amino acids and water • Widely distributed in tissues including liver and renal tubules, and prostate 1/30/2021 25 • The activity of γ-GT in plasma is raised whenever there is cholestasis, and it is a very sensitive index of liver pathology • It is also affected by ingestion of alcohol, even in the absence of recognizable liver disease • Drugs such as phenytoin induce enzyme activity • In acute hepatic damage, changes in γ-GT activity parallel those of the aminotransferases 1/30/2021 26 C. Tests of the Liver’s biosynthetic capacity a) SERUM PROTEINS (albumin) • The liver is the major source of most the serum proteins • The parenchymal cells are responsible for synthesis of albumin, fibrinogen and other coagulation factors and most of the α and ß globulins • It is the most useful indicator of hepatic function • Because the half life of albumin in serum is as long as 20 days, the serum albumin level is not a reliable indicator of hepatic protein synthesis in acute liver disease 1/30/2021 27 • Albumin synthesis is affected not only in liver disease but also by nutritional status, hormonal balance and osmotic pressure. Liver is the only site of synthesis of albumin • The serum levels are typically depressed in patients with cirrhosis and ascites • Normal serum values range from 3.5g/dl - 4.5 g/dl • Corticosteroids and thyroid hormone stimulate albumin synthesis by increasing the concentration of albumin mRNA and tRNA in hepatocytes • Albumin levels below 3g/dl in hepatitis should raise the suspicion of chronic liver disease like cirrhosis which usually reflects decreased albumin synthesis 1/30/2021 28 • Hypoalbuminemia is not specific for liver disease and may occur in protein malnutrition, nephrotic syndrome and chronic protein losing enteropathies b) SERUM CERULOPLASMIN • Ceruloplasmin is the major copper-carrying protein in the blood, synthesized in the liver • Normal plasma levels are 0.2-0.4g/L • This is an important diagnostic marker in Wilson disease, in which the plasma level is usually low c) PROTHROMBIN TIME (PT) • Clotting is the end result of a complex series of enzymatic reactions that involve at least 13 factors 1/30/2021 29 • The liver is the major site of synthesis of 11 blood coagulation proteins • Most of these are present in excess and abnormalities of coagulation only result when there is substantial impairment in the ability of the liver to synthesize these factors • Normal control usually is in the range of 9-11 seconds 1/30/2021 30