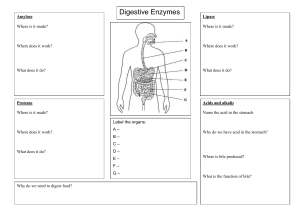
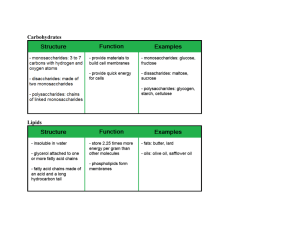
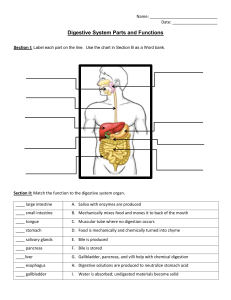
Monday 18/01/2021 B3.6: HOW THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WORKS STARTER ACTIVITY: Retrieving prior knowledge Based on what we have learnt so far, label each organs of the digestive system in order. Write in your worksheet. Salivary glands- mouth A ____________________________ Oesophagus B ____________________________ Liver C ____________________________ Stomach D ____________________________ Pancreas E ____________________________ Small intestine F ____________________________ Large intestine G ____________________________ CHALLENGE Do you remember what is the difference between ‘egestion’ and ‘excretion’? SELF-ASSESS CHALLENGE QUESTION Egestion is the removal of undigested food from the body through the anus as faeces. Excretion is the removal of waste products, derived from cells’ metabolism, from the body. Examples are: (1) removal of carbon dioxide from the lungs; (2) removal of urea from the kidneys, and (3) removal of various toxins from the skin. RECALLING IMPORTANT KEY POINTS • The digestive system is the organ system that breaks food down into small molecules; absorbs small molecules in the bloodstream (villi) and egests undigested food (through anus). • Digestion is helped by enzymes, which are biological catalysts that speed up the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy of that reaction. All enzymes are PROTEINS and they are NOT used up in the reactions they catalyse. Monday 18/01/2021 B3.6: HOW THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WORKS Learning objective Be able to demonstrate and apply your knowledge & understanding of enzymes involved in digestion (breaking down) of various food molecules. Lesson learning outcomes Recall the main organs of the human digestive system and the processes that take place in them. Compare the enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Discuss how various factors affect these enzymes differently. Key words previously learnt Enzyme, activation energy, active-site, absorption, villi and microvilli, egestion New key words Carbohydrase, amylase, Protease, Pepsin, Tripsin Lipase LO1: Recall the main organs of the human digestive system and the processes that take place in them. INDEPENDENT ACTIVITY: For each name of process, match the correct definition of what happens and put in the correct sequence. Write the full sentence in your book . In the digestive system the following processes take place: 1)_____________________________________________________ 2)_____________________________________________________ 3)_____________________________________________________ 4)_____________________________________________________ Absorption • removal of undigested food from the body through the anus as faeces. Ingestion • large and insoluble molecules are broken down by enzymes into small and soluble molecules. Egestion • food is introduced in the body by swallowing. Digestion • in the small intestine small and soluble molecules pass into the blood stream through the villi. LO1: Recall the main organs of the human digestive system and the processes that take place in them. SELF-ASSESSMENT: Check that you have done these correctly In the digestive system the following processes take place: 1) Ingestion: food is introduced in the body by swallowing. 2) Digestion: large and insoluble molecules are broken down by enzymes into small and soluble molecules. 3) Absorption: in the small intestine small and soluble molecules pass into the blood stream through the villi. 4) Egestion: removal of undigested food from the body through the anus as faeces. LO2: Compare the enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats. INDEPENDENT TASK: Extract the information from the videoclip to answer the questions in your worksheet. Amylase Protease Lipase Acids and alkalis Where is it made? Where is it made? Where is it made? Name the acid in the stomach Where does it work? Where does it work? Where does it work? Why do we have acid in the stomach? What does it do? What does it do? What does it do? https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z9pv34j/revision/3 LO2: Compare the enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats. INDEPENDENT TASK: Extract the information from the videoclip to answer the questions in your worksheet. Amylase Protease Lipase Acids and alkalis Where is it made? Where is it made? • Salivary glands • Stomach • Pancreas (Pepsin) • Small intestine • Pancreas (Tripsin) • Small intestine Where does it Where does it work? work? • Mouth • Stomach • Small intestine • Small intestine Where is it made? Name the acid in • Pancreas the stomach • Small intestine Hydrochloric acid What does it do? Breaks down carbohydrates into maltose What does it do? Breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol What does it do? Breaks down proteins into amino acids Where does it work? • Small intestine Why do we have acid in the stomach? Hydrochloric acid helps to break down nutrients, such as proteins. It also protects from harmful bacterial and viral infections. LO3: Discuss how various factors affect these enzymes differently. Enzymes that catalyse (speed up) reactions in different parts of the digestive system have different optimal pH. In order to work properly they have to have a specific value of pH. What would happen if the pH was not optimal? INDEPENDENT WORK In your books answer the following summary questions Figure 1 Plenary challenge In your books, write a sentence that links as many key words as possible from the list below (15 key words in total!) amylase protease lipase stomach enzymes acidic pH alkaline curve catalyse carbohydrates fats amino acids optimum proteins CHALLENGE QUESTION Explain the importance of the digestion of food in terms of the molecules involved and the role of enzymes in the gut. [6 marks]