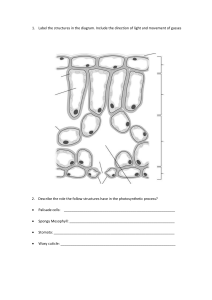
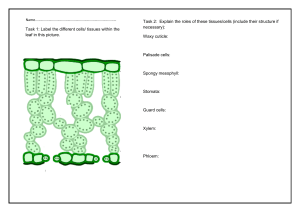
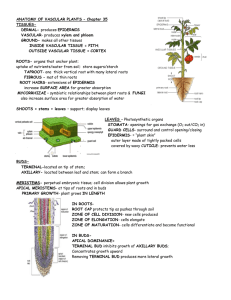
1) Root hairs, which absorb the water and minerals in the majority of plants, are the extensions of root A) collenchyma tissue. B) pericycle. C) endodermis. D) epidermal cells. E) parenchyma. 2) Palisade parenchyma, a ground tissue, performs which of the following functions? A) storage of food B) photosynthesis C) aerobic respiration D) transport of water and minerals E) transport of food 3) Which of the following is derived from the ground tissue system? A) root hair B) cuticle C) periderm D) pith E) phloem 4) Adventitious roots in monocots are very helpful in coastal ecosystems to reduce A) water absorption. B) evaporation. C) soil erosion. D) nutrient absorption. E) decomposition. 5) An association between the roots of a terrestrial plant with soil fungus is referred as A) parasitism. B) symbiosis. C) autotrophism. D) heterotrophism. E) saprobism. 6) Storage roots, stems, and leaves are some of the evolutionary adaptations of plants. Which of the following are listed in the order of modified root, stem, and leaf? A) rhizome, bulb, tuber B) bulb, stolon, spine C) rhizome, stolon, tendril D) stolon, rhizome, bulb E) tendril, rhizome, spine 7) Guard cells of stomata in leaves of plants are modified A) mesophyll cells. B) epidermal cells. C) palisade mesophyll cells. D) sclerenchyma cells. E) collenchyma cells. 8) Which tissue is responsible for the recovery and rapid growth of damaged leaves of grass grazed by sheep in a pasture? A) parenchyma B) apical meristem C) axillary buds D) mesophyll E) intercalary meristem 9) The outermost layer of the vascular cylinder of a root is called the A) pericycle. B) cortex. C) xylem. D) phloem. E) endodermis. 10) Mesophyll in leaves is located between the A) epidermis and endodermis. B) epidermis and xylem. C) phloem and epidermis. D) stomata and mesophyll. E) upper and lower epidermis. 11) The role of genes and their activation and inactivation during cell differentiation is based on A) cell-to-cell communication. B) cell division. C) cell elongation. D) cell growth. E) cell development. 12) Secondary growth in eudicot stems and roots is caused by A) apical meristem. B) axillary bud. C) lateral meristem. D) secondary xylem. E) secondary phloem. 13) Which of the following environmental factors plays a critical role in plant photosynthesis? A) CO2 and O2 B) O2 and light C) O2 and chlorophyll in mesophyll D) light and CO2 E) light, chlorophyll, and CO2 14) Which tissue is the innermost layer of the cortex in roots? A) pericycle B) endodermis C) vascular cylinder D) mesophyll E) ground tissue C 18) The vascular cambium is ________ and produces secondary vascular tissue. A) one cell thick B) two cells thick C) three cells thick D) irregular in thickness E) composed of multiple layers 19) Which part of a plant absorbs most of the water and minerals taken up from the soil? A) root cap B) root hairs C) the thick parts of the roots near the base of the stem D) storage roots E) sections of the root that have secondary xylem 20) Which cells are no longer capable of carrying out the process of DNA transcription? A) tracheids B) mature mesophyll cells C) companion cells D) meristematic cells E) glandular cells 21) ________ is to xylem as ________ is to phloem. A) Sclerenchyma cell; collenchyma cell B) Apical meristem; vascular cambium C) Vessel element; sieve-tube member D) Cortex; pith E) Vascular cambium; cork cambium 22) Which of the following tissue types transport water and minerals over long distances in angiosperms? A) parenchyma cells B) collenchyma cells C) sclerenchyma cells D) vessel elements E) sieve-tube elements 23) Which of the following have unevenly thickened primary walls that support young, growing parts of the plant and provide flexibility? A) parenchyma cells B) collenchyma cells C) sclerenchyma cells D) tracheids and vessel elements E) sieve-tube elements 24) Which of the following are most responsible for supporting mature, nongrowing parts of the plant? A) parenchyma cells B) collenchyma cells C) trichomes D) tracheids and vessel elements E) sieve-tube elements 25) The vascular bundle in the shape of a single central cylinder in a root is called the A) cortex. B) stele. C) endodermis. D) periderm. E) pith. 26) One important difference between the anatomy of roots and the anatomy of leaves is that A) only leaves have phloem and only roots have xylem. B) root cells have cell walls and leaf cells do not. C) leaves have mesophyll tissue but roots do not. D) vascular tissue is found in roots but is absent from leaves. E) leaves have epidermal tissue but roots do not. 27) A student examining leaf cross sections under a microscope finds many loosely packed cells with relatively thin cell walls. The cells have numerous chloroplasts. What type of cells are they? A) parenchyma B) xylem C) endodermis D) collenchyma E) sclerenchyma 28) Which of the following cell types retains the ability to undergo cell division? A) a sclereid B) a parenchyma cell 2 mm from the tip of a root C) a functional sieve-tube element D) a tracheid E) a stem fiber 29) Axillary buds A) are initiated by the cork cambium. B) have dormant meristematic cells. C) are composed of a series of internodes lacking nodes. D) grow immediately into shoot branches. E) do not form a vascular connection with the primary shoot. 30) A plant has the following characteristics: a taproot system, several growth rings evident in a cross section of the stem, and a layer of bark around the outside. Which of the following best describes the plant? A) herbaceous eudicot B) woody eudicot C) woody monocot D) herbaceous monocot E) woody annual 31) Compared to most animals, the growth of most plants is best described as A) perennial. B) weedy. C) indeterminate. D) derivative. E) primary. 32) Lateral meristems produce A) dermal and ground tissue. B) lateral tissues. C) pith. D) secondary tissues. E) shoots and roots. D 33) Plants contain meristems whose major function is to A) attract pollinators. B) absorb ions. C) photosynthesize. D) produce more cells. E) produce flowers. 34) Which of the following statements about growth in plants is true? A) Primary growth is localized at meristems, whereas secondary growth is localized at buds. B) Some plants lack secondary growth. C) Secondary growth occurs only in stems. D) Reproductive structures are produced by secondary growth. E) Monocots have only primary growth, and eudicots have only secondary growth. 35) Additional vascular tissue produced as secondary growth in a root originates from which cells? A) vascular cambium B) apical meristem C) endodermis D) phloem E) xylem A 36) Lateral meristem activity results in production of A) secondary xylem. B) leaves. C) trichomes. D) tubers. E) cortex. 37) Which of the following is a true statement? A) Flowers may have secondary growth. B) Secondary growth is a common feature of eudicot leaves. C) Secondary growth is produced by both the vascular cambium and the cork cambium. D) Primary growth and secondary growth alternate in the life cycle of a plant. E) Plants with secondary growth are typically the smallest ones in an ecosystem. 38) Gas exchange, which is necessary for photosynthesis, can occur most easily in which leaf tissue? A) epidermis B) palisade mesophyll C) spongy mesophyll D) vascular tissue E) bundle sheath 39) CO2 enters the inner spaces of the leaf through the A) cuticle. B) epidermal trichomes. C) stoma. D) phloem. E) walls of guard cells. 40) The driving force that pushes the root tip through the soil is primarily A) continuous cell division in the root cap at the tip of the root. B) continuous cell division just behind the root cap in the center of the apical meristem. C) elongation of cells behind the root apical meristem. D) the elongation of root hairs. E) continuous cell division of root cap cells. 41) The shoot elongation in a growing bud is due to A) cell division at the shoot apical meristem. B) cell elongation directly below the shoot apical meristem. C) cell division localized in each internode. D) cell elongation localized in each internode. E) cell division at the shoot apical meristem and cell elongation directly below the shoot apical meristem. 42) The following question is based on parts of a growing primary root. I. root cap II. zone of elongation III. zone of cell division IV. zone of cell differentiation V. apical meristem Which of the following is the correct sequence from the growing tips of the root upward? A) I, II, V, III, IV B) III, V, I, II, IV C) II, IV, I, V, III D) IV, II, III, I, V E) I, V, III, II, IV 43) Which of the following root tissues gives rise to lateral roots? A) endodermis B) phloem C) cortex D) epidermis E) pericycle 44) Pores on the leaf surface that function in gas exchange are called A) hairs. B) xylem cells. C) phloem cells. D) stomata. E) sclereids. 45) A person working with plants may increase the lateral branches by which of the following? A) pruning shoot tips B) deep watering of the roots C) fertilizing D) treating the plants with auxins E) feeding the plants nutrients 46) The dominant type of tissue that makes up most of the wood of a tree is A) primary xylem. B) secondary xylem. C) secondary phloem. D) mesophyll cells. E) vascular cambium. 47) If you were able to walk into an opening cut into the center of a large redwood tree, when you exit from the middle of the trunk (stem) outward, you would cross, in order, A) the annual rings, new xylem, vascular cambium, phloem, and bark. B) the secondary xylem, cork cambium, phloem, and periderm. C) the vascular cambium, oldest xylem, and newest xylem. D) the secondary xylem, secondary phloem, and vascular cambium. E) the summer wood, bark, and phloem. 28.2 Art Questions Figure 28.1 1) Which of the following statements about the cells shown in the photograph in Figure 28.1 is true? A) They are parenchyma cells. B) They are photosynthetic. C) They are usually found in roots. D) They are phloem cells. E) They are parenchyma cells and photosynthetic. 2) The characteristic feature of typical parenchyma tissue is A) a thick cell wall. B) large intercellular space. C) lignin filled intercellular spaces. D) inability to divide. E) transportation. Figure 28.2 3) A monocot stem is represented by A) I only. B) II only. C) III only. D) IV only. E) both I and III. 4) A plant that is at least 3 years old is represented by A) I only. B) II only. C) III only. D) IV only. E) both I and III. 5) A typical eudicot root is represented by A) I only. B) II only. C) III only. D) IV only. E) both I and III. 1) Suppose George Washington completely removed the bark from around the base of a cherry tree but was stopped by his father before cutting the tree down. The leaves retained their normal appearance for several weeks, but the tree eventually died. The tissue(s) that George left functional was/were the A) phloem. B) xylem. C) cork cambium. D) cortex. E) companion and sieve-tube members. B 2) As a youngster, you drive a nail in the trunk of a young tree that is 3 meters tall. The nail is about 1.5 meters from the ground. Fifteen years later, you return and discover that the tree has grown to a height of 30 meters. About how many meters above the ground is the nail? A) 0.5 B) 1.5 C) 3.0 D) 15.0 E) 28.5 B 28.4 End-of-Chapter Questions 1) Most of the growth of a plant body is the result of A) cell differentiation. B) cell division. C) morphogenesis. D) cell elongation. D 2) The innermost layer of the root cortex is the A) core. B) pericycle. C) endodermis. D) pith. 3) Heartwood and sapwood consist of A) bark. B) periderm. C) secondary xylem. D) secondary phloem. E) cork. 4) Which of the following arise, directly or indirectly, from meristematic activity? A) secondary xylem B) dermal tissue C) leaves D) all of the above 5) Which of the following would not be seen in a cross section through the woody part of a root? A) sclerenchyma cells B) sieve-tube elements C) parenchyma cells D) root hairs 1) Which one of the following is an adaptation by plants to life on land? A) lack of waxy cuticle B) Calvin cycle of photosynthesis C) xylem tracheids and vessels D) Krebs cycle of respiration 2) Which of the following was an essential adaptive feature for the evolution of plants from water to the land? A) minimizing the evaporative loss of water B) using light more effectively C) acquiring CO2 from the air D) acquiring water from the ground 3) Given that early land plants most likely share a common ancestor with green algae, the earliest land plants were most likely A) nonvascular plants that grew leafless photosynthetic shoots above the shallow fresh water in which they lived. B) species that did not exhibit alternation of generations. C) vascular plants with well-defined root systems. D) plants with well-developed leaves. 4) The architecture and distribution of the root system and production of proteins in plants are directly relevant to the availability ________ in soil. A) of carbon dioxide B) and richness of nitrates C) of fungal association D) of water 5) The symplast is the continuum of cytosol connected by A) extracellular spaces. B) apoplastic route. C) plasmodesmata. D) symplastic route. 6) Which of the following determines the direction of water movement across the membrane? A) cell health B) a difference in water potential C) size of the cell D) shape of the cell 7) Plants do not have a circulatory system like that of some animals. If a water molecule did "circulate" (that is, go from one point in a plant to another and back in the same day), it would require the activity of A) only the xylem. B) only the phloem. C) only the endodermis. D) both the xylem and the phloem. 8) Plasmodesmata can change in number, and when dilated can provide a passageway for A) macromolecules such as RNA and proteins. B) ribosomes. C) chloroplasts. D) mitochondria. 9) Typically, on average, what percentage of a plant's fresh biomass is water? A) 70-75 B) 65-75 C) 80-90 D) 75-80 10) Which of the following would be least likely to affect osmosis in plants? A) proton pumps in the membrane B) a difference in solute concentrations C) receptor proteins in the membrane D) aquaporins 11) The movement of water across biological membranes can best be predicted by A) negative charges in the cell wall. B) prevailing weather conditions. C) aquaporins. D) water potentials. 15) Compared to a cell with few aquaporins in its membrane, a cell containing many aquaporins will A) have a faster rate of osmosis. B) have a lower water potential. C) have a higher water potential. D) have a faster rate of active transport. 16) Water flows into the source end of a sieve tube because A) sucrose has diffused into the sieve tube, making it hypotonic. B) sucrose has been actively transported into the sieve tube, making it hypertonic. C) water pressure outside the sieve tube forces in water. D) the companion cell of a sieve tube actively pumps in water. B 17) What is the role of proton pumps in root hair cells? A) establish ATP gradients B) maintain the H+ gradient C) pressurize xylem transport D) eliminate excess electrons 18) One would expect to find the highest density of aquaporins in which of the following? A) the plasma membrane of guard cells B) the pits of a tracheid C) the plasma membrane of parenchyma cells in a ripe fruit D) the plasma membrane of a mature mesophyll cell in a leaf 19) If isolated plant cells with a water potential averaging -0.5 MPa are placed into a solution with a water potential of -0.3 MPa, which of the following would be the most likely outcome? A) The pressure potential of the cells would increase. B) Water would move out of the cells. C) The cell walls would rupture, killing the cells. D) Solutes would move out of the cells. 20) Guard cells do which of the following? A) protect the endodermis B) accumulate K+ in order to close the stomata C) contain chloroplasts that import K+ directly into the cells D) help balance the photosynthesis-transpiration compromise 21) Photosynthesis begins to decline when leaves wilt because A) chloroplasts within wilted leaves are incapable of photosynthesis. B) CO2 accumulates in the leaves and inhibits the enzymes needed for photosynthesis. C) there is insufficient water for photolysis during the light reactions. D) stomata close, restricting CO2 entry into the leaf. D22) The opening of stomata is thought to involve A) an increase in the solute concentration of the guard cells. B) a decrease in the solute concentration of the stoma. C) active transport of water out of the guard cells. D) decreased turgor pressure in the guard cells. 23) The following factors may sometimes play a role in the movement of sap through xylem. Which one depends on the direct expenditure of ATP by the plant? A) capillarity of water within the xylem B) evaporation of water from leaves C) cohesion among water molecules D) concentration of ions in the symplast 24) In which plant cell or tissue would the pressure component of water potential most often be negative? A) leaf mesophyll cell B) stem xylem C) stem phloem D) root cortex cell 25) Water potential is generally most negative in which of the following parts of a plant? A) mesophyll cells of the leaf B) xylem vessels in leaves C) xylem vessels in roots D) cells of the root cortex 26) Which of the following has the lowest (most negative) water potential? A) root cortical cells B) root xylem C) trunk xylem D) leaf air spaces 27) Active transport would be least important in the normal functioning of which of the following plant tissue types? A) leaf transfer cells B) stem tracheid element C) root endodermal cells D) leaf mesophyll cells 28) Which of the following essential nutrients plays an essential role in the opening and closing of the stomatal aperture? A) Fe B) Bo C) Mg D) K 29) What is the driving force for the movement of solutes in the phloem of plants? A) gravity B) a difference in water potential (Ψ) between the source and the sink C) root pressure D) transpiration of water through the stomata 30) Which of the following is a correct statement about sugar movement in phloem? A) Diffusion can account for the observed rates of transport. B) Movement can occur both upward and downward in the plant. C) Sugar is translocated from sinks to sources. D) Only phloem cells with nuclei can perform sugar movement. 31) Phloem transport is described as being from source to sink. Which of the following would most accurately complete this statement about phloem transport as applied to most plants in the late spring? Phloem transports ________ from the ________ source to the ________ sink. A) amino acids; root; mycorrhizae B) sugars; leaf; apical meristem C) nucleic acids; flower; root D) proteins; root; leaf 32) Arrange the following five events in an order that explains the mass flow of materials in the phloem. 1. Water diffuses into the sieve tubes. 2. Leaf cells produce sugar by photosynthesis. 3. Solutes are actively transported into sieve tubes. 4. Sugar is transported from cell to cell in the leaf. 5. Sugar moves down the stem. A) 2, 1, 4, 3, 5 B) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 C) 2, 4, 3, 1, 5 D) 4, 2, 1, 3, 5 33) For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their relationship. (a) The average size of particles that constitute silt (b) The average size of particles that constitute clay A) Item (a) is larger than item (b). B) Item (a) is smaller than item (b). C) Item (a) is exactly or very approximately equal to item (b). D) Item (a) bears no relationship to item (b). 34) For this pair of items, choose the option that best describes their relationship. (a) The amount of molybdenum in a gram of dried plant material (b) The amount of sulfur in a gram of dried plant material A) Item (a) is greater than item (b). B) Item (a) is less than item (b). C) Item (a) is exactly or very approximately equal to item (b). D) There is not enough information to make a meaningful comparison. 35) Which of the following would be in the lowest concentration in an actively growing shoot tip? A) zinc B) nitrogen C) phosphorus D) potassium 36) Atmospheric nitrogen can be fixed by nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Arrange the following forms of nitrogen from the atmospheric N stage to the final form that enters the roots. 1. Ammonia 2. Nitrogen gas 3. Ammonium ion 4. Nitrite 5. Nitrate A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 B) 2, 1, 3, 5, 4 C) 2, 1, 5, 4, 3 D) 2, 1, 3, 4, 5 37) If you wanted to increase the cation exchange and water retention capacity of loamy soil, what should you do? A) Adjust the soil pH to 7.9. B) Add clay to the soil. C) Practice no-till agriculture. D) Add fertilizer containing potassium, calcium, and magnesium to the soil. 38) Several properties are characteristic of a soil in which typical plants would grow well. Of the following, which would be the least conducive to plant growth? A) abundant humus B) numerous soil organisms C) compacted soil D) high porosity 39) Why does overwatering a plant kill it? A) Water does not have all the necessary minerals a plant needs to grow. B) Water neutralizes the pH of the soil. C) The roots are deprived of oxygen. D) Water supports the growth of root parasites. 40) Which of the following soil minerals is most likely leached away during a hard rain? A) Na+ B) K+ C) Ca2+ D) NO341) The NPK percentages on a package of fertilizer refer to the A) total protein content of the three major ingredients of the fertilizer. B) percentages of manure collected from different types of animals. C) relative percentages of organic and inorganic nutrients in the fertilizer. D) percentages of three important mineral nutrients. 42) Most of the dry weight of a plant is derived from A) NO3- and CO2. B) K+ and CO2. C) PO43- and K+. D) H2O and CO2. 43) In hydroponic culture, what is the purpose of bubbling air into the solute? A) to keep dissolved nutrients evenly distributed B) to provide oxygen to the root cells C) to inhibit the growth of aerobic algae D) to inhibit the growth of anaerobic bacteria 44) Which two elements make up more than 90% of the dry weight of plants? A) carbon and nitrogen B) oxygen and hydrogen C) nitrogen and oxygen D) oxygen and carbon 45) The bulk of a plant's dry weight is derived from A) soil minerals. B) CO2. C) the hydrogen from H2O. D) the oxygen from H2O. 46) Which of the following elements is required for the stability of cell walls? A) zinc B) chlorine C) calcium D) molybdenum 47) Synthesis of which of the following compounds in a mature leaf would be least impacted by a temporary soil nitrogen deficiency? A) chlorophyll B) DNA C) RNA D) cellulose 48) What is a major function of magnesium in plants? A) to be a component of lignin-biosynthetic enzymes B) to be a component of DNA and RNA C) to be a component of chlorophyll D) to be active in amino acid formation 49) Copper plays a critical role in ________ of plant cells. A) water splitting in photosynthesis B) redox reactions and lignin-biosynthetic enzymes C) cytochromes D) cofactor for enzymes needed for nitrogen fixation 50) Reddish-purple coloring of leaves, especially along the margins of young leaves, is a typical symptom of deficiency of which element? A) C B) Mg2+ C) N D) P 51) A corn (Zea mays) mutant is developed that is impaired in magnesium uptake. The most likely phenotypic expression would be A) chlorosis, especially in the older leaves. B) a purple tinge to actively growing shoots. C) severely stunted root growth and branching. D) a reduction in leaf surface area. 52) If an African violet has chlorosis, which of the following elements might be a useful addition to the soil? A) chlorine B) molybdenum C) iodine D) magnesium 53) Iron deficiency is often indicated by yellowing in newly formed leaves. This suggests that iron A) is a relatively immobile nutrient in plants. B) is tied up in formed chlorophyll molecules. C) is concentrated in the xylem of older leaves. D) is concentrated in the phloem of older leaves. 54) Which of the following, if used as a fertilizer, would be most immediately available for plant uptake? A) NH3 B) N2 C) CN2H2 D) NO355) The enzyme complex nitrogenase catalyzes the reaction that reduces atmospheric nitrogen to A) N2. B) NH3. C) NO2-. D) NO+. 56) In a root nodule, the gene coding for nitrogenase A) is inactivated by leghemoglobin. B) is absent in active bacteroids. C) is found in the cells of the pericycle. D) is part of the Rhizobium genome 57) The most efficient way to increase essential amino acids in crop plants for human consumption would be to A) breed for higher yield of deficient amino acids. B) increase the amount of fertilizer used on fields. C) use 20-20-20 fertilizer instead of 20-5-5 fertilizer. D) engineer nitrogen-fixing nodules into crop plants lacking them. 58) If a plant is infected with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, what is the most probable effect on the plant? A) It gets chlorosis. B) It dies. C) It will have a higher concentration of N2 in its roots and shoots. D) It will likely grow faster than an uninfected plant. 59) You are weeding your garden when you accidentally expose some roots of your pea plants. You notice swellings (root nodules) on the roots and there is a reddish tinge to the ones you accidentally damaged. Most likely your pea plants A) suffer from a mineral deficiency. B) are benefiting from a mutualistic bacterium. C) are developing offshoots from the root. D) contain developing insect pupa. 60) Which of the following statements about nitrogen fixation in root nodules is true? A) The plant contributes the nitrogenase enzyme. B) The process is relatively inexpensive in terms of ATP costs. C) Leghemoglobin helps maintain a low O2 concentration within the nodule. D) The process tends to deplete nitrogen compounds in the soil. 61) Upregulation of leghemoglobin biosynthesis in a leguminous species would most likely indicate A) the plant is suffering from a mineral deficiency. B) the successful inoculation of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. C) the plant is suffering from water stress. D) an increase in the biosynthesis of amino acids. B62) An example of a mutualistic association between a plant and a fungus would be A) nitrogen fixation. B) Rhizobium infection. C) mycorrhizae. D) parasitic infection 63) Hyphae form a covering over roots. These hyphae create a large surface area that helps to do which of the following? A) aid in absorbing minerals and ions B) maintain cell shape C) increase cellular respiration D) protect the roots from ultraviolet light A 64) Which of the following is a primary difference between ectomycorrhizae and endomycorrhizae? A) Endomycorrhizae have thicker, shorter hyphae than ectomycorrhizae. B) Endomycorrhizae, but not ectomycorrhizae, form a dense sheath over the surface of the root. C) Ectomycorrhizae do not penetrate root cells, whereas endomycorrhizae grow into invaginations of the root cell membranes. D) Ectomycorrhizae are found in woody plant species; about 85% of plant families form ectomycorrhizae. 65) The earliest vascular plants on land had underground stems (rhizomes) but no roots. Water and mineral nutrients were most likely obtained by A) absorption by hairs and trichomes. B) absorption by mycorrhizae. C) osmosis through the root hairs. D) diffusion across the cuticle of the rhizome. 66) A rootless, green plant is found growing on the branches and trunks of rain forest trees, but lacks any apparent adaptation for collecting rainwater. This plant is most likely A) an epiphyte. B) a nitrogen-fixing plant. C) a carnivorous plant. D) a parasite. 67) What are epiphytes? A) aerial vines common in tropical regions B) haustoria used for anchoring to host plants and obtaining xylem sap C) plants that live in poor soil and digest insects to obtain nitrogen D) plants that grow on other plants but do not obtain nutrients from their hosts 68) Carnivorous plants have evolved mechanisms that trap and digest small animals. The products of this digestion are used to supplement the plant's supply of A) energy. B) carbohydrates. C) minerals. D) water. 69) Rhizobia, actinomycetes, and cyanobacteria all share the common feature that they can A) increase water uptake in plants. B) increase nutrient availability in the soil for plants. C) kill parasites in the soil. D) fix atmospheric nitrogen. 70) Why is nitrogen fixation an essential process? A) Nitrogen fixation can only be done by certain prokaryotes. B) Fixed nitrogen is often the limiting factor in plant growth. C) Nitrogen fixation is very expensive in terms of metabolic energy. D) Nitrogen fixers are sometimes symbiotic with legumes. 71) In what way do nitrogen compounds differ from other minerals needed by plants? A) Only nitrogen can be lost from the soil. B) Only nitrogen requires the action of bacteria to be made available to plants. C) Only nitrogen is held by cation exchange capacity in the soil. D) Only nitrogen can be absorbed by root hairs. 72) Nitrogen fixation is a process that A) recycles nitrogen compounds from dead and decaying materials. B) converts ammonia to ammonium. C) releases nitrate from the rock substrate. D) converts nitrogen gas into ammonia. 73) Which of the following would be the most effective strategy to remove toxic heavy metals from a soil? A) heavy irrigation to leach out the heavy metals B) application of fertilizers to compete with heavy metal uptake C) adding plant species that have the ability to take up and accumulate heavy metals D) inoculating soil with mycorrhizae to avoid heavy metal uptake 74) Which of the following plant structures shares the most common features and functions with a fungal hyphae? A) stomata B) vascular cambium C) lenticels D) root hairs 75) A plant developed a mineral deficiency after being treated with a fungicide. What is the most probable cause of the deficiency? A) Mineral receptor proteins in the plant membrane were not functioning. B) Mycorrhizal fungi were killed. C) Active transport of minerals was inhibited. D) Proton pumps reversed the membrane potential. 76) Pine seedlings grown in sterile potting soil grow much slower than seedlings grown in soil from the area where the seeds were collected. This is most likely because A) the sterilization process kills the root hairs as they emerge from the seedling. B) the normal symbiotic fungi are not present in the sterilized soil. C) water and mineral uptake is faster when mycorrhizae are present. D) B and C. D 77) Some botanists argue that the entire plant should be considered as a single unit rather than a composite of many individual cells. Which of the following cellular structures best supports this view? A) cell wall B) cell membrane C) vacuole D) plasmodesmata D 78) Root hairs are most important to a plant because they A) anchor a plant in the soil. B) store starches. C) increase the surface area for absorption. D) provide a habitat for nitrogen-fixing bacteria. 79) A water molecule could move all the way through a plant from soil to root to leaf to air and pass through a living cell only once. This living cell would be a part of which structure? A) the Casparian strip B) a guard cell C) the root epidermis D) the endodermis 80) The Casparian strip in plant roots is correctly described by which of the following? A) It aids in the uptake of nutrients. B) It provides energy for the active transport of minerals into the stele from the cortex. C) It ensures that all minerals are absorbed from the soil in equal amounts. D) It ensures that all water and dissolved substances must pass through a cell membrane before entering the stele. 81) What drives the flow of water through the xylem? A) passive transport by the endodermis B) the number of companion cells in the phloem C) the evaporation of water from the leaves D) active transport by tracheid and vessel elements 82) What is the main force by which most of the water within xylem vessels moves toward the top of a tree? A) active transport of ions into the stele B) atmospheric pressure on roots C) evaporation of water through stoma D) the force of root pressure 83) Most of the water taken up by a plant is A) used as a solvent. B) used as a hydrogen source in photosynthesis. C) lost during transpiration. D) used to keep cells turgid. 84) Which cells in a root form a protective barrier to the vascular system where all materials must move through the symplast? A) pericycle B) cortex C) epidermis D) endodermis D 85) The water lost during transpiration is a side effect of the plant's exchange of gases. However, the plant derives some benefit from this water loss in the form of A) evaporative cooling. B) mineral transport. C) increased turgor. D) evaporative cooling and mineral transport. D 86) Ignoring all other factors, what kind of day would result in the fastest delivery of water and minerals to the leaves of a tree? A) cool, dry day B) warm, dry day C) warm, humid day D) very hot, dry, windy day 87) Which of the following experimental procedures would most likely reduce transpiration while allowing the normal growth of a plant? A) subjecting the leaves of the plant to a partial vacuum B) increasing the level of carbon dioxide around the plant C) putting the plant in drier soil D) decreasing the relative humidity around the plant 88) As a biologist, it is your job to look for plants that have evolved structures with a selective advantage in dry, hot conditions. Which of the following adaptations would be least likely to meet your objective? A) CAM plants that grow rapidly B) small, thick leaves with stomata on the lower surface C) a thick cuticle on fleshy leaves D) plants that do not produce abscisic acid and have a short, thick taproot 89) Most of the dry weight of a plant is the result of uptake of A) water and minerals through root hairs. B) water and minerals through mycorrhizae. C) CO2 through stoma. D) CO2 and O2 through stomata in leaves. 90) Which of the following elemental ions plays a critical role in opening and closing of stomata? A) nitrogen B) potassium C) magnesium D) calcium