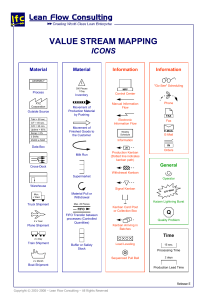
Kaizan • Kaizen means continuous improvement • involves everyone in the organization in small improvements using conventional knowledge and tools • without large capital investments • focusing on eliminating waste • If something can be improved, a measure must exist by which improvement can be quantified – quality characteristics 5’S • 5S represents 5 disciplines for maintaining a visual workplace (visual controls and information systems) • Foundational to Kaizen Kanban • Kanban is the term used for the visual & physical signaling system that ties together the whole Lean Production system • Visualize the workflow • Split the work into pieces, write each item on a card and put on the wall. • Use named columns to illustrate where each item is in the workflow. • Limit WIP (work in progress) – assign explicit limits to how many items may be in progress at each workflow state. • Measure the lead time (average time to complete one item, sometimes called “cycle time”), optimize the process to make lead time as small and predictable as possible. Just In Time (JIT) WHAT IT IS • Management philosophy • “Pull” system though the plant WHAT IT REQUIRES • Employee participation • • • • Industrial engineering/basics Continuing improvement Total quality control Small lot sizes WHAT IT DOES • Attacks waste • Exposes problems and bottlenecks • Achieves streamlined production WHAT IT ASSUMES • Stable environment 7 Types of Waste • Transportation • Inventory • Motion • Waiting • Over-processing • Over-production • Defects Poka Yoke • The process of Zero Defects is also known as “Mistake Proofing” or “Fail-Safe” or “Error-proofing”. • Inexpensive • Very effective • • • • • • • • • • • • • Bill of Materials (BOM) CRM DRP EOQ EDI ERP FMEA FIFO & LIFO GRN GUS Classification Kitting Lead time Lean manufacturing • • • • • • • • • • • • • MRP I MRP II OEE Pareto Principle PDCA QFD RFID Reverse Auction Reverse logistics Six sigma TOC VMI WIP